Benefits of Napa Syrup A Comprehensive Guide.

Napa Syrup is a widely used over-the-counter medication in Bangladesh, primarily prescribed for its effective pain-relieving and fever-reducing properties. Manufactured by Beximco Pharmaceuticals, this syrup is a trusted option for children and adults alike, thanks to its safety profile and accessibility. Below, we’ll explore its uses, benefits, and precautions to help you understand why Napa Syrup is such a staple in many households.
What is Napa Syrup?
Napa Syrup contains Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) as its active ingredient, a well-known antipyretic (fever reducer) and analgesic (pain reliever). It is available in a liquid form, making it easier for children and those who have difficulty swallowing tablets.
Benefits of Napa Syrup
- Fever Reduction
Napa Syrup is highly effective in lowering fever caused by conditions like the common cold, flu, and other infections.
It helps regulate the body's temperature, providing relief within a short period.
- Pain Relief
The syrup is used to alleviate mild to moderate pain, including headaches, toothaches, and body aches.
It is often prescribed after vaccinations to reduce post-immunization discomfort in children.


- Safe for Children
Napa Syrup is designed for children, with precise dosages based on age and weight. Its liquid form ensures easy administration.
It is free from harmful additives, making it one of the safest choices for young patients.
- Fast Absorption
The liquid formulation allows for quick absorption into the bloodstream, leading to faster relief compared to some tablet forms.
- Eases Sore Throat and Minor Aches
It can relieve discomfort caused by a sore throat, cold, or minor injuries, helping children stay comfortable while recovering from illnesses.
- Widely Available and Affordable
Napa Syrup is readily available in pharmacies across Bangladesh at an affordable price, making it accessible for all economic groups.
When to Use Napa Syrup
Fever associated with infections or vaccinations
Mild to moderate pain such as headaches, toothaches, or muscle aches
General discomfort due to common colds or flu
Dosage Guidelines
The dosage of Napa Syrup depends on the age and weight of the patient. It is crucial to follow a doctor’s prescription or the guidelines provided on the packaging. Typically:
For children aged 1–5 years: 5–10 ml every 4–6 hours
For children aged 6–12 years: 10–20 ml every 4–6 hours
Always ensure a minimum gap of 4 hours between doses and do not exceed 4 doses within 24 hours.
Precautions to Consider
- Avoid Overdosing
Overdosing on paracetamol can lead to serious liver damage. Always measure the dose accurately using a measuring spoon or cup.
- Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions, such as rashes or breathing difficulties. In such cases, discontinue use and consult a doctor immediately.
- Consultation for Chronic Conditions
If the patient has liver or kidney problems, it is essential to consult a physician before using Napa Syrup.
- Storage and Handling
Store the syrup in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight, and keep it out of reach of children.
- Do Not Mix with Other Medications
Avoid using other medications containing paracetamol alongside Napa Syrup to prevent an accidental overdose.
Side Effects
Napa Syrup is generally well-tolerated, but some rare side effects include:
Nausea or vomiting
Skin rash or itching
Abdominal pain
If any of these occur, seek medical attention immediately.
Conclusion
Napa Syrup is a reliable and effective medication for managing fever and mild to moderate pain, especially in children. Its affordability, safety, and fast action make it a preferred choice in many households. However, responsible usage is key to ensuring its effectiveness and preventing potential risks. Always consult a healthcare professional if you’re unsure about the appropriate dosage or if symptoms persist.
By understanding the benefits and proper use of Napa Syrup, you can confidently use it as a first-line treatment for common ailments in children and adults alike.
Composition of Napa Syrup: A Detailed Look
Napa Syrup is a widely used over-the-counter medication primarily prescribed for relieving pain and reducing fever. Manufactured by Beximco Pharmaceuticals, this syrup is commonly administered to children due to its easy-to-swallow liquid form. In this blog, we will delve into the key ingredients of Napa Syrup and understand how each component contributes to its effectiveness.
