Some popular food products in Africa and their uses in Nigeria
What is Garri?? West African food.
Garri is a staple food widely consumed in West Africa, especially in Nigeria, Ghana, and Togo. It is made from cassava, a starchy root crop that is also known as yuca or manioc.
To make garri, cassava roots are peeled, washed, and grated. The grated cassava is then left to ferment for a few days, during which time it is dried in the sun or in an oven. The dried cassava is then milled into a fine powder, which can be stored for long periods.
Garri has many ways in which it can be eaten. It can be soaked in hot water and stirred very well to make eba, which is then eaten with soup, stew, or sauce. It can also be used to make a popular Nigerian snack called garri soakings, which consists of garri mixed with sugar, milk, and groundnuts. In addition, garri can be fried in oil to make a crunchy snack, or used as a base for drinks like garri and sugar cane juice.
source: pixabay
How to produce Garri
Harvest and wash the cassava: Cassava is harvested from the farm and washed to remove dirt and debris.
Peel and wash the cassava: The cassava is peeled with a knife or a mechanical peeler, and then washed again to remove any remaining dirt or peel.
Grate the cassava: The peeled cassava is then grated using a grater or a mechanical grating machine. The grated cassava is usually placed in a clean, large bowl or basin.
Ferment the grated cassava: The grated cassava is left to ferment for 2-3 days in a cool and dry place. During fermentation, lactic acid bacteria breaks down the cassava, making it easier to process and increasing its nutritional value.
Press the cassava: After fermentation, the cassava is pressed to remove excess water. This can be done manually using a cloth sack or a manual machine.
Sieve and dry the cassava: The pressed cassava is then sieved to remove any lumps or fibers. The sieved cassava is spread out on a clean surface, such as a tarpaulin or concrete slab, and left to dry in the sun for a few days. This method is not normally used in Nigeria. The Nigerian method is by frying it using a fryer....
Mill the dried cassava: Once the cassava is completely dry, it is milled into a fine powder using a mill or a mortar and pestle.
Package the garri: The final product is packaged in plastic bags or containers, ready for storage or consumption. Package like Ijebu garri.
In Nigeria, we don't normally dry it ooo, we fry it. Some even use palm oil to change the garri's colour to yellow.

source: pixabay
Which country produces Garri more?
Nigeria is the largest producer of garri in the world. Garri is a staple food in Nigeria, and it is consumed by millions of people across the country. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Nigeria produces over 60% of the world's cassava, which is the main raw material used in making garri. Other countries in West Africa, such as Ghana and Togo, also produce and consume garri, but on a smaller scale compared to Nigeria.
Why do Nigerians love Garri?
Garri is a popular food in Nigeria made from cassava, a starchy root vegetable. Nigerians love garri for several reasons:
Availability and Affordability: Cassava is a common crop in Nigeria, and garri is relatively cheap and readily available in most parts of the country. This makes it a popular food choice for many Nigerians.
Versatility: Garri is a versatile food that can be prepared in several ways. It can be eaten as a snack or a full meal, and can be cooked in different forms such as eba, garri soakings, garri fufu, garri flakes etc. It can also be paired with different soups and stews.
Nutritional Value: Garri is a good source of carbohydrates, fiber, and some essential nutrients like potassium, iron, and vitamin C. It can provide energy and sustain satiety for long periods.
Cultural Significance: Garri is an important part of Nigerian cuisine and culture. It is often associated with the rural areas and considered a staple food in many Nigerian households.
Taste and Texture: Garri has a unique sour taste and granular texture which some people find enjoyable.
Garri is loved by Nigerians for its availability, affordability, versatility, nutritional value, cultural significance, taste and texture.
Yam Production in Africa
Yam is an important crop in many parts of Africa, particularly West and Central Africa. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Africa produces about 96% of the world's yam, with Nigeria being the largest producer, followed by Ghana, Cote d'Ivoire, and Benin.
Yam is a key source of food and income for millions of people in Africa. It is consumed in different forms, such as boiled, fried, roasted, mashed, and pounded into a paste called pounded yam. Yam is also used in traditional African dishes, such as yam porridge, yam pottage, and yam fufu.

