Hello everyone welcome to my blog.
A protein is a complex substance which occurs naturally in all living things. It is made up of series of amino acids and it is responsible for the formation of many essential biological compounds such as antibodies, enzymes, and hormones.
Proteins can be categorized based on functions and activities and this includes;
🔸Storage
These are the type of protein usually found in milk, egg white, and Plant seeds. They serve as biological reserves for organisms thus making them rich in metal ions and amino acids.
(Eg; Ferritin)
🔸Transport
These are type of Proteins found within the membrane. They aid in transportation of materials across biological membranes using a method known as facilitated diffusion.
(Eg; Carrier proteins, Channel Proteins, and gated channel Proteins)
🔸Signal
These types of Proteins play a vital role in brain functions. They control the response of cells to various external signals.
(Eg; Thyroid hormone, progesterone and testosterone)
🔸Contractile
These are proteins that mediate contraction of cytoskeletons, cardiac and skeleton muscles. They are usually found in the muscle and can also be classified under structural Proteins.
(Eg; Actin and Myosin)
🔸Enzyme
These are Proteins that enhances various biochemical reactions in the body. They regulate the speed of reaction by either increasing or decreasing the activation energy of a biochemical reaction.
(Eg; Amylase.. found in saliva)
🔸Defense
These type of proteins are regarded as antibodies. They help to eliminate foreign substances in the body through neutralization and engulfment.
(Eg; lysozyme)
🔸Structure
The structural Protein is considered to be the most abundant protein in nature primarily due to the level of abundance of collagen in the mammalian body.
This type of Proteins are usually used for extracellular matrix, cell culture, material science applications, and cytoskeletal research.
Let's look at the list of some structural Proteins, their location and primary functions
| STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | MAIN LOCATION | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|
| Keratin | Skin, hair, internal organs | Protection |
| Actin | Muscles | Contraction |
| Troponin | Muscles | Regulate the binding of Myosin to Actin |
| Actinin | Non-muscle cells | Causes the cohesiveness of cytoskeletons |
| Mucin | Plasma membrane | Receptors |
| Tropomyosin | Muscles | Regulates the binding of Myosin to Actin |
| Collagen | Rough endoplasmic retoculum | Structural support |
| Vimentin | Mesenchymal | Formation of cytoskeletal protein sheets |
| Decorin | Connective tissues & extracellular matrix | Covers the surface of adult bones in movable joints |
| Biglycan | X chromosome | It enhances the inhibition effect of TGF-ß |
| Myosin | Muscle | Muscle contraction |
| Fibrinogen | Liver | coagulation cascade |
| Spectrin | Plasma membrane | Covers the cytoplasmic surface of vertebrates. |

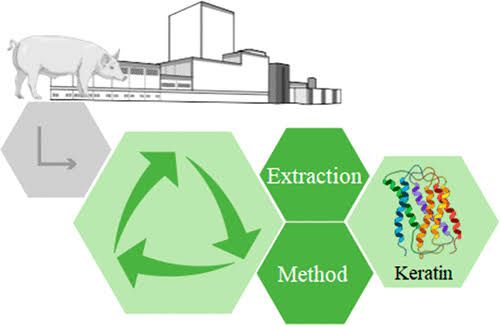
Keratin is a type of structural protein that helps in the protection and strengthing of the hair, skin, and nails. It is also found in animal horns, feathers, and wool of different animals.
Here I will be showing us steps on how to extract Keratin protein from feathers.
🔺I will start by preparing of solution of sodium sulphide and sodium hydroxide using 2L of distilled water.
