Growing up in Africa
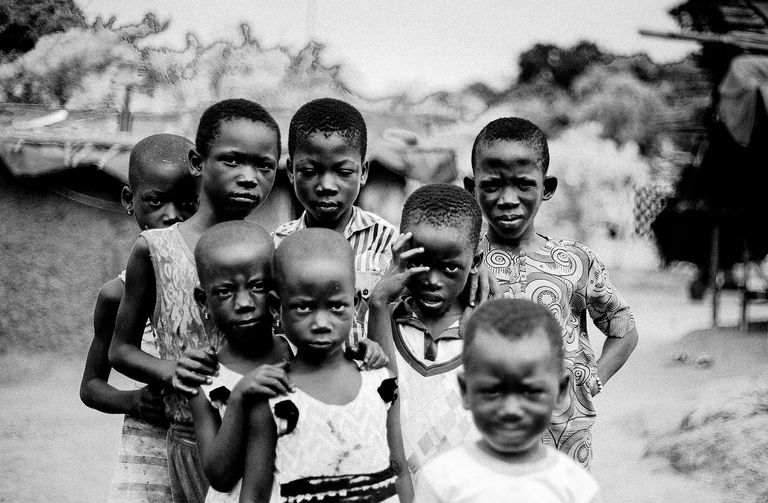
Growing up in Africa can be a diverse and enriching experience, as Africa is a continent with a vast array of cultures, languages, and traditions. While it's important to note that Africa is not a homogeneous entity and experiences can vary widely across countries and regions, I can provide you with some general insights into what growing up in Africa might be like.

Source
Cultural Diversity: Africa is known for its cultural diversity, with over 3,000 distinct ethnic groups and more than 2,000 languages spoken. Growing up in Africa exposes you to a rich tapestry of traditions, customs, and beliefs. You have the opportunity to learn about and appreciate different cultural practices, festivals, music, dance, and art forms.
Strong Community Ties: African societies often place a strong emphasis on community and extended family. Growing up, you are likely to experience a sense of belonging and interconnectedness with your family, neighbors, and broader community. Extended family members often play a significant role in a child's upbringing, providing support, guidance, and care.
Outdoor Lifestyle: Many parts of Africa have a warm climate, which encourages an outdoor lifestyle. Growing up, you may have opportunities to explore natural landscapes, play sports, and engage in outdoor activities like hiking, swimming, or traditional games. Africa's diverse geography, including savannas, rainforests, deserts, and coastlines, offers a wide range of outdoor experiences.
Challenges and Resilience: Africa, like any other continent, faces its share of challenges. Some areas may experience poverty, inadequate access to education, healthcare, and infrastructure. However, growing up in such circumstances can also foster resilience, resourcefulness, and a strong sense of community. Many African societies have a spirit of resilience and a determination to overcome challenges.
Education: Access to education varies across the continent, but efforts have been made to improve educational opportunities in many African countries. Growing up, you may attend local schools, which can provide a mix of formal education and cultural learning. Education is often seen as a pathway to social mobility and personal growth.
Language and Communication: Africa is home to a wide range of languages, including Arabic, Swahili, Hausa, Zulu, Amharic, and many more. Growing up, you may learn multiple languages, including your local language and possibly an international language such as English, French, or Portuguese. Multilingualism is common, facilitating communication and cultural exchange.

SourceRich Natural and Wildlife Heritage: Africa is renowned for its diverse wildlife, including iconic animals like elephants, lions, giraffes, and rhinoceroses. Growing up in Africa, you may have opportunities to visit national parks, game reserves, and wildlife sanctuaries, enabling you to appreciate and understand the importance of conservation and environmental sustainability.
These points offer a general overview, but it's essential to remember that Africa is a vast and diverse continent, and experiences can vary significantly depending on the country, region, and individual circumstances.