source: pixabay
Yam production in Africa faces a number of challenges, including pests and diseases, poor soil fertility, inadequate storage facilities, and limited access to markets. To address these challenges, a number of initiatives have been launched to promote sustainable yam production in Africa.
Uses of yam in Nigeria
Yam is a highly versatile crop that is used in a wide range of dishes in Africa. It is an important staple food in many African countries, particularly in Nigeria. Here are some common uses of yam in Nigeria:
Boiled yam: Boiled yam is a simple and popular way to prepare yam in Nigeria. The boiled yam is usually served with different types of soups, stews or sauces. Most times with palm oil.
Yam porridge: Yam porridge is a dish made by boiling yam with vegetables and other ingredients such as tomatoes, onions, and spices. It is a common breakfast or lunch dish in many African countries, and in Nigeria in particular. This very one is my favourite dish, the greatest of all dishes (GOAD).
Yam pottage: Yam pottage is similar to yam porridge, but it is thicker and often mashed. It is usually prepared with different types of vegetables in Nigeria. Vegetable like spinach, pumpkin leave and lots more.
Yam fufu: Yam fufu is a dough-like food that is made by boiling yam and pounding it into a smooth paste. It is typically served with soup or stew. Soups like eguisi, afang, okra, bitter leave soup, groundnut soup and more.
Roasted yam: Roasted yam is a popular street food in many parts of Nigeria. It is usually roasted over an open fire and served with palm oil or sauces, such as egg sauce or fish sauce.
Yam chips: Yam chips are a healthier alternative to potato chips and are becoming increasingly popular in Nigeria. They are usually made by slicing yam into thin pieces and frying them until crispy. They are mostly roadside food and are served with grinded pepper or stew.
In other parts of Nigeria, mostly the south western region, they use the yam peels for what we call amala.
Maize production in Africa
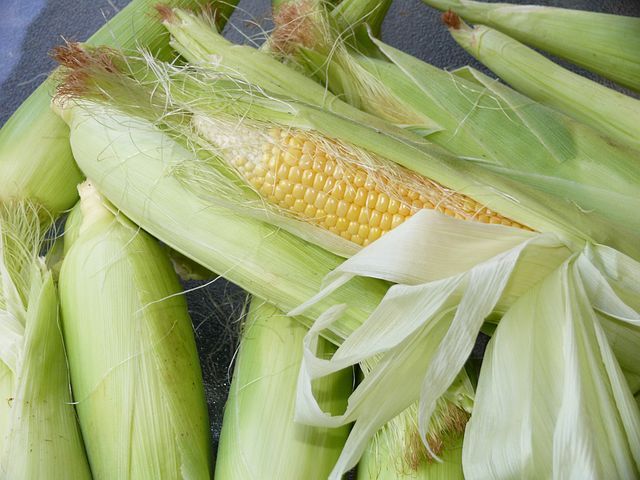
Maize (also known as corn) is an important crop in many parts of Africa, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa. It is a versatile crop that can be used for food, animal feed, and industrial purposes. Africa produces about 6% of the world's maize, with the largest producers being South Africa, Nigeria, and Ethiopia.
Maize is an important source of food for millions of people in Africa, and it is consumed in many forms, such as porridge, grits, and bread. In addition, maize is also used to make other food products such as snacks, breakfast cereals, and beer.
However, maize production in Africa faces a number of challenges, including pests and diseases, poor soil fertility, climate change, and limited access to things such as seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation equipments. These challenges can result in low yields and post-harvest losses, which can negatively impact food security and livelihoods in many rural communities.
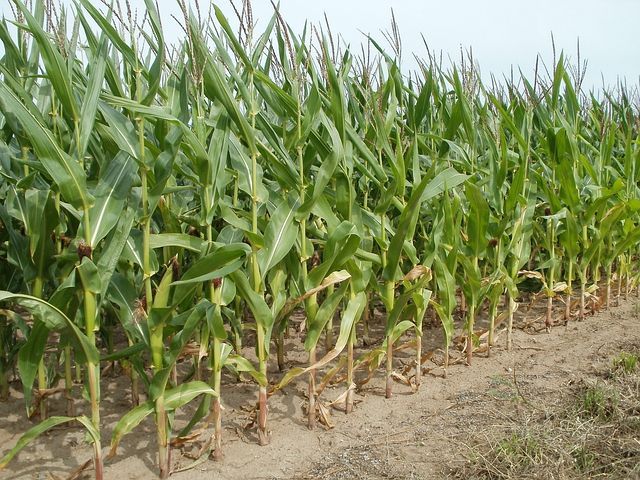