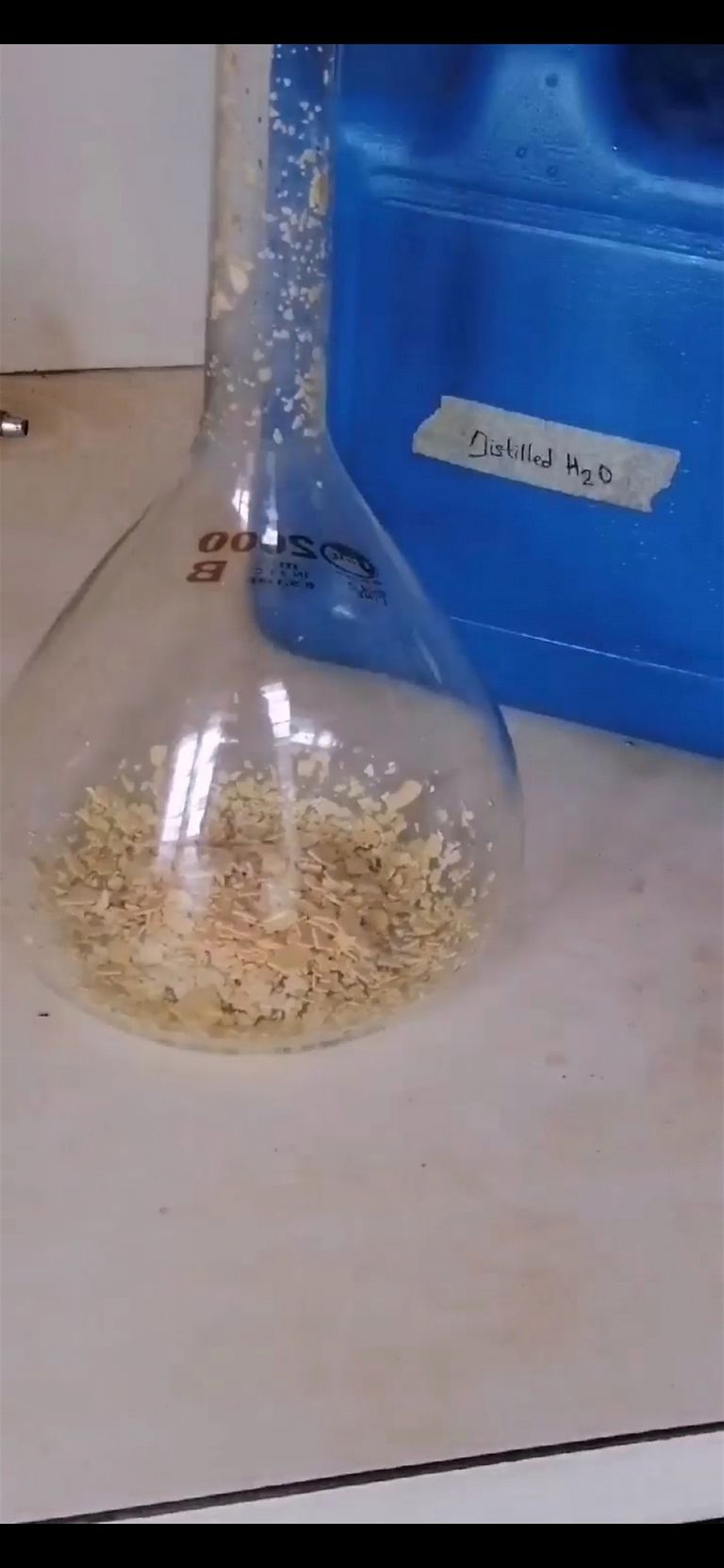
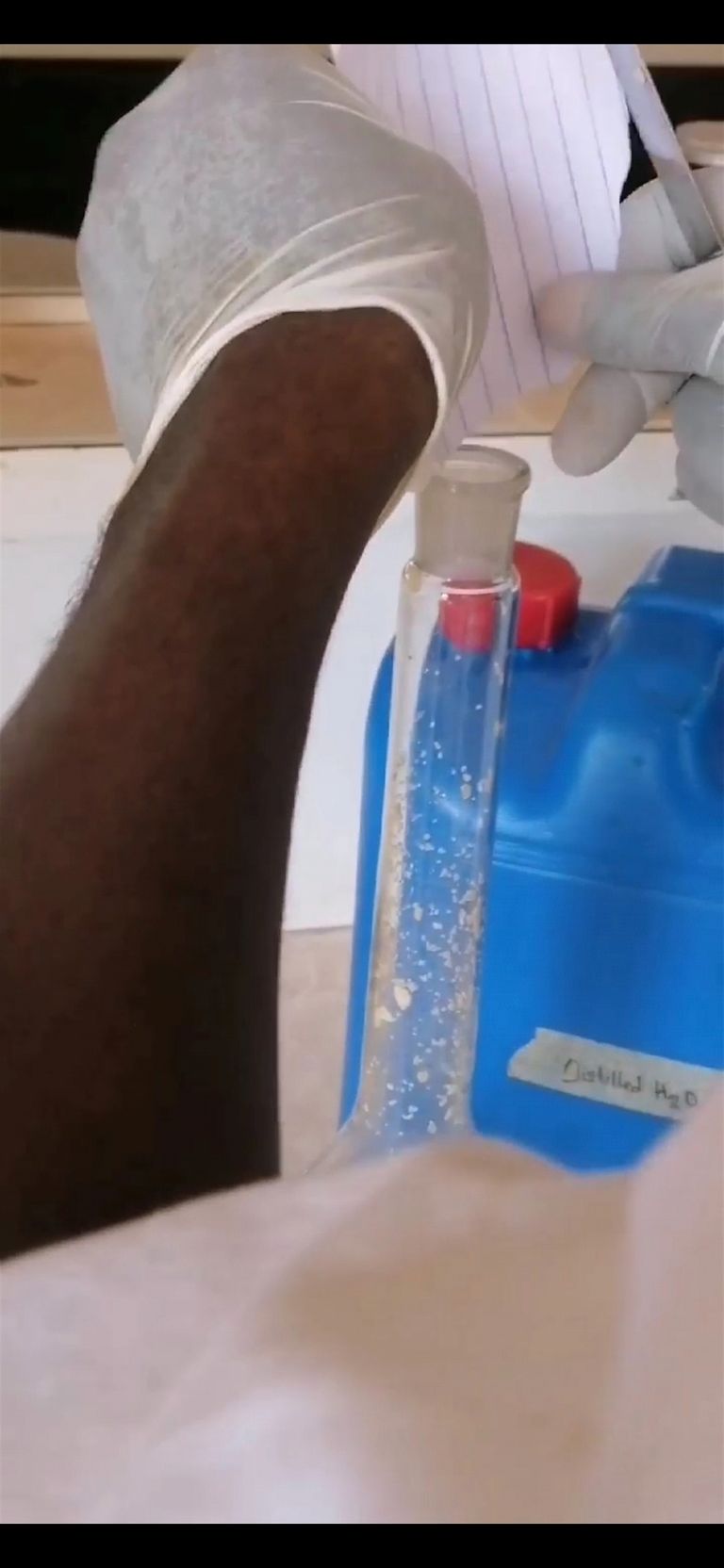


🔺After preparing the solution above, pour it inside a beaker containing feathers (eg; chicken feathers). After pouring, make sure that the feathers