
The domain name bitcoin.org was registered on 18 August 2008. On 31 October 2008, a link to a paper authored by Satoshi Nakamoto titled Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System was posted to a cryptography mailing list. Nakamoto implemented the bitcoin software as open-source code and released it in January 2009. Nakamoto's identity remains unknown.
On 3 January 2009, the bitcoin network was created when Nakamoto mined the starting block of the chain, known as the genesis block. Embedded in the coinbase of this block was the text "The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks". This note references a headline published by The Times and has been interpreted as both a timestamp and a comment on the instability caused by fractional-reserve banking. : 18
The receiver of the first bitcoin transaction was Hal Finney, who had created the first reusable proof-of-work system (RPoW) in 2004. Finney downloaded the bitcoin software on its release date, and on 12 January 2009 received ten bitcoins from Nakamoto. Other early cypherpunk supporters were creators of bitcoin predecessors: Wei Dai, creator of b-money, and Nick Szabo, creator of bit gold. In 2010, the first known commercial transaction using bitcoin occurred when programmer Laszlo Hanyecz bought two Papa John's pizzas for ₿10,000 from Jeremy Sturdivan.
Blockchain analysts estimate that Nakamoto had mined about one million bitcoins before disappearing in 2010 when he handed the network alert key and control of the code repository over to Gavin Andresen. Andresen later became lead developer at the Bitcoin Foundation. Andresen then sought to decentralize control. This left opportunity for controversy to develop over the future development path of bitcoin, in contrast to the perceived authority of Nakamoto's contributions.

2011–2012
After early "proof-of-concept" transactions, the first major users of bitcoin were black markets, such as Silk Road. During its 30 months of existence, beginning in February 2011, Silk Road exclusively accepted bitcoins as payment, transacting 9.9 million in bitcoins, worth about $214 million. : 222
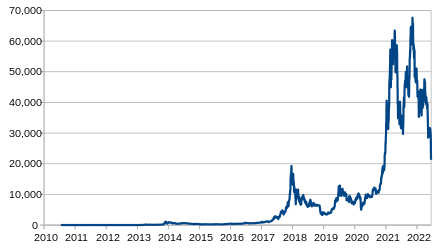
In 2011, the price started at $0.30 per bitcoin, growing to $5.27 for the year. The price rose to $31.50 on 8 June. Within a month, the price fell to $11.00. The next month it fell to $7.80, and in another month to $4.77.
In 2012, bitcoin prices started at $5.27, growing to $13.30 for the year. By 9 January the price had risen to $7.38, but then crashed by 49% to $3.80 over the next 16 days. The price then rose to $16.41 on 17 August, but fell by 57% to $7.10 over the next three days.
The Bitcoin Foundation was founded in September 2012 to promote bitcoin's development and uptake.
On 1 November 2011, the reference implementation Bitcoin-Qt version 0.5.0 was released. It introduced a front end that used the Qt user interface toolkit. The software previously used Berkeley DB for database management. Developers switched to LevelDB in release 0.8 in order to reduce blockchain synchronization time.[citation needed] The update to this release resulted in a minor blockchain fork on 11 March 2013. The fork was resolved shortly afterwards.[citation needed] Seeding nodes through IRC was discontinued in version 0.8.2. From version 0.9.0 the software was renamed to Bitcoin Core. Transaction fees were reduced again by a factor of ten as a means to encourage microtransactions.[citation needed] Although Bitcoin Core does not use OpenSSL for the operation of the network, the software did use OpenSSL for remote procedure calls. Version 0.9.1 was released to remove the network's vulnerability to the Heartbleed bug.

2013–2016
In 2013, prices started at $13.30 rising to $770 by 1 January 2014.
In March 2013 the blockchain temporarily split into two independent chains with different rules due to a bug in version 0.8 of the bitcoin software. The two blockchains operated simultaneously for six hours, each with its own version of the transaction history from the moment of the split. Normal operation was restored when the majority of the network downgraded to version 0.7 of the bitcoin software, selecting the backwards-compatible version of the blockchain. As a result, this blockchain became the longest chain and could be accepted by all participants, regardless of their bitcoin software version. During the split, the Mt. Gox exchange briefly halted bitcoin deposits and the price dropped by 23% to $37 before recovering to the previous level of approximately $48 in the following hours.
The US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) established regulatory guidelines for "decentralized virtual currencies" such as bitcoin, classifying American bitcoin miners who sell their generated bitcoins as Money Service Businesses (MSBs), that are subject to registration or other legal obligations.
In April, exchanges BitInstant and Mt. Gox experienced processing delays due to insufficient capacity resulting in the bitcoin price dropping from $266 to $76 before returning to $160 within six hours. The bitcoin price rose to $259 on 10 April, but then crashed by 83% to $45 over the next three days.