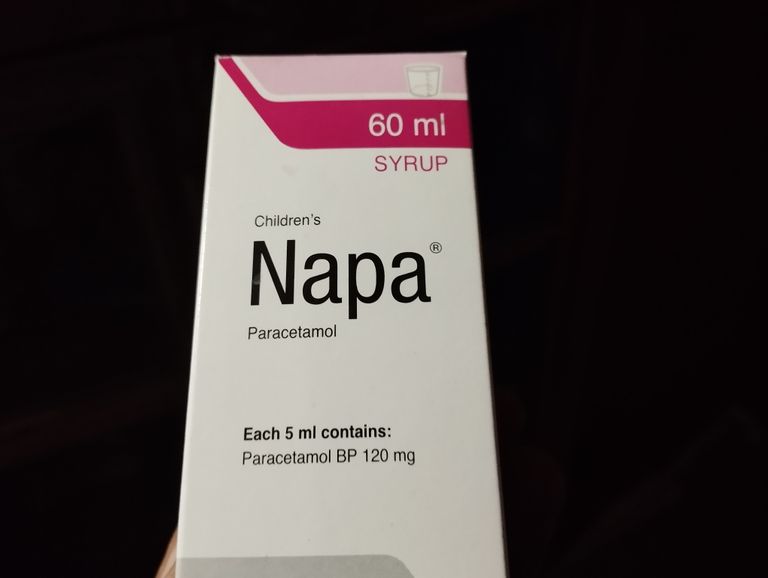

- Active Ingredient: Paracetamol
The primary active ingredient in Napa Syrup is Paracetamol, also known as Acetaminophen. This component is responsible for the syrup’s analgesic (pain-relieving) and antipyretic (fever-reducing) properties. Paracetamol works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins in the brain, which are chemicals that cause pain and inflammation. It is effective in treating mild to moderate pain such as headaches, toothaches, and muscle aches, as well as in reducing fever caused by infections or illnesses.
Concentration: Napa Syrup typically contains 120 mg of Paracetamol per 5 mL of syrup, making it suitable for pediatric use.
- Sweeteners and Flavoring Agents
To make the syrup palatable for children, sweeteners and flavoring agents are added. These components mask the bitter taste of Paracetamol and enhance the overall taste of the syrup. Common flavoring agents used in Napa Syrup include fruit flavors like orange or strawberry.
Purpose: Improves taste and ensures compliance in younger patients.
- Preservatives
Preservatives are included in Napa Syrup to extend its shelf life and maintain its safety for consumption over time. These substances prevent the growth of harmful bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms.
Common Preservatives: Sodium benzoate and potassium sorbate are frequently used preservatives in liquid medications like Napa Syrup.
- Stabilizers and Thickeners
Stabilizers and thickeners ensure that the syrup maintains a consistent texture and does not separate into different layers during storage. They also help evenly distribute the active ingredient in the liquid, ensuring accurate dosing.
Examples: Glycerin and xanthan gum are often used in formulations like Napa Syrup.
- Solvent: Purified Water
The base of Napa Syrup is purified water, which serves as the medium for dissolving all other ingredients. This ensures a liquid form that is easy to measure and administer.
- Coloring Agents (Optional)
In some versions of Napa Syrup, mild coloring agents are used to give the liquid an appealing look. These agents are safe for consumption and approved by regulatory authorities.
Safety and Usage Guidelines
Although Napa Syrup is considered safe when used as directed, it is essential to follow dosage instructions carefully, especially for children. Overdosing on Paracetamol can lead to severe liver damage. Always consult a healthcare provider before administering Napa Syrup to ensure appropriate usage.
Conclusion
Napa Syrup is a trusted medication that combines the effective pain-relieving and fever-reducing properties of Paracetamol with ingredients that ensure ease of administration and long-term stability. By understanding its composition, users can be confident in its safe and effective use.
If you are using Napa Syrup or considering it for your child, always follow the recommended dosage and consult a doctor if symptoms persist.
The Harmful Effects of Noise Pollution
Noise pollution, also known as environmental noise or sound pollution, is a growing concern in urban and industrial areas. Defined as unwanted or harmful levels of noise, it disrupts the natural balance and negatively impacts both humans and the environment. This article explores the detrimental effects of noise pollution on health, society, and the ecosystem.
What is Noise Pollution?