Cultural diversity in Africa
Cultural diversity in Africa is one of the continent's defining characteristics. With over 3,000 distinct ethnic groups and more than 2,000 languages spoken, Africa is home to a remarkable range of cultures, traditions, and customs. Here are some key aspects of cultural diversity in Africa:
Ethnic Groups: Africa is inhabited by numerous ethnic groups, each with its own unique culture, language, and history. Examples include the Yoruba in Nigeria, Zulu in South Africa, Maasai in Kenya and Tanzania, Ashanti in Ghana, Berber in North Africa, and many more. Each group has its own customs, social structures, and artistic expressions.
Languages: Africa is incredibly linguistically diverse, with a multitude of languages spoken across the continent. Some prominent language families include Niger-Congo (which includes Swahili, Yoruba, Zulu, and many others), Afro-Asiatic (which includes Arabic, Amharic, and Hausa), and Nilo-Saharan (which includes Dinka, Luo, and others). The presence of numerous languages reflects the richness and complexity of African cultural heritage.
Traditional Beliefs and Religions: Traditional African religions are diverse and vary from one region to another. Many Africans follow indigenous belief systems that involve animism, ancestral worship, and a deep connection to nature. Islam, Christianity, and other world religions have also spread throughout the continent, often blending with local beliefs and practices to form unique syncretic religious expressions.
Art and Craftsmanship: African art is renowned for its diversity and aesthetic beauty. From intricate wood carvings to colorful textiles, vibrant beadwork, and expressive masks, African art reflects the cultural and spiritual values of different communities. Art forms are often deeply rooted in rituals, storytelling, and social ceremonies, serving as a means of preserving and passing down cultural traditions.
Music, Dance, and Festivals: Music and dance are integral parts of African culture. Each region has its own musical traditions, incorporating various instruments such as drums, xylophones, stringed instruments, and wind instruments. Traditional dances are performed on various occasions, including festivals, weddings, and initiation ceremonies. Festivals, such as the Mardi Gras in Cape Verde or the Timkat festival in Ethiopia, showcase the diversity and vibrancy of African celebrations.
Oral Traditions: African cultures have a rich heritage of oral traditions, including storytelling, proverbs, folktales, and oral histories. These traditions are often passed down from generation to generation, preserving cultural knowledge, values, and wisdom. Storytelling serves as a way of transmitting moral lessons, history, and cultural identity.
https://pixabay.com/it/illustrations/vaso-portare-donne-brocca-7045642/Cuisine: African cuisine is diverse and reflects the availability of local ingredients and culinary traditions. Staple foods vary across regions and include grains like maize, millet, sorghum, and rice, along with a wide array of vegetables, fruits, and spices. Popular dishes include injera from Ethiopia, jollof rice from West Africa, tagines from North Africa, and bobotie from South Africa.
It's important to note that Africa's cultural diversity is vast, and this overview only scratches the surface. Each ethnic group and region within Africa has its own unique customs, practices, and contributions to the continent's cultural mosaic.
Challenges in Africa
Africa faces a range of challenges that vary across countries and regions. While it's important to recognize that Africa is a diverse continent with significant progress made in many areas, here are some common challenges that persist in certain parts of Africa:
Poverty: Many African countries face high levels of poverty, with a significant proportion of the population living below the poverty line. Limited access to basic necessities such as clean water, sanitation, healthcare, and education exacerbates the issue. Economic inequality, unequal distribution of resources, and lack of job opportunities contribute to the persistence of poverty in some areas.
Health Issues: Africa is burdened by several health challenges, including infectious diseases such as HIV/AIDS, malaria, tuberculosis, and neglected tropical diseases. Limited access to healthcare infrastructure, inadequate funding, and shortages of healthcare professionals pose significant obstacles to addressing these health issues effectively. Additionally, recent challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic have put additional strain on healthcare systems across the continent.
Education: While improvements have been made in access to education, many African countries still struggle with providing quality education to all their citizens. Challenges include inadequate school infrastructure, lack of qualified teachers, and low enrollment rates, particularly in rural areas. Gender disparities and cultural barriers also affect girls' access to education in certain regions.