source: pixabay
Uses of maize in Nigeria
Here are some of the common uses of maize in Nigeria:
Food: Maize is a food in Nigeria and is used to make various dishes such as pap (ogi), cornmeal porridge, tuwo, kunu, and boiled corn. It is also used to make snacks such as roasted corn, popcorn, and corn chips.
Livestock feed: Maize is an important source of feed for livestock, particularly poultry, pigs, and cattle. Maize meal is often used as a key ingredient in animal feed, and maize silage can be used as a forage crop for cattle.
Industrial uses: Maize is also used in several industrial applications such as the production of starch, corn syrup, and ethanol. It is also used in the production of biodegradable plastics, fabrics, and paper products.
Traditional medicine: In some parts of Nigeria, maize is used in traditional medicine to treat many ailments such as diarrhea, constipation, and high blood pressure. The leaves are used as a remedy for skin infections.

source: pixabaySeed production: Maize is also an important crop for seed production in Nigeria. Farmers can earn income by producing and selling high-quality maize seeds, which are used by other farmers to plant their crops.
Export: Nigeria also exports maize to other countries. The country is a significant exporter of maize to neighbouring West African countries such as Niger, Benin, and Togo.
Beans production in Africa
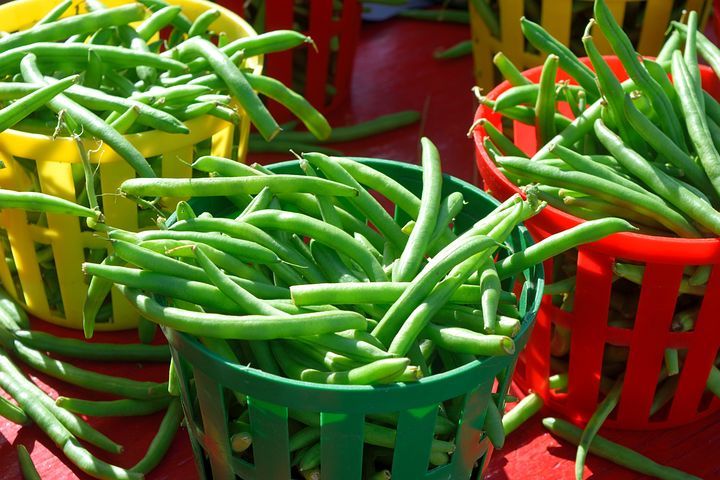
Beans are an important crop in Africa, providing a key source of protein and other nutrients for millions of people. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Africa produces about 28% of the world's beans, with the largest producers being Tanzania, Ethiopia, and Uganda.
Beans are an important source of food in Africa, and are consumed in many forms, such as boiled beans, jollof beans, moi moi, bean stew, and bean cakes. In addition, beans can also be processed into flour, which is used to make various food products such as cakes and snacks.
Uses of beans in Nigeria
Beans are a popular food crop in Nigeria, and are used in many ways in the country. Here are some of the common uses of beans in Nigeria:
Food: Beans are very versatile food in Nigeria, that are used to make lots of dishes such as beans porridge, akara (bean cakes), moi moi (bean pudding), and ewa agoyin (bean stew). These dishes are often served with rice, yam, or other starchy foods, and are popular source of protein and other nutrients.
Snacks: Beans are also used to make snacks such as akara. These snacks are often sold by street vendors and are a popular snack food in Nigeria.
Traditional medicine: In some parts of Nigeria, beans are used in traditional medicine to treat different sicknesses, such as constipation, diarrhea, and high blood pressure. The leaves of some bean plants are also used as a remedy for skin infections.
Income generation: Beans can also be an important source of income for farmers in Nigeria. Farmers can sell their beans at local markets or to food processing companies, and can earn a good income from their crop.

