Bismillaher Rahmanir Rahim.
Assalamu Alaikum Wa Rahmatullahi Wa Barakatuhu
Dear Companions Today I want to share with you some words about the evils of killing foetuses.Welcom to this post and congratulations to all
Rain is one of nature's most essential and beautiful phenomena, playing a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth. It is a form of precipitation where water droplets fall from the atmosphere to the ground, originating from clouds. Rain is vital for replenishing freshwater sources, supporting ecosystems, and maintaining the water cycle, which in turn sustains all forms of life. While rain has numerous benefits, it can also be destructive under certain circumstances. This discussion delves into the concept of rain, its types, and how it can both benefit and harm the environment and human activities.

source
What is Rain?
Rain is essentially water in the form of droplets that has condensed from atmospheric vapor and falls under the influence of gravity. The process begins when water evaporates from oceans, lakes, rivers, and other water bodies due to the heat from the sun. The water vapor rises into the atmosphere, where it cools and condenses into tiny droplets, forming clouds. When these droplets combine and grow large enough, they become too heavy to remain suspended in the air and fall to the Earth as rain.
Types of Rain
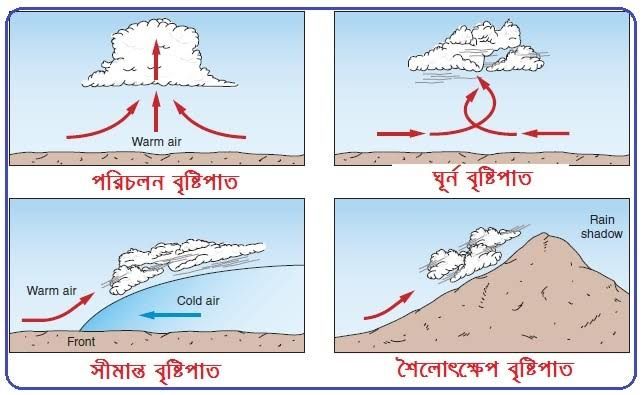
Rain can be categorized into several types, depending on the mechanism that causes it. These types include:
- Convectional Rain
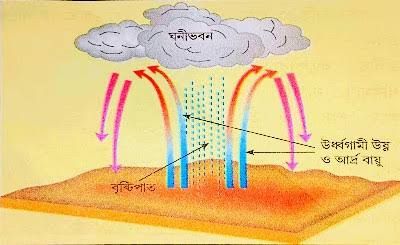
Convectional rain occurs when the sun heats the Earth’s surface, causing the air near the ground to warm up and rise. As the warm air ascends, it cools and condenses, forming clouds. When these clouds become saturated, rain falls. This type of rain is common in tropical regions where intense heat causes the rapid evaporation of water. Convectional rain is often short-lived but can be heavy, leading to sudden downpours.
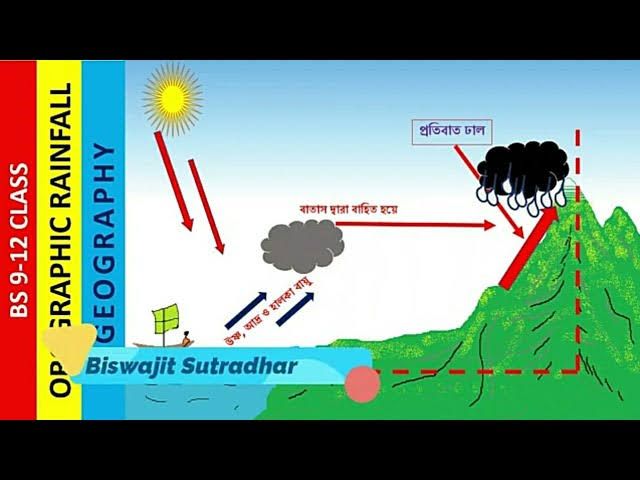
Orographic or Relief Rain
Orographic rain occurs when moist air is forced to ascend over a mountain range. As the air rises, it cools, leading to condensation and precipitation. The windward side of the mountain, which faces the prevailing winds, receives a significant amount of rainfall, while the leeward side, sheltered from the wind, tends to be dry, creating a "rain shadow." This type of rain is typical in mountainous regions.Frontal or Cyclonic Rain
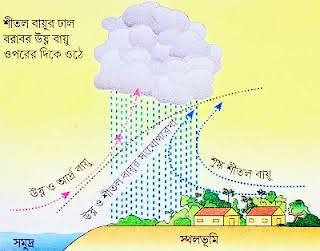
Frontal rain occurs when two air masses of different temperatures meet, typically a warm air mass and a cold air mass. The warm air, being lighter, is forced to rise over the cold air. As the warm air rises, it cools, and the moisture it carries condenses into clouds, eventually leading to rain. This type of rain is common in temperate regions and is usually associated with weather fronts.Monsoonal Rain
Monsoonal rain is driven by seasonal winds that reverse direction based on temperature differences between land and ocean. This phenomenon is most pronounced in South Asia, where monsoon winds bring heavy rains during the summer months. Monsoonal rains are critical for agriculture in many parts of the world but can also lead to flooding and other disasters.