Governance and Corruption: Some African countries face governance challenges, including political instability, corruption, and weak institutions. These issues can hinder development, discourage foreign investment, and impede effective service delivery. Transparency, accountability, and good governance remain important areas for improvement.
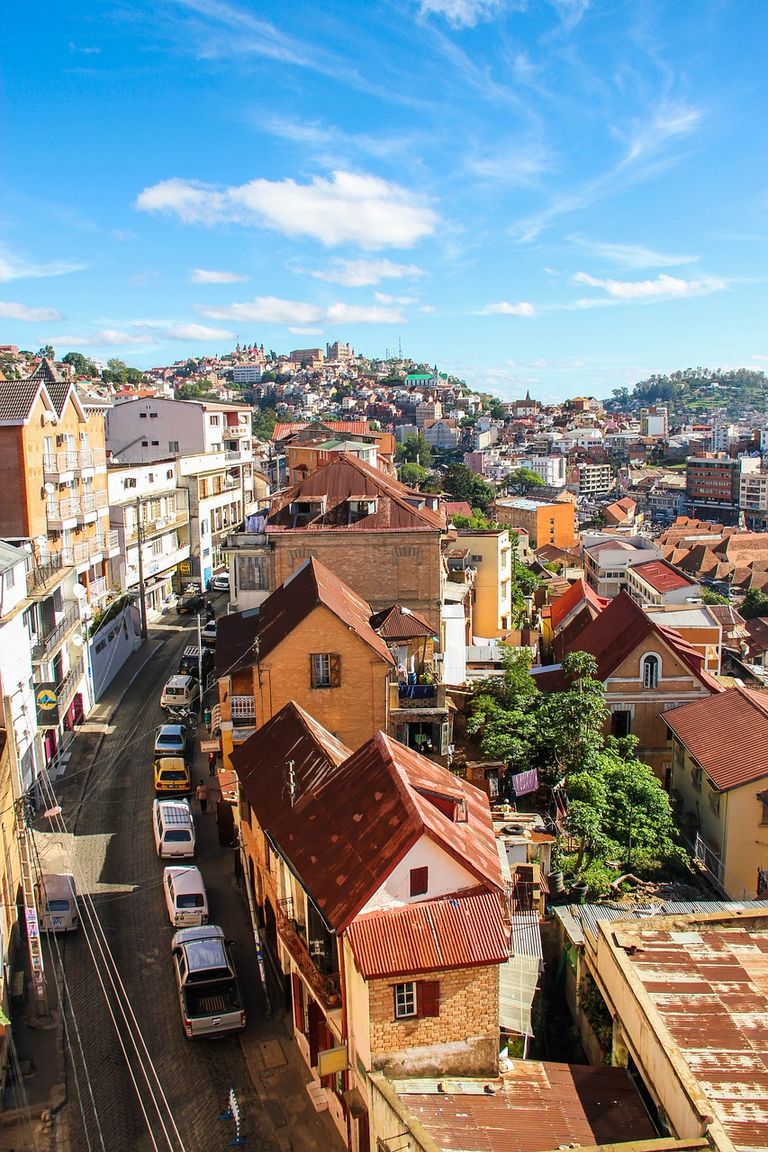

https://pixabay.com/it/photos/citt%C3%A0-antananarivo-vecchia-citt%C3%A0-2150061/Conflict and Instability: Several regions in Africa have experienced conflicts and civil unrest, leading to displacement of populations, loss of lives, and destruction of infrastructure. Conflicts often arise from political, ethnic, or religious tensions, competition over resources, or historical grievances. These conflicts hamper development, disrupt social cohesion, and impede efforts to address other challenges.
Climate Change and Environmental Issues: Africa is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including droughts, floods, desertification, and loss of biodiversity. These environmental challenges affect agricultural productivity, water resources, food security, and livelihoods, especially in rural areas where agriculture is a primary source of income.
Infrastructure Development: Inadequate infrastructure, including transportation networks, electricity grids, and telecommunications systems, poses challenges to economic development and connectivity within and across African countries. Insufficient investment, maintenance, and planning hinder progress in this area.
