Rahmanir Rahim
Assalamu Alaikum Wa Rahmatullahi Wa Barakatuhu
Dear Companions Today I want to share with you some words about the evils of killing foetuses.Welcom to this post and congratulations to all.
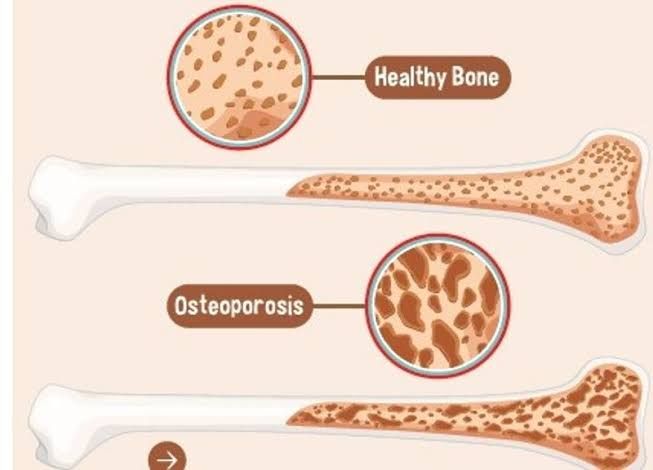
Introduction:
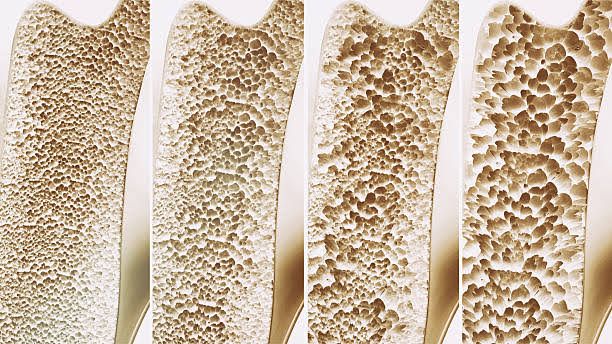
Osteoporosis is a prevalent bone disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to an increased risk of fractures. This comprehensive guide delves into the symptoms, causes, remedies, and management strategies for osteoporosis.
source
Symptoms:
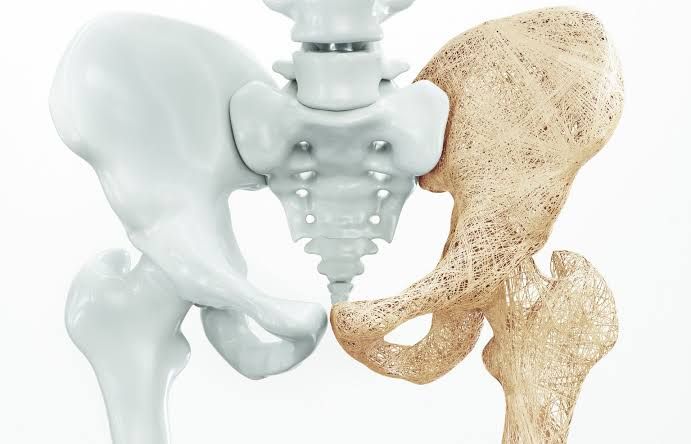
Fractures: Osteoporosis weakens bones, making them more prone to fractures, particularly in the spine, hip, and wrist. Fractures can occur with minimal trauma or even during routine activities.
Loss of Height: Compression fractures in the spine can cause a gradual loss of height and a stooped posture, known as kyphosis.
source
Back Pain: Vertebral fractures may result in chronic back pain, which can be severe and debilitating.
Reduced Mobility: Fractures and bone weakness can limit mobility and independence, impacting daily activities and quality of life.
Causes:
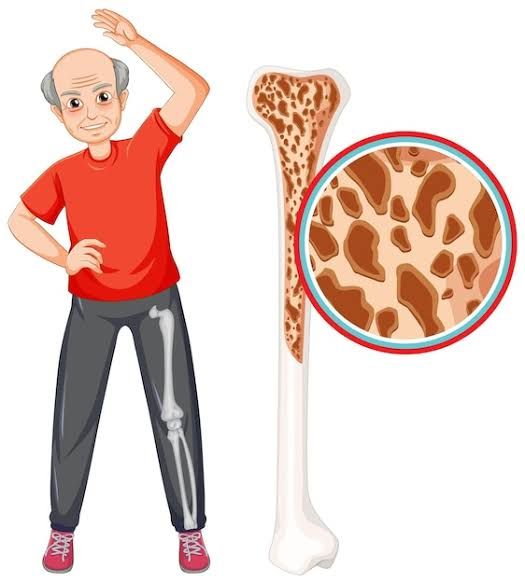
Age: Aging is a significant risk factor for osteoporosis. As people age, bone density naturally decreases, and bone regeneration slows down.
source
Gender: Women are at a higher risk of osteoporosis, especially after menopause when estrogen levels decline, leading to accelerated bone loss.
Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions such as hyperthyroidism or overactive parathyroid glands can disrupt hormone levels and contribute to bone loss.
source
Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of calcium and vitamin D can weaken bones, as these nutrients are essential for bone health.
Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of weight-bearing exercise can lead to reduced bone density and strength.
Genetics: Family history of osteoporosis or a personal history of fractures may increase the risk.
Medications: Long-term use of certain medications, such as corticosteroids or some anticonvulsants, can weaken bones and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Remedies:
Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrients essential for bone health is crucial. Good dietary sources of calcium include dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods. Sun exposure and supplementation are recommended for vitamin D.
source
Exercise: Weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises help build and maintain bone density. Activities like walking, dancing, and weightlifting are beneficial.
Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help prevent further bone loss.
source
Fall Prevention: Taking measures to prevent falls, such as removing tripping hazards, installing grab bars, and wearing appropriate footwear, can reduce the risk of fractures.
Medications: In some cases, medications such as bisphosphonates, hormone therapy, or denosumab may be prescribed to slow bone loss and reduce fracture risk.
Management:
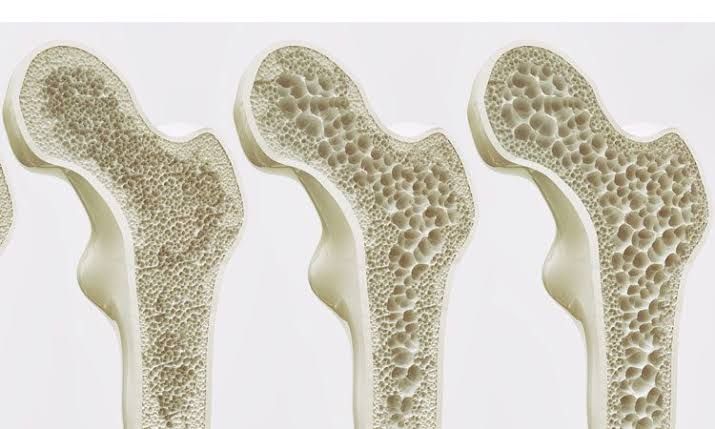
Diagnosis: Osteoporosis is diagnosed through bone density testing, typically using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans. Early detection allows for timely intervention and management.
Treatment Plan: A personalized treatment plan, considering factors such as age, sex, medical history, and fracture risk, is essential. This may include a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular monitoring.
Regular Monitoring: Periodic follow-up appointments and bone density tests are necessary to evaluate treatment effectiveness and adjust the management plan as needed.
Patient Education: Educating patients about osteoporosis, its risk factors, and preventive measures empowers them to actively participate in their own care and make informed lifestyle choices.
Multidisciplinary Approach: Managing osteoporosis often involves collaboration between primary care physicians, endocrinologists, rheumatologists, physical therapists, and other healthcare professionals to address various aspects of the disease comprehensively.
source
Osteoporosis is a serious and prevalent bone disease that requires comprehensive management to mitigate its impact on individuals' health and quality of life. By understanding the symptoms, causes, remedies, and management strategies outlined in this guide, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage osteoporosis effectively. Early detection, lifestyle modifications, appropriate nutrition, regular exercise, and medical interventions are key components of a holistic approach to managing osteoporosis and reducing the risk of fractures. Through ongoing education, support, and collaboration with healthcare providers, individuals can maintain strong and healthy bones as they age, promoting overall well-being and independence.
Upvoted. Thank You for sending some of your rewards to @null. Read my last posts to make sure that BLURT burning is profitable for you. Before using this bot please make sure your account has at least 100 BP. Get more BLURT:
@ mariuszkarowski/how-to-get-automatic-upvote-from-my-accounts@ blurtbooster/blurt-booster-introduction-rules-and-guidelines-1699999662965@ nalexadre/blurt-nexus-creating-an-affiliate-account-1700008765859@ kryptodenno - win BLURT POWER delegationNote: This bot will not vote on AI-generated content