are fully submerged inside the solution then you move to setting up your heater which will be used in heating the solution while stirring.
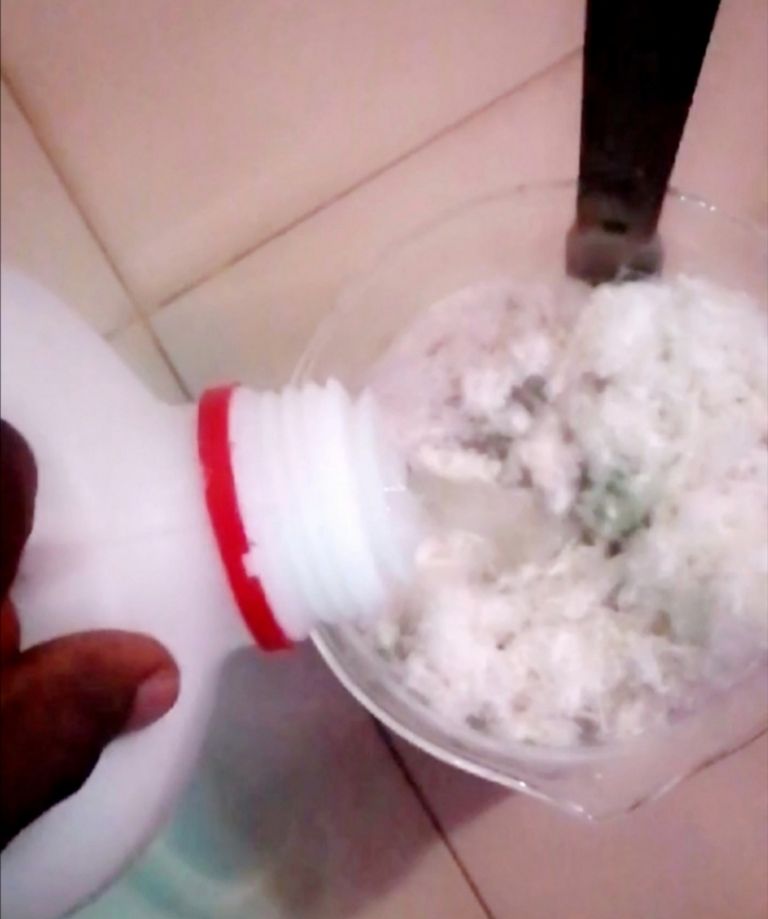
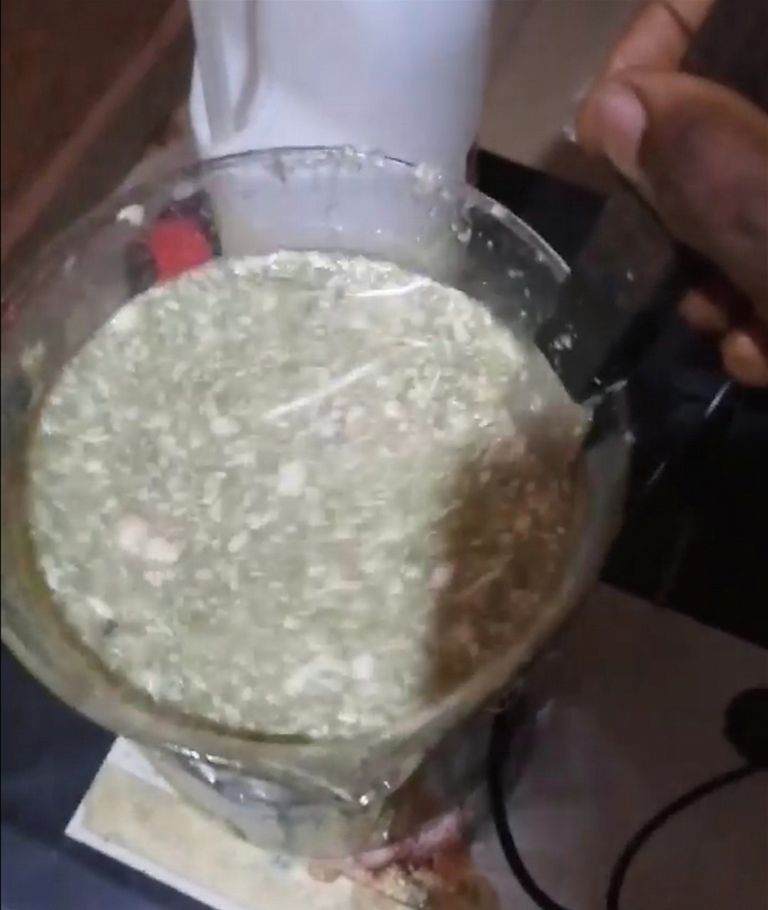


