In recent years, personalized medicine and genetic testing have emerged as revolutionary approaches to healthcare, offering tailored treatments and interventions based on an individual's unique genetic makeup. This innovative field holds the promise of more effective therapies, improved patient outcomes, and a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms. In this article, we will explore the features, advantages, disadvantages, potential improvements, and conclusion of personalized medicine and genetic testing.
Features of Personalized Medicine and Genetic Testing:
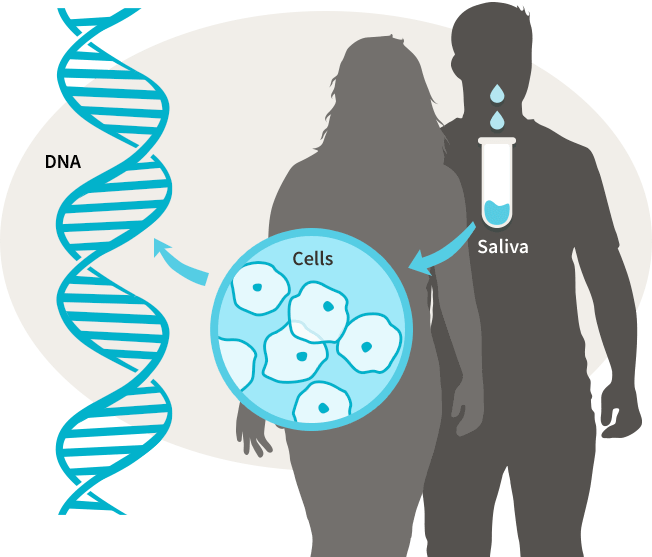
Genetic Profiling: Personalized medicine utilizes genetic testing to analyze an individual's DNA and identify specific genetic variations associated with disease risk, drug response, and treatment outcomes.
Tailored Treatments: Based on the results of genetic testing, healthcare providers can personalize treatment plans to target the underlying genetic factors contributing to a patient's condition. This may involve selecting the most appropriate medication, dosage, or treatment approach for each individual.
Predictive Risk Assessment: Genetic testing can also provide valuable insights into an individual's risk of developing certain diseases or conditions, allowing for proactive interventions and preventive measures to mitigate risk factors.
Precision Diagnosis: By analyzing genetic data, healthcare providers can achieve more precise diagnoses and classifications of diseases, enabling earlier detection and intervention for improved patient outcomes.
Advantages of Personalized Medicine and Genetic Testing:
Improved Treatment Efficacy: Personalized medicine allows for more targeted and effective treatments tailored to each individual's genetic profile, resulting in better therapeutic outcomes and reduced adverse effects.
Preventive Care: Genetic testing can identify individuals at increased risk of developing certain diseases, allowing for early intervention, lifestyle modifications, and preventive measures to reduce disease incidence and severity.
Optimized Drug Selection: Genetic testing can inform healthcare providers about an individual's likelihood of responding to specific medications, enabling the selection of the most effective and appropriate treatment options while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Enhanced Disease Management: Personalized medicine facilitates proactive disease management strategies by identifying genetic factors that influence disease progression, enabling more timely and targeted interventions to slow or halt disease progression.
Disadvantages of Personalized Medicine and Genetic Testing:
Cost: Genetic testing and personalized medicine approaches can be expensive, limiting access for individuals without adequate financial resources or insurance coverage.
Ethical Considerations: The use of genetic information raises ethical concerns related to patient privacy, informed consent, and potential discrimination based on genetic predispositions or traits.
Limited Data Interpretation: Despite advances in genetic testing technology, interpreting genetic data remains complex and challenging, leading to the potential for misinterpretation or misdiagnosis.
Psychosocial Impacts: Genetic testing results may have psychological and emotional implications for individuals and their families, including anxiety, uncertainty, and stigma associated with certain genetic conditions.
Potential Improvements in Personalized Medicine and Genetic Testing:
Cost Reduction: Efforts to reduce the cost of genetic testing and personalized medicine approaches through technological innovations, streamlined processes, and increased insurance coverage can improve accessibility and affordability for patients.
Education and Awareness: Increasing public and healthcare provider education and awareness about the benefits, limitations, and ethical considerations of genetic testing and personalized medicine can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare.
Standardized Guidelines: Developing standardized guidelines and best practices for the interpretation and clinical implementation of genetic testing results can improve consistency, accuracy, and reliability across healthcare settings.
Integration with Healthcare Systems: Integrating genetic testing and personalized medicine approaches into existing healthcare systems and electronic health records can facilitate seamless data sharing, collaboration among healthcare providers, and patient-centered care delivery.
Conclusion:
Personalized medicine and genetic testing represent a paradigm shift in healthcare, offering tailored treatments and interventions based on an individual's unique genetic makeup. While these approaches hold immense promise for improving patient outcomes, they also pose challenges related to cost, ethics, data interpretation, and psychosocial impacts. By addressing these challenges through cost reduction, education, standardized guidelines, and integration with healthcare systems, we can unlock the full potential of personalized medicine and genetic testing to revolutionize healthcare delivery and improve the lives of patients worldwide.
Upvoted. Thank You for sending some of your rewards to @null. Read my last posts to make sure that BLURT burning is profitable for you. Before using this bot please make sure your account has at least 100 BP. Get more BLURT:
@ mariuszkarowski/how-to-get-automatic-upvote-from-my-accounts@ blurtbooster/blurt-booster-introduction-rules-and-guidelines-1699999662965@ nalexadre/blurt-nexus-creating-an-affiliate-account-1700008765859@ kryptodenno - win BLURT POWER delegation