It's crucial to note that Africa is a vast and diverse continent, and the challenges faced can vary significantly from one country to another. There are also numerous ongoing efforts, both by governments and international organizations, to address these challenges and promote sustainable development in Africa.
Education system in Africa
The education systems in Africa vary across countries, and it's important to note that Africa is a diverse continent with different educational approaches, policies, and levels of development. However, there are some common themes and challenges that can be observed in many African education systems:
Access to Education: Despite progress in recent years, access to quality education remains a significant challenge in many African countries, particularly in rural and marginalized areas. Factors such as poverty, gender disparities, inadequate infrastructure, and long distances to schools can hinder access to education for certain populations.
Early Childhood Education: Early childhood education is gaining recognition as a crucial foundation for children's development. However, access to quality early childhood education programs is limited in many African countries. Efforts are being made to expand access and improve the quality of early childhood education, recognizing its importance in preparing children for formal schooling.
Basic Education: Primary and secondary education are considered fundamental for building a strong educational foundation. Many African countries have made progress in increasing primary school enrollment rates, but challenges such as overcrowded classrooms, lack of resources, and insufficient numbers of qualified teachers persist. Secondary education faces additional challenges, including limited availability of schools, high dropout rates, and a lack of vocational and technical training options.
Quality of Education: Ensuring quality education is a significant challenge across Africa. Factors such as inadequate teacher training, outdated curricula, and limited learning resources can affect the quality of education. There is a growing recognition of the need to focus on improving teaching methods, curriculum relevance, and student-centered approaches to enhance learning outcomes.
Tertiary Education: Tertiary education, including universities and vocational institutions, is an important part of the education system in Africa. However, challenges such as limited access, affordability, and a mismatch between skills taught and the needs of the job market exist. Efforts are being made to expand access to tertiary education, enhance the quality of teaching and research, and promote relevant skills development.

https://pixabay.com/it/photos/ajt-bin-haddu-marocco-citt%C3%A0-ksar-4730154/Language of Instruction: Language of instruction can be a complex issue in African education systems due to linguistic diversity. In many countries, colonial languages (such as English, French, or Portuguese) are used as the medium of instruction, which can create barriers for students who speak different languages at home. There are ongoing debates and efforts to promote the use of local languages in education to improve learning outcomes and preserve cultural heritage.
Education Financing: Adequate and sustainable financing for education is crucial but remains a challenge in many African countries. Limited government budgets for education, high levels of poverty, and competing priorities make it difficult to allocate sufficient resources to the education sector. As a result, reliance on external funding and aid is often necessary to support education initiatives.
It's important to note that while challenges exist, there are also numerous positive developments and initiatives in African education systems. Efforts are being made to improve access, quality, and relevance of education, and many countries are investing in education as a means of fostering sustainable development and empowering their populations.
Language and Communication in African countries
Language and communication in African countries are incredibly diverse due to the continent's rich linguistic heritage. Africa is home to over 2,000 languages, which can be classified into several language families, including Niger-Congo, Afro-Asiatic, Nilo-Saharan, and Khoisan, among others. Here are some key aspects of language and communication in African countries:
Linguistic Diversity: African countries exhibit a remarkable range of languages. Each country typically has multiple languages spoken within its borders, reflecting the diverse ethnic groups and cultures present. For example, Nigeria is home to over 500 languages, while Cameroon has more than 200 languages.
Official Languages: Many African countries have one or more official languages, often inherited from their colonial history. English, French, Portuguese, and Arabic are the most commonly used official languages. English is widely spoken in countries like Nigeria, Ghana, Kenya, and Uganda, while French is prevalent in countries such as Senegal, Ivory Coast, and Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Indigenous Languages: Indigenous African languages play a crucial role in daily communication, especially within local communities and families. These languages are often used in informal settings, such as in homes, marketplaces, and cultural events. They are vital for preserving cultural heritage, identity, and intergenerational transmission of knowledge.