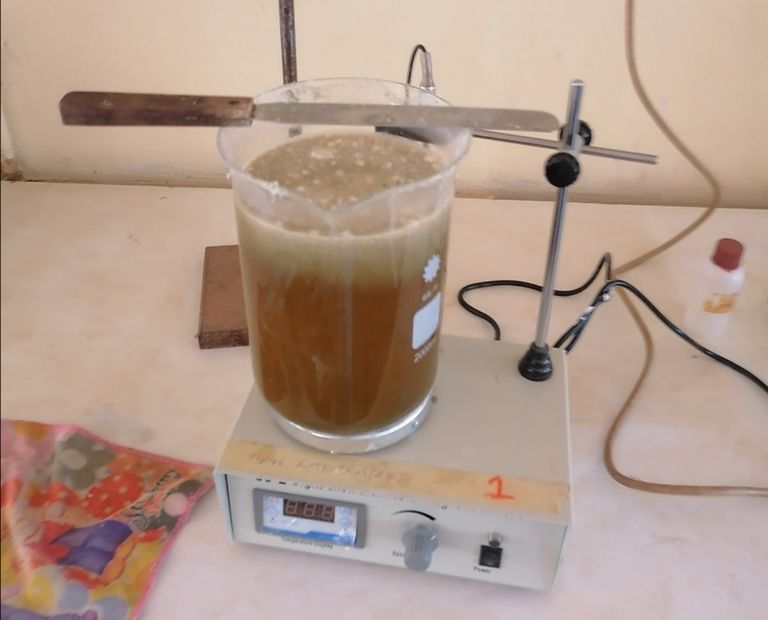
🔺The stirring should be made for 6hrs on a constant heat supply. The temperature of the heater should be maintained between 39°C to 49°C in other to avoid low heat or excess heat transfer.