On 15 May 2013, US authorities seized accounts associated with Mt. Gox after discovering it had not registered as a money transmitter with FinCEN in the US. On 23 June 2013, the US Drug Enforcement Administration listed ₿11.02 as a seized asset in a United States Department of Justice seizure notice pursuant to 21 U.S.C. § 881. This marked the first time a government agency had seized bitcoin. The FBI seized about ₿30,000 in October 2013 from the dark web website Silk Road, following the arrest of Ross William Ulbricht. These bitcoins were sold at blind auction by the United States Marshals Service to venture capital investor Tim Draper. Bitcoin's price rose to $755 on 19 November and crashed by 50% to $378 the same day. On 30 November 2013, the price reached $1,163 before starting a long-term crash, declining by 87% to $152 in January 2015.
On 5 December 2013, the People's Bank of China prohibited Chinese financial institutions from using bitcoins. After the announcement, the value of bitcoins dropped, and Baidu no longer accepted bitcoins for certain services. Buying real-world goods with any virtual currency had been illegal in China since at least 2009.
In 2014, prices started at $770 and fell to $314 for the year. On 30 July 2014, the Wikimedia Foundation started accepting donations of bitcoin.
In 2015, prices started at $314 and rose to $434 for the year. In 2016, prices rose and climbed up to $998 by 1 January 2017.
Release 0.10 of the software was made public on 16 February 2015. It introduced a consensus library which gave programmers easy access to the rules governing consensus on the network. In version 0.11.2 developers added a new feature which allowed transactions to be made unspendable until a specific time in the future. Bitcoin Core 0.12.1 was released on 15 April 2016, and enabled multiple soft forks to occur concurrently. Around 100 contributors worked on Bitcoin Core 0.13.0 which was released on 23 August 2016.
In July 2016, the CheckSequenceVerify soft fork activated. In August 2016, the Bitfinex cryptocurrency exchange platform was hacked in the second-largest breach of a Bitcoin exchange platform up to that time, and 119,756 bitcoin, worth about $72 million at the time, were stolen.
In October 2016, Bitcoin Core's 0.13.1 release featured the "Segwit" soft fork that included a scaling improvement aiming to optimize the bitcoin blocksize.[citation needed] The patch was originally finalized in April, and 35 developers were engaged to deploy it.[citation needed] This release featured Segregated Witness (SegWit) which aimed to place downward pressure on transaction fees as well as increase the maximum transaction capacity of the network. [non-primary source needed] The 0.13.1 release endured extensive testing and research leading to some delays in its release date.[citation needed] SegWit prevents various forms of transaction malleability.[non-primary source needed]

2017–2019
Research produced by the University of Cambridge estimated that in 2017, there were 2.9 to 5.8 million unique users using a cryptocurrency wallet, most of them using bitcoin. On 15 July 2017, the controversial Segregated Witness [SegWit] software upgrade was approved ("locked-in"). Segwit was intended to support the Lightning Network as well as improve scalability. SegWit was subsequently activated on the network on 24 August 2017. The bitcoin price rose almost 50% in the week following SegWit's approval. On 21 July 2017, bitcoin was trading at $2,748, up 52% from 14 July 2017's $1,835. Supporters of large blocks who were dissatisfied with the activation of SegWit forked the software on 1 August 2017 to create Bitcoin Cash, becoming one of many forks of bitcoin such as Bitcoin Gold.
Prices started at $998 in 2017 and rose to $13,412.44 on 1 January 2018, after reaching its all-time high of $19,783.06 on 17 December 2017.
China banned trading in bitcoin, with first steps taken in September 2017, and a complete ban that started on 1 February 2018. Bitcoin prices then fell from $9,052 to $6,914 on 5 February 2018.[101] The percentage of bitcoin trading in the Chinese renminbi fell from over 90% in September 2017 to less than 1% in June 2018.
Throughout the rest of the first half of 2018, bitcoin's price fluctuated between $11,480 and $5,848. On 1 July 2018, bitcoin's price was $6,343. The price on 1 January 2019 was $3,747, down 72% for 2018 and down 81% since the all-time high.
In September 2018, an anonymous party discovered and reported an invalid-block denial-of-server vulnerability to developers of Bitcoin Core, Bitcoin ABC and Bitcoin Unlimited. Further analysis by bitcoin developers showed the issue could also allow the creation of blocks violating the 21 million coin limit and CVE-2018-17144 was assigned and the issue resolved.[non-primary source needed]
Bitcoin prices were negatively affected by several hacks or thefts from cryptocurrency exchanges, including thefts from Coincheck in January 2018, Bithumb in June, and Bancor in July. For the first six months of 2018, $761 million worth of cryptocurrencies was reported stolen from exchanges. Bitcoin's price was affected even though other cryptocurrencies were stolen at Coinrail and Bancor as investors worried about the security of cryptocurrency exchanges. In September 2019 the Intercontinental Exchange (the owner of the NYSE) began trading of bitcoin futures on its exchange called Bakkt. Bakkt also announced that it would launch options on bitcoin in December 2019. In December 2019, YouTube removed bitcoin and cryptocurrency videos, but later restored the content after judging they had "made the wrong call".