Multilingualism: Multilingualism is common in Africa, with many individuals speaking multiple languages. People may use a local or indigenous language for daily interactions, while also being proficient in an official language for formal contexts such as education, administration, and business. Additionally, some individuals may speak regional lingua francas, such as Swahili in East Africa or Lingala in Central Africa.

https://pixabay.com/it/photos/le-persone-uomini-africani-casuale-7271043/Language Policies: African countries vary in their language policies, which can range from promoting a single national language to embracing multilingualism. Some countries have implemented policies to promote the use of local languages in education and government, recognizing the importance of linguistic diversity and the benefits of mother tongue-based education.
Communication Technologies: Communication technologies, particularly mobile phones and the internet, have had a significant impact on communication in Africa. Mobile phones have become prevalent, even in remote areas, enabling people to stay connected and facilitating communication in local languages through voice calls, text messages, and social media platforms.
Oral Traditions: Africa has a rich tradition of oral communication, including storytelling, proverbs, and oral histories. These forms of communication serve as important means of transmitting cultural knowledge, values, and entertainment. Oral traditions play a vital role in preserving and passing down cultural heritage from one generation to another.
Sign Language: Sign languages are also used in African countries to facilitate communication for individuals with hearing impairments. Some countries have recognized sign languages as official languages and have made efforts to provide accessibility and inclusivity for the deaf community.
It's important to recognize that the linguistic landscape in Africa is complex and varies across countries and regions. The linguistic diversity of the continent enriches its cultural tapestry, but it can also present challenges for communication and education. Efforts are being made to promote linguistic diversity, preserve endangered languages, and ensure equitable access to education and information in diverse languages.
Rich Natural and Wildlife Heritage in Africa
Africa is renowned for its rich natural and wildlife heritage, making it a popular destination for nature enthusiasts, wildlife photographers, and adventurers. The continent's diverse ecosystems and iconic wildlife contribute to its unique appeal. Here are some key aspects of Africa's natural and wildlife heritage:

https://pixabay.com/it/photos/africa-venditore-banane-frutta-1129037/
Biodiversity: Africa is incredibly biodiverse, with a wide range of habitats and ecosystems. From the vast savannas of East Africa, the dense rainforests of Central Africa, to the arid deserts of the Sahara and the Okavango Delta's wetlands, Africa encompasses a variety of landscapes that support a remarkable array of plant and animal species.
Iconic Wildlife: Africa is home to some of the world's most iconic and awe-inspiring wildlife species. African elephants, lions, giraffes, zebras, cheetahs, rhinoceroses, hippos, and wildebeests are just a few examples of the remarkable creatures that roam the continent. These species attract tourists from around the world and contribute to the allure of African safaris and wildlife conservation efforts.
National Parks and Reserves: Africa boasts numerous national parks and wildlife reserves that are dedicated to the conservation and protection of its natural and wildlife heritage. These protected areas, such as the Serengeti National Park in Tanzania, Kruger National Park in South Africa, Maasai Mara National Reserve in Kenya, and Etosha National Park in Namibia, provide havens for wildlife and offer visitors the opportunity to experience Africa's natural wonders up close.
Migration Phenomena: Africa is home to some of the most impressive wildlife migrations on the planet. The Great Wildebeest Migration, which takes place annually between the Serengeti in Tanzania and the Maasai Mara in Kenya, involves the movement of millions of wildebeests, zebras, and other herbivores in search of fresh grazing lands. This phenomenon showcases the incredible spectacle of nature's cycles and the interdependence of species.
Endangered Species and Conservation: Africa is also home to several endangered species, including the African elephant, black rhinoceros, mountain gorilla, and African wild dog. Conservation efforts are crucial in protecting these species from habitat loss, poaching, and other threats. Many organizations and initiatives are dedicated to conservation, including anti-poaching patrols, community-based conservation programs, and sustainable tourism practices.
Birdlife: Africa is a paradise for birdwatchers, with over 2,300 bird species recorded on the continent. From the vibrant plumage of African parrots to the majestic African fish eagle, bird enthusiasts can enjoy spotting a diverse range of avian species across various habitats.