Drizzle
Drizzle is a form of light rain consisting of very small droplets. It often occurs under conditions of weak convection or in situations where there is a stable, saturated air mass with little vertical motion. Though drizzle does not significantly affect visibility or cause flooding, it can lead to slippery conditions and contribute to the dampness of an area.Acid Rain
Acid rain is a type of rain that contains harmful levels of sulfuric and nitric acids, usually caused by pollution from industrial processes and the burning of fossil fuels. When these pollutants mix with water vapor in the atmosphere, they create acid rain, which can have detrimental effects on the environment, such as soil degradation, damage to plant life, and the acidification of water bodies.
Benefits of Rain
Rain is essential to life on Earth and provides numerous benefits. Some of the key advantages include:
- Water Supply
Rainfall is a primary source of freshwater, which is crucial for drinking, agriculture, and industry. It replenishes rivers, lakes, and underground aquifers, ensuring a continuous supply of water for various human and ecological needs.
Agriculture
Rain supports agriculture by watering crops and helping maintain soil moisture. In many regions, rainfed agriculture is the backbone of the local economy. Crops such as rice, wheat, and maize rely heavily on rainfall, particularly in areas where irrigation systems are underdeveloped or unavailable.Ecosystem Support
Rain nourishes ecosystems by providing water to plants, animals, and microorganisms. It helps maintain forests, grasslands, and wetlands, which are home to a diverse range of species. Additionally, rainwater carries nutrients from the atmosphere to the soil, promoting plant growth and the overall health of ecosystems.Temperature Regulation
Rain plays a role in regulating Earth's temperature by cooling the atmosphere. The process of rain formation involves the transfer of heat from the Earth's surface to the atmosphere, which helps reduce surface temperatures, especially in hot climates.Air Quality
Rain helps improve air quality by washing away dust, pollen, and other airborne pollutants. After a rainfall, the air tends to be cleaner and fresher, benefiting people, especially those with respiratory conditions like asthma or allergies.
Harms and Dangers of Rain
Despite its benefits, rain can also have harmful effects, particularly when it occurs in excess or under specific conditions.
Flooding
Heavy or prolonged rainfall can lead to flooding, especially in areas with poor drainage or near water bodies. Flooding can cause significant damage to property, infrastructure, and crops, displace populations, and result in loss of life. Urban areas are particularly vulnerable due to the prevalence of impermeable surfaces like roads and buildings, which prevent water from being absorbed into the ground.Soil Erosion
Rainfall, particularly when it is heavy, can lead to soil erosion. As water flows over the land, it carries away the top layer of soil, which contains vital nutrients needed for plant growth. This can reduce agricultural productivity and lead to the degradation of natural landscapes. Deforestation and poor land management practices can exacerbate soil erosion during rainfall.Landslides
In hilly or mountainous regions, intense rainfall can trigger landslides, especially in areas where the soil has been loosened due to deforestation, mining, or construction. Landslides can bury homes, block roads, and disrupt communities, causing extensive damage and loss of life.Acid Rain
As mentioned earlier, acid rain can cause significant environmental damage. It degrades soil quality, harms aquatic life by increasing the acidity of water bodies, and damages man-made structures, particularly those made of limestone or marble. Acid rain also affects forests by leaching away essential nutrients from the soil and damaging tree leaves.Hail and Storms
During severe thunderstorms, rain can be accompanied by hail, strong winds, and lightning. These storms can damage crops, buildings, vehicles, and power lines. In extreme cases, storms may lead to flash flooding, power outages, and casualties. Hailstorms, in particular, can destroy crops and pose a hazard to animals and humans.Health Risks
Prolonged periods of rain can lead to health problems. Stagnant water left after heavy rain creates breeding grounds for mosquitoes, increasing the risk of diseases like malaria and dengue. Additionally, damp conditions can promote the growth of mold and fungi, which can cause respiratory issues.
Rain is a double-edged sword in its relationship with humans and the environment. On one hand, it provides essential water for drinking, agriculture, and ecosystem sustenance. It helps regulate temperatures and cleanses the air. On the other hand, when rain occurs in excess or under particular conditions, it can lead to flooding, soil erosion, landslides, and other hazards. Acid rain, a byproduct of human activities, poses a unique environmental threat. Understanding the dynamics of rain and managing its effects, both positive and negative, is critical to our survival and well-being.

Upvoted. Thank You for sending some of your rewards to @null. Get more BLURT:
@ mariuszkarowski/how-to-get-automatic-upvote-from-my-accounts@ blurtbooster/blurt-booster-introduction-rules-and-guidelines-1699999662965@ nalexadre/blurt-nexus-creating-an-affiliate-account-1700008765859@ kryptodenno - win BLURT POWER delegationNote: This bot will not vote on AI-generated content