After stirring for 6hrs, the colour of the feather solution will change from brown to dark green.
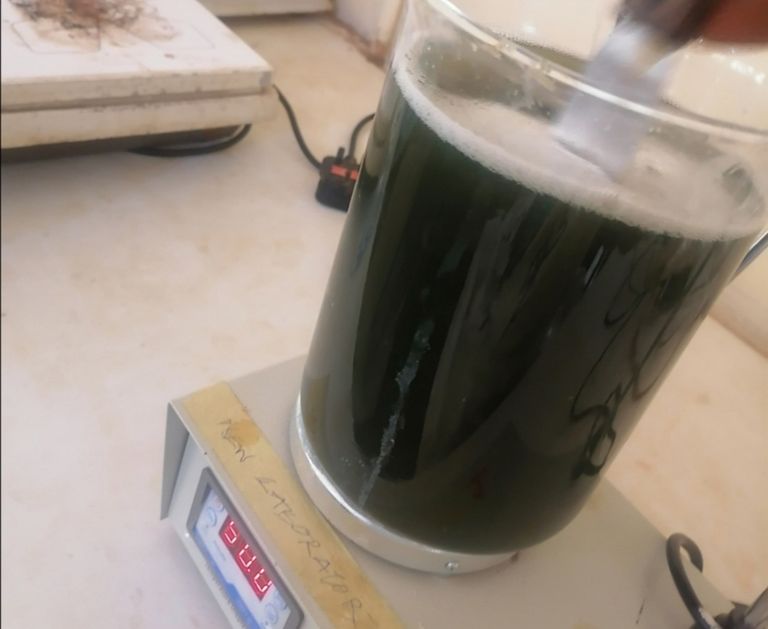


🔺After the 6hrs stirring is completed, I will proceed with my first filtration process. This process takes time as the solution is thick thus making it to slowly pass through the filter paper.
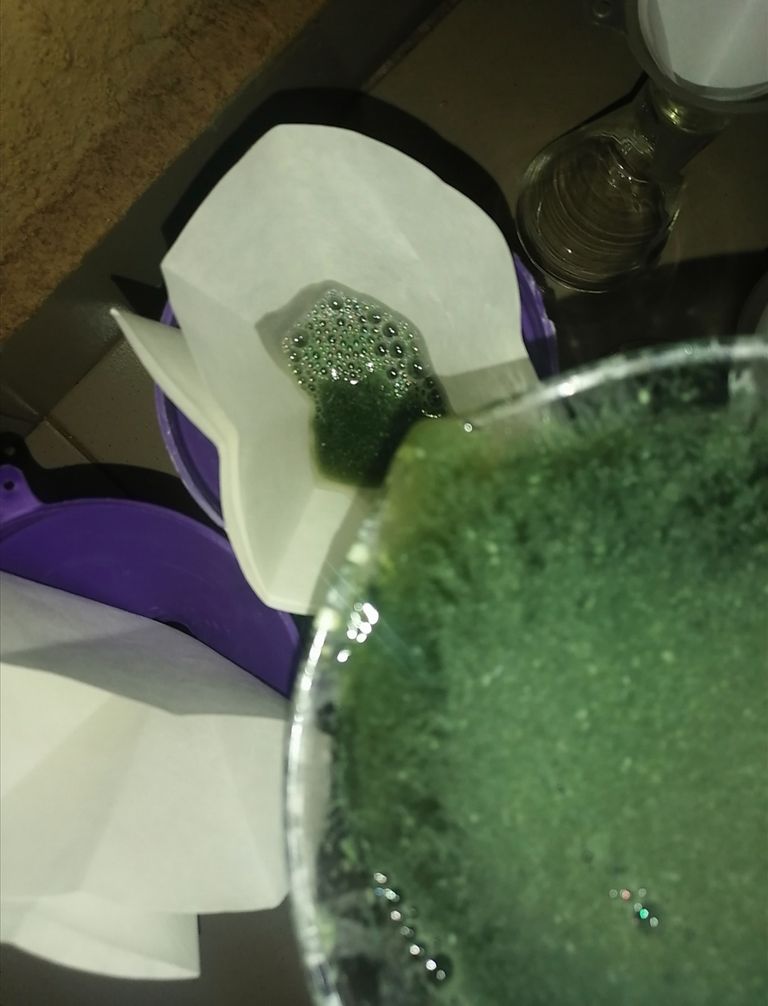