Ecotourism: The natural and wildlife heritage of Africa provides a foundation for ecotourism, which promotes responsible travel and sustainable practices. Safaris, nature walks, birdwatching expeditions, and eco-lodges offer visitors the opportunity to experience Africa's natural wonders while supporting local communities and conservation initiatives.

https://pixabay.com/it/photos/batteria-festival-africano-5949725/
It's important to note that while Africa's natural and wildlife heritage is remarkable, it also faces challenges such as habitat loss, poaching, climate change, and human-wildlife conflicts. Efforts are being made by governments, conservation organizations, and local communities to protect and preserve Africa's natural and wildlife heritage for future generations.
Best countries to grow up in, in Africa
Determining the "best" countries to grow up in Africa can depend on various factors, including education, healthcare, safety, social opportunities, and economic prospects. It's important to note that every country has its own strengths and challenges, and the perception of what makes a country ideal can vary among individuals. However, here are a few countries in Africa that are often recognized for providing relatively favorable conditions for children and youth:
Mauritius: Mauritius consistently ranks high in various indices related to quality of life and human development in Africa. It has a well-developed education system, universal healthcare, low crime rates, and a stable economy. The country also boasts beautiful beaches, a vibrant multicultural society, and a strong emphasis on environmental sustainability.
Seychelles: Known for its stunning natural beauty and pristine beaches, Seychelles is another country that offers a high quality of life. It has a well-functioning healthcare system, high literacy rates, and a stable political environment. The government places a strong emphasis on sustainable development and environmental conservation.
Botswana: Botswana has made significant progress in terms of education and healthcare, with a relatively high literacy rate and a well-managed healthcare system. The country is known for its commitment to wildlife conservation and has a stable political climate. Botswana's economy, driven by diamond mining and tourism, provides economic opportunities.
Rwanda: Rwanda has made remarkable strides in recent years in terms of economic development, education, and healthcare. The country has invested heavily in education, resulting in high literacy rates and improved access to schooling. Rwanda has also focused on post-genocide reconciliation and creating a safe and secure environment for its citizens.
South Africa: South Africa has a relatively developed infrastructure and offers a wide range of opportunities in education, healthcare, and entertainment. The country has a diverse cultural landscape, vibrant cities, and a well-developed arts and sports scene. However, it's important to note that South Africa also faces challenges such as inequality, crime rates, and social issues that can affect certain communities.
https://pixabay.com/it/photos/astante-a-passeggio-smartphone-4335726/
These countries are just a few examples, and there are other African countries that provide favorable conditions for children to grow up. It's worth considering that individual experiences and perspectives may vary, and it's essential to conduct thorough research and consider personal priorities and circumstances when evaluating the suitability of a country for upbringing.
Some valued sports in Africa
Africa has a rich sporting culture, and several sports hold significant value and popularity across the continent. Here are some of the most valued sports in Africa:
Football (Soccer): Football is by far the most popular and beloved sport in Africa. African countries have produced some of the world's finest football players, and the continent's national teams have achieved success on the global stage. African football leagues, such as the South African Premier Soccer League, Egyptian Premier League, and Nigerian Professional Football League, draw large crowds and passionate support.
Athletics: Athletics, particularly track and field events, hold great importance in Africa. African athletes have excelled in long-distance running, sprinting, and field events at international competitions, including the Olympic Games and World Championships. Kenya and Ethiopia, in particular, have produced many renowned long-distance runners.
Rugby: Rugby is gaining popularity in Africa, with the sport growing in participation and fan base. South Africa, in particular, has a strong rugby culture and has achieved success at the international level, winning the Rugby World Cup multiple times. Other African countries, such as Kenya, Namibia, and Zimbabwe, also have competitive rugby teams.
Cricket: Cricket has a significant following in African countries that were former British colonies, such as South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Kenya. South Africa's national cricket team has been highly competitive and has produced world-class players. The sport also has a growing presence in other countries, with grassroots development programs expanding its reach.