source: pixabayLivestock feed: Beans can also be used as animal feed, particularly for poultry and pigs. Bean meal is often used as a key ingredient in animal feed, and can help to improve the nutritional value of the feed.
The leaves: In most pasts of the country, the beans leaves is used to make soup. Mostly in some of the northern region, the fresh beans leaves is plucked out for soup purposes.
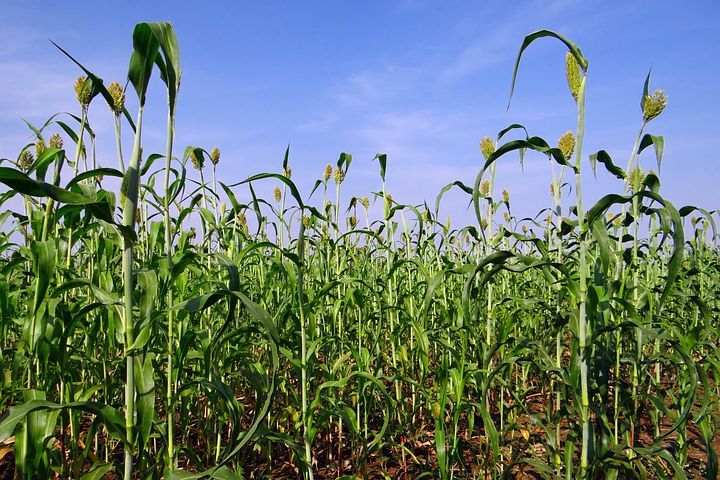
Guinea corn production in Africa
Guinea corn, also known as sorghum, is an important cereal crop that is widely grown in Africa. It is a hardy crop that can tolerate drought and poor soil conditions, and is therefore well-suited to many regions of the continent.
Uses of Guinea corn in Nigeria
Guinea corn, also known as sorghum, is an important crop in Nigeria, and is used for many purposes. Here are some of the common uses of guinea corn in Nigeria:
Food: Guinea corn is a staple food in many parts of Nigeria, and is used to make a variety of dishes such as tuwon dawa (a type of porridge), fura (a type of snack made from guinea corn flour), and kunu (a traditional drink made from guinea corn). It is often served with soups or stews, and is a popular source of carbohydrates and other nutrients.
Livestock feed: Guinea corn is also used as animal feed in Nigeria, particularly for poultry and cattle. The crop residue, such as the stems and leaves, can also be used as fodder for livestock.
Alcoholic beverages: Guinea corn is used to make a variety of alcoholic beverages in Nigeria, including pito, and burukutu, a popular local beer. The grain is fermented to produce the beverage, which is often sold by street vendors and in local bars.