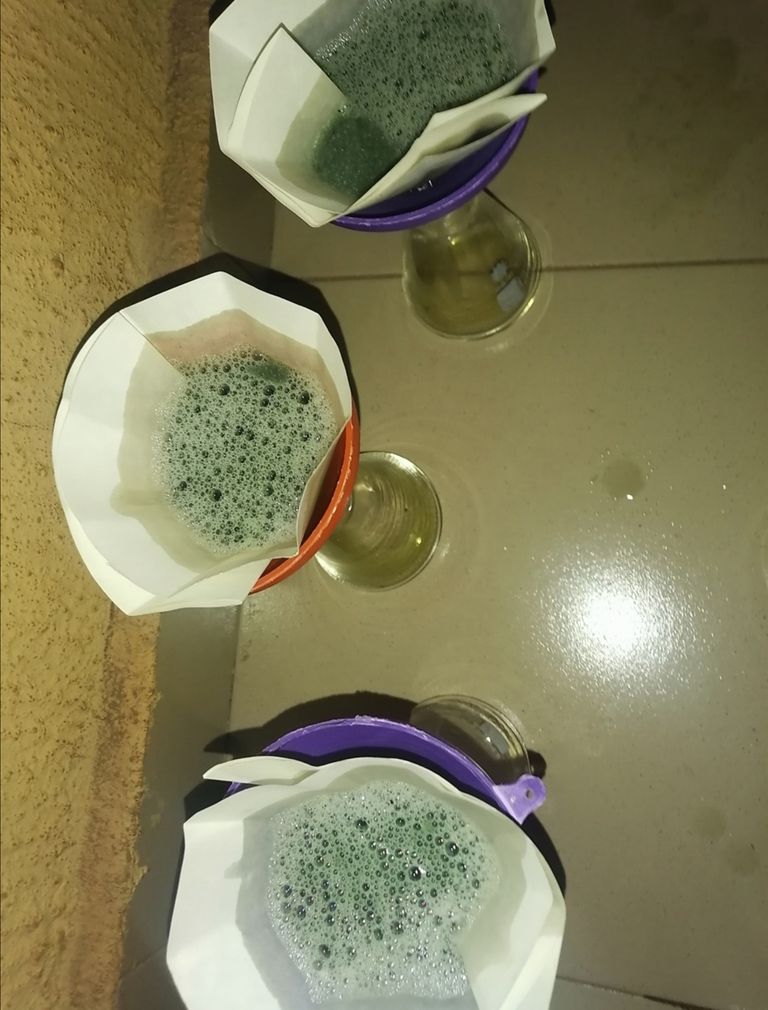


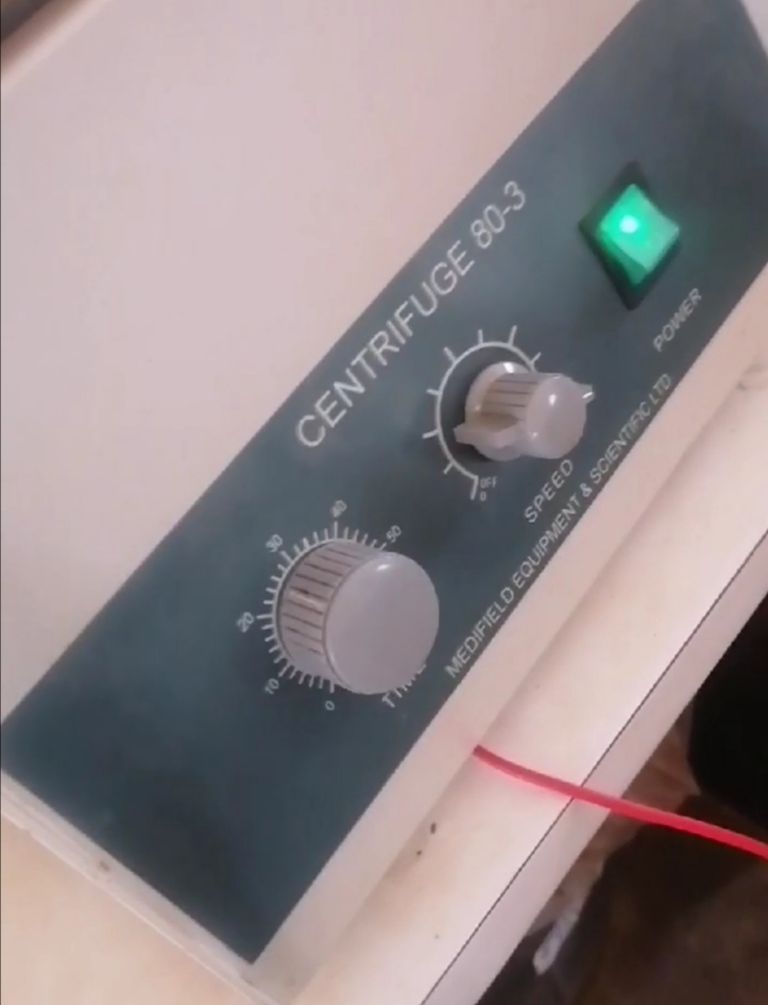
🔺After the first filtration, the filtrate is collected in a test tube and placed inside a centrifuge for 34 minutes. This is to further separate the contents of the filtered solution by taking advantage of the difference in their densities.