Noise pollution occurs when sound levels exceed the normal threshold of human tolerance, typically measured in decibels (dB). Prolonged exposure to noise above 85 dB can cause severe health issues. Common sources include traffic, industrial operations, construction activities, loud music, and urban crowding. Noise pollution is often overlooked compared to other forms of pollution, but its consequences can be equally damaging.
- Effects on Human Health
The most significant impact of noise pollution is on human health. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels can lead to:
a. Hearing Loss
Continuous exposure to loud noises can damage the auditory system, resulting in temporary or permanent hearing loss. This is particularly common among individuals working in noisy environments such as factories or construction sites.
b. Cardiovascular Issues
Studies have shown a strong link between noise pollution and heart problems. Chronic noise exposure can increase blood pressure, elevate stress hormone levels, and contribute to heart disease.
c. Sleep Disturbances
Noise pollution disrupts sleep patterns, leading to insomnia and reduced sleep quality. Poor sleep can result in fatigue, irritability, and impaired cognitive functioning.
d. Mental Health Disorders
Continuous exposure to noise can lead to anxiety, depression, and stress. It impairs concentration, increases frustration, and affects overall mental well-being.
e. Reduced Productivity
Noise pollution, especially in workplaces or study environments, hampers focus and efficiency. It distracts individuals, making it difficult to complete tasks effectively.
- Social and Economic Impact
Noise pollution affects society in numerous ways, including:
a. Reduced Quality of Life
High noise levels in residential areas reduce the overall quality of life. People living near airports, busy roads, or industrial zones often experience frustration and a sense of helplessness due to constant noise exposure.
b. Property Value Decline
Properties located in noisy areas often have lower market values. Noise pollution discourages potential buyers and investors, impacting the local real estate market.
c. Increased Accidents
Noise pollution can distract drivers, leading to accidents on the road. It also hampers communication, making it challenging to hear warnings or alarms in emergency situations.
- Environmental Consequences
Noise pollution affects not just humans but also the ecosystem. Key environmental impacts include:
a. Disturbance to Wildlife
Animals rely on sound for communication, navigation, and survival. Excessive noise disrupts their natural behaviors, leading to disorientation, migration, or even extinction of certain species.
b. Marine Life Impact
Underwater noise from ships, submarines, and industrial activities severely affects marine creatures. It disrupts communication among aquatic species, particularly whales and dolphins, which rely on echolocation.
c. Ecosystem Imbalance
Noise pollution alters predator-prey dynamics by masking important sounds in the environment. This creates a ripple effect that can destabilize entire ecosystems.
- Sources of Noise Pollution
Understanding the sources is essential for controlling noise pollution. Common contributors include:
Traffic Noise: Vehicles, honking, and road construction.
Industrial Noise: Machinery and factory operations.
Construction Activities: Drilling, hammering, and heavy machinery.
Recreational Noise: Loudspeakers, music concerts, and public gatherings.
Household Noise: Appliances, televisions, and domestic arguments.
- Strategies to Combat Noise Pollution
Reducing noise pollution requires collective efforts from individuals, communities, and governments. Some effective measures include:
a. Legislation and Policies
Governments should enforce strict noise control laws, such as limiting vehicle honking, regulating construction hours, and monitoring industrial noise.
b. Urban Planning
Developing green zones, soundproofing buildings, and using noise barriers in urban areas can reduce noise pollution significantly.
c. Awareness Campaigns
Educating the public about the harmful effects of noise pollution and promoting behavioral changes, such as using headphones instead of loudspeakers, can help minimize noise.
d. Technological Solutions
Innovations like quieter machinery, noise-canceling devices, and improved transportation systems can contribute to noise reduction.
e. Personal Actions
Individuals can take small steps, such as lowering the volume of music, avoiding unnecessary honking, and planting trees around their homes.
Conclusion
Noise pollution is a silent but serious threat to human health, societal harmony, and environmental stability. It demands immediate attention and action to prevent further damage. By adopting sustainable practices, raising awareness, and enforcing regulations, we can create a quieter, healthier, and more peaceful world for future generations.
The Harmful Effects of Noise Pollution
Noise pollution, also known as environmental noise or sound pollution, is a growing concern in urban and industrial areas. Defined as unwanted or harmful levels of noise, it disrupts the natural balance and negatively impacts both humans and the environment. This article explores the detrimental effects of noise pollution on health, society, and the ecosystem.