source: pixabayIndustrial uses: Guinea corn can also be processed into flour, which is used to make various food products such as baked goods, snacks, and breakfast cereals. The crop residue can also be used to produce biofuels and other industrial products.
Income generation: Guinea corn can be an important source of income for farmers in Nigeria. Farmers can sell their guinea corn at local markets or to food processing companies, and can earn a good income from their crop.
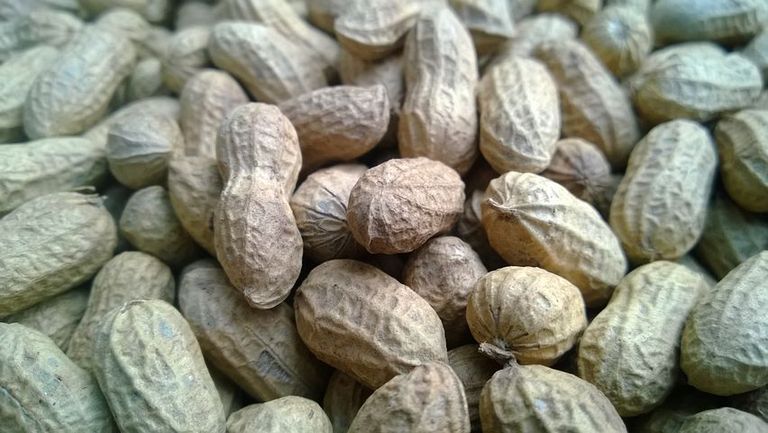
Groundnut production in Africa
Groundnut, also known as peanut, is an important crop in Africa, both for food and for income generation. Africa is the second-largest producer of groundnuts in the world, after Asia. The top groundnut producing countries in Africa include Nigeria, Sudan, Senegal, Ghana, and Mali. These countries account for the majority of groundnut production on the continent.
Groundnuts are typically grown in the rainy season, and require well-drained soil and adequate rainfall. They are often intercropped with other crops such as maize or sorghum, and are typically harvested by hand.
Groundnut is an important crop in Africa, and plays a critical role in food security and economic development in many regions of the continent. Its versatility and nutritional value make it a valuable crop for farmers and consumers.

source: pixabay
Uses of groundnut in Nigeria
Here are some of the common uses of groundnut in Nigeria:
Food: Groundnut is a popular food in Nigeria, and is used in making dishes such as soups, stews, and snacks. It is often ground into a paste, which is used as a base for sauces and soups. Groundnut is also used to make a popular snack called kulikuli, which is made by frying groundnut paste with spices and seasonings.
Oil: Groundnut is an important source of oil in Nigeria, and is used for cooking and frying. Groundnut oil is popular because of its high smoke point, which makes it ideal for deep-frying.
Livestock feed: Groundnut is also used as animal feed in Nigeria, particularly for poultry and cattle. The crop residue, such as the stems and leaves, can also be used as fodder for livestock.
Industrial uses: Groundnut can be processed into various products, including peanut butter, roasted peanuts, and peanut flour. The oil extracted from groundnut can also be used in the manufacture of soap, cosmetics, and other industrial products.

source: pixabayIncome generation: Groundnut can be an important source of income for farmers in Nigeria. Farmers can sell their groundnut at local markets or to food processing companies, and can earn a good income from their crop.
Rice production in Africa
Rice is an important crop in Africa, and plays a critical role in food security and economic development in many regions of the continent. Here are some key facts about rice production in Africa: Africa is a major producer of rice, with the top rice-producing countries in Africa include Nigeria, Madagascar, Tanzania, Mali, and Senegal. These countries account for the majority of rice production on the continent.
Uses of rice in Nigeria
Here are some of the common uses of rice in Nigeria:
Jollof rice: This is a popular rice dish in Nigeria, which is typically made with rice, tomato sauce, onions, and spices. It is often served at parties and special occasions.
Fried rice: This is another popular rice dish in Nigeria, which is made with rice, vegetables, and sometimes meat or shrimp.
Rice and stew: This is a simple dish of rice served with a tomato-based stew, often made with meat or fish. It is a common everyday meal in Nigeria, but mostly prepared on Sundays.
Rice porridge: Rice porridge is a popular breakfast dish in Nigeria, which is made by cooking rice with milk and sugar. Let me not confuse you all. It is what we cal kunun geda.

source: pixabayIncome generation: Rice is an important source of income for farmers in Nigeria, as well as for traders and processors. Many farmers grow rice as a cash crop, and sell it at local markets or to processing companies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, agriculture is a vital sector in Africa, providing food, income, and employment opportunities for millions of people. The continent is home to a diverse range of crops, including yam, maize, beans, guinea corn, groundnut, and rice, each with their unique uses and benefits. These crops plays an important role in food security and economic development in Africa, and are used for a variety of purposes, including food, animal feed, and industrial applications.