After the 34 minutes of centrifugation is completed, the test tube is removed and the lower part of the solution in the test tube is refilterd while the other upper part which is less dense is discarded.
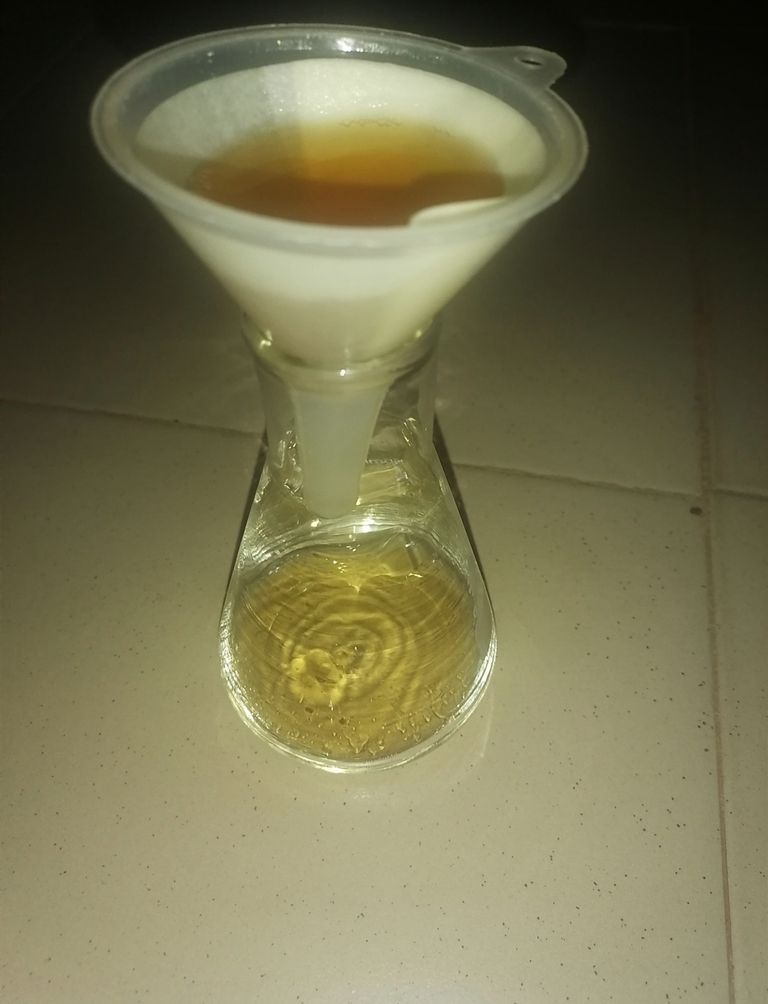


🔺After the final filtration, the residue in the filter paper is collected while the filtrate is discarded. This residue is a protein known as Keratin.