In February 2019, Canadian cryptocurrency exchange Quadriga Fintech Solutions failed with approximately $200 million missing. By June 2019 the price had recovered to $13,000.
2020–present
Bitcoin price in US dollars:
On 13 March 2020, bitcoin fell below $4,000 during a broad market selloff, after trading above $10,000 in February 2020. On 11 March 2020, 281,000 bitcoins were sold, held by owners for only thirty days. This compared to ₿4,131 that had laid dormant for a year or more, indicating that the vast majority of the bitcoin volatility on that day was from recent buyers. During the week of 11 March 2020, cryptocurrency exchange Kraken experienced an 83% increase in the number of account signups over the week of bitcoin's price collapse, a result of buyers looking to capitalize on the low price. These events were attributed to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In August 2020, MicroStrategy invested $250 million in bitcoin as a treasury reserve asset. In October 2020, Square, Inc. placed approximately 1% of total assets ($50 million) in bitcoin. In November 2020, PayPal announced that US users could buy, hold, or sell bitcoin. On 30 November 2020, the bitcoin value reached a new all-time high of $19,860, topping the previous high of December 2017. Alexander Vinnik, founder of BTC-e, was convicted and sentenced to five years in prison for money laundering in France while refusing to testify during his trial. In December 2020, Massachusetts Mutual Life Insurance Company announced a bitcoin purchase of US$100 million, or roughly 0.04% of its general investment account.
On 19 January 2021, Elon Musk placed the handle #Bitcoin in his Twitter profile, tweeting "In retrospect, it was inevitable", which caused the price to briefly rise about $5000 in an hour to $37,299. On 25 January 2021, Microstrategy announced that it continued to buy bitcoin and as of the same date it had holdings of ₿70,784 worth $2.38 billion. On 8 February 2021 Tesla's announcement of a bitcoin purchase of US$1.5 billion and the plan to start accepting bitcoin as payment for vehicles, pushed the bitcoin price to $44,141. On 18 February 2021, Elon Musk stated that "owning bitcoin was only a little better than holding conventional cash, but that the slight difference made it a better asset to hold". After 49 days of accepting the digital currency, Tesla reversed course on 12 May 2021, saying they would no longer take bitcoin due to concerns that "mining" the cryptocurrency was contributing to the consumption of fossil fuels and climate change. The decision resulted in the price of bitcoin dropping around 12% on 13 May. During a July bitcoin conference, Musk suggested Tesla could possibly help bitcoin miners switch to renewable energy in the future and also stated at the same conference that if bitcoin mining reaches, and trends above 50 percent renewable energy usage, that "Tesla would resume accepting bitcoin." The price for bitcoin rose after this announcement.
In June 2021, the Legislative Assembly of El Salvador voted legislation to make bitcoin legal tender in El Salvador.[j] The law took effect on 7 September. The implementation of the law has been met with protests and calls to make the currency optional, not compulsory.According to a survey by the Central American University, the majority of Salvadorans disagreed with using cryptocurrency as a legal tender, and a survey by the Center for Citizen Studies (CEC) showed that 91% of the country prefers the dollar over bitcoin. As of October 2021, the country's government was exploring mining bitcoin with geothermal power and issuing bonds tied to bitcoin. According to a survey done by the Central American University 100 days after the Bitcoin Law came into force: 34.8% of the population has no confidence in bitcoin, 35.3% has little confidence, 13.2% has some confidence, and 14.1% has a lot of confidence. 56.6% of respondents have downloaded the government bitcoin wallet; among them 62.9% has never used it or only once whereas 36.3% uses bitcoin at least once a month. In 2022, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) urged El Salvador to reverse its decision after bitcoin lost half its value in two months. The IMF also warned that it would be difficult to get a loan from the institution.
Also In June, the Taproot network software upgrade was approved, adding support for Schnorr signatures, improved functionality of Smart contracts and Lightning Network. The upgrade was installed in November.
On 16 October 2021, the SEC approved the ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF, a cash-settled futures exchange-traded fund (ETF). The first bitcoin ETF in the United States gained 5% on its first trading day on 19 October 2021.
On 25 March 2022, Pavel Zavalny stated that Russia might accept bitcoin for payment for oil and gas exports, in response to sanctions stemming from the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. On 27 April 2022 Central African Republic adopted bitcoin as legal tender alongside the CFA franc. On May 10, 2022, the bitcoin price fell to $31,324, as a result of a collapse of a UST stablecoin experiment named Terra, with bitcoin down more than 50% since the November 2021 high. By June 13, 2022, the Celsius Network (a decentralized finance loan company) halted withdrawals and resulted in the bitcoin price falling below $20,000.
Congratulations, your post has been curated by @techclub
Manually curated by
@samhenrytenplus