Basketball: Basketball has been steadily gaining popularity in Africa, fueled by the success of African players in the NBA (National Basketball Association). African countries like Nigeria and Senegal have strong national basketball teams and have produced talented players who have gone on to compete at the highest level globally.
Boxing: Boxing has a long-standing tradition in Africa, with several African boxers achieving success at the professional level. Countries like Ghana, Nigeria, and South Africa have produced notable boxing champions, and the sport continues to have a dedicated following across the continent.

https://pixabay.com/it/photos/riso-suya-di-manzo-il-cibo-africano-6697968/Volleyball: Volleyball is popular in several African countries, with national teams participating in continental and international competitions. Countries like Egypt, Tunisia, and Cameroon have strong volleyball traditions and have had success in both men's and women's competitions.
Handball: Handball has a significant following in some African countries, particularly in North Africa. Egypt and Tunisia, in particular, have strong handball programs and have performed well at the African Handball Cup of Nations and other international tournaments.
It's important to note that sports preferences can vary across different regions and countries in Africa. Additionally, indigenous African sports, such as Mancala, Dambe (traditional boxing), and Nguni Stick Fighting, hold cultural significance in certain communities but may not have widespread recognition or popularity beyond their respective regions.
Staying in Africa
Staying in Africa offers a unique and diverse experience that encompasses rich cultural heritage, natural beauty, and a sense of community. While the continent faces its share of challenges, including poverty, political instability, and infrastructure development, Africa also presents opportunities for growth, adventure, and personal enrichment. Here are some key points to consider when reflecting on staying in Africa:
Cultural Diversity: Africa is a continent of immense cultural diversity, with each country and region offering its own unique traditions, languages, and customs. This diversity provides an enriching and vibrant environment for individuals looking to immerse themselves in different cultures and broaden their perspectives.
Natural Wonders: Africa boasts stunning natural landscapes, including expansive savannas, lush rainforests, breathtaking coastlines, and iconic wildlife. The continent's national parks and reserves provide opportunities for safaris, wildlife encounters, and eco-tourism, allowing residents to connect with nature and experience its awe-inspiring beauty.

https://pixabay.com/it/illustrations/donna-nero-africano-ritratto-7804671/Warm and Welcoming Communities: African communities are often known for their warmth, hospitality, and strong sense of community. Living in Africa can offer a close-knit social environment, where people support and care for one another, fostering a sense of belonging and interconnectedness.
Business and Economic Opportunities: Africa is home to a rapidly growing economy and a burgeoning middle class. The continent presents opportunities for entrepreneurship, investment, and career growth, particularly in sectors such as technology, agriculture, renewable energy, and infrastructure development.
Personal and Professional Growth: Living in Africa can provide individuals with unique opportunities for personal and professional growth. Engaging with diverse communities, navigating different cultural contexts, and confronting challenges can foster resilience, adaptability, and intercultural competence.
Challenges and Resilience: It's important to acknowledge that Africa faces various challenges, including poverty, healthcare disparities, and political instability. However, the resilience and resourcefulness exhibited by African communities and individuals in the face of adversity can be inspiring, and efforts are being made to address these challenges and foster sustainable development.
The decision to stay in Africa depends on individual circumstances, aspirations, and personal preferences. It's crucial to conduct thorough research, consider safety and security factors, and weigh the opportunities and challenges specific to the country or region of interest. Africa's diverse tapestry of cultures, natural wonders, and economic potential makes it a compelling and rewarding place to stay for many individuals.
Round up
Africa is a continent of remarkable cultural diversity, abundant natural beauty, and a strong sense of community. It offers a range of opportunities for personal growth, adventure, and professional development. Despite facing challenges such as poverty and political instability, Africa's resilience and potential for positive change are evident.

https://pixabay.com/it/photos/uomini-artisti-di-strada-africano-5966213/
Conclusion
From the vibrant traditions and languages to the breathtaking wildlife and landscapes, Africa captures the hearts of those who experience it. Whether considering the rich cultural heritage, the value placed on sports, or the potential for economic opportunities, staying in Africa can be a transformative experience that offers a unique and fulfilling lifestyle.