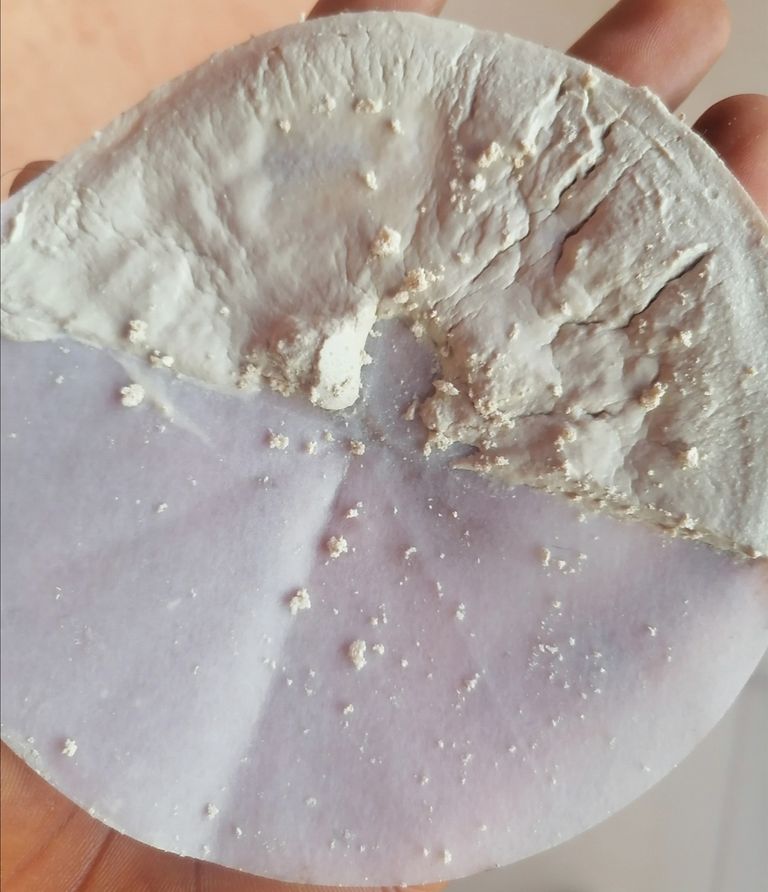


Keratin can easily be gotten by consuming foods rich in biotin, vitamin A, and zinc nutrients. These nutrients supports the production of Keratin and are contained in foods such as eggs, carrots, salmon, mangoes, sweet potatoes, garlic, onions, etc.
It strengthens the hair, nails and skin thus protecting them against structural damage.
It keeps the hair softer, repairs damages and eliminates fizz.
It aids faster hair growth and hair regeneration.
It also reduces texture and increase styling manageability of the hair.
People, especially women do go for Keratin treatment in other to improve their hair quality.
- Side effects of Keratin treatment
In as much as there are no apparent side effects of Keratin, certain compounds used in addition with Keratin during Keratin treatment can lead to a wide range of side effects such as; eye irritation, headaches, dizziness, sore throat, coughing, wheezing, nausea, chest pain, etc.

Proteins are very essential compounds which aid in the proper functioning of the body. They are made up of one or more chains of amino acids which are regarded as the building blocks.
There are different types of Proteins which are classified based on activity and use. None is more important than the other as they all aid in carrying out various body functions effectively.
NOTE: ALL UNSOURCED IMAGES WERE CAPTURED USING MY HUAWEI Y9s PHONE CAMERA
.jpeg)