What is Noise Pollution?
Noise pollution occurs when sound levels exceed the normal threshold of human tolerance, typically measured in decibels (dB). Prolonged exposure to noise above 85 dB can cause severe health issues. Common sources include traffic, industrial operations, construction activities, loud music, and urban crowding. Noise pollution is often overlooked compared to other forms of pollution, but its consequences can be equally damaging.
- Effects on Human Health
The most significant impact of noise pollution is on human health. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels can lead to:
a. Hearing Loss
Continuous exposure to loud noises can damage the auditory system, resulting in temporary or permanent hearing loss. This is particularly common among individuals working in noisy environments such as factories or construction sites.
b. Cardiovascular Issues
Studies have shown a strong link between noise pollution and heart problems. Chronic noise exposure can increase blood pressure, elevate stress hormone levels, and contribute to heart disease.
c. Sleep Disturbances
Noise pollution disrupts sleep patterns, leading to insomnia and reduced sleep quality. Poor sleep can result in fatigue, irritability, and impaired cognitive functioning.
d. Mental Health Disorders
Continuous exposure to noise can lead to anxiety, depression, and stress. It impairs concentration, increases frustration, and affects overall mental well-being.
e. Reduced Productivity
Noise pollution, especially in workplaces or study environments, hampers focus and efficiency. It distracts individuals, making it difficult to complete tasks effectively.
- Social and Economic Impact
Noise pollution affects society in numerous ways, including:
a. Reduced Quality of Life
High noise levels in residential areas reduce the overall quality of life. People living near airports, busy roads, or industrial zones often experience frustration and a sense of helplessness due to constant noise exposure.
b. Property Value Decline
Properties located in noisy areas often have lower market values. Noise pollution discourages potential buyers and investors, impacting the local real estate market.
c. Increased Accidents
Noise pollution can distract drivers, leading to accidents on the road. It also hampers communication, making it challenging to hear warnings or alarms in emergency situations.
- Environmental Consequences
Noise pollution affects not just humans but also the ecosystem. Key environmental impacts include:
a. Disturbance to Wildlife
Animals rely on sound for communication, navigation, and survival. Excessive noise disrupts their natural behaviors, leading to disorientation, migration, or even extinction of certain species.
b. Marine Life Impact
Underwater noise from ships, submarines, and industrial activities severely affects marine creatures. It disrupts communication among aquatic species, particularly whales and dolphins, which rely on echolocation.
c. Ecosystem Imbalance
Noise pollution alters predator-prey dynamics by masking important sounds in the environment. This creates a ripple effect that can destabilize entire ecosystems.
- Sources of Noise Pollution
Understanding the sources is essential for controlling noise pollution. Common contributors include:
Traffic Noise: Vehicles, honking, and road construction.
Industrial Noise: Machinery and factory operations.
Construction Activities: Drilling, hammering, and heavy machinery.
Recreational Noise: Loudspeakers, music concerts, and public gatherings.
Household Noise: Appliances, televisions, and domestic arguments.
- Strategies to Combat Noise Pollution
Reducing noise pollution requires collective efforts from individuals, communities, and governments. Some effective measures include:
a. Legislation and Policies
Governments should enforce strict noise control laws, such as limiting vehicle honking, regulating construction hours, and monitoring industrial noise.
b. Urban Planning
Developing green zones, soundproofing buildings, and using noise barriers in urban areas can reduce noise pollution significantly.
c. Awareness Campaigns
Educating the public about the harmful effects of noise pollution and promoting behavioral changes, such as using headphones instead of loudspeakers, can help minimize noise.
d. Technological Solutions
Innovations like quieter machinery, noise-canceling devices, and improved transportation systems can contribute to noise reduction.
e. Personal Actions
Individuals can take small steps, such as lowering the volume of music, avoiding unnecessary honking, and planting trees around their homes.
Conclusion
Noise pollution is a silent but serious threat to human health, societal harmony, and environmental stability. It demands immediate attention and action to prevent further damage. By adopting sustainable practices, raising awareness, and enforcing regulations, we can create a quieter, healthier, and more peaceful world for future generations.