Reblog:
Do you know that the total number of bone in your body is 206?, Hope you know that without bone in your body you can't move, Today we will be speaking about bone and I believe at the end of these write-up you will know many things about you yourself and your body bone, Happy viewing !!!

BONES
Bones are the hard organs that form the skeleton of the body both in Human being and animals. Bones give support to many organs in the body and it comes in varieties of shapes and sizes, bones are often stereotyped as a protective and supportive frame work of the body. Bones stores nutrients, minerals and lipid and also produces blood cell that gives nourishment to the body.
Types of Bone
The bone can be grouped into six types based on their structures; the following are the classifications of bone based on structure;
- Long bones
- Short bones
- Flat bones
- Irregular bones
- Sesamoid bones
- Sutural bones
Long bones: These are the longer type of bones in the body; they consist of shaft which is the main part and number of endings. Long bones are usually longer than their width and it’s made up of mostly compact bone, it has lesser amount of marrow. Examples of long bones are;
i. Femur (which are the leg bones)
ii. Ulna (which are the arm bone)
iii. Radius (which are the arm bone)
iv. Tibia (which are the leg bone)
v. Fibula (which are the leg bone)

Long Bone
Short bones: They are approximately cube-shaped bones with length similar to width/depth/diameter. They have only a thin layer of compact bone surrounding a spongy interior. Examples are;
i. Cuboid bone (The ankle bone)
ii. Lunate bone (The wrist bone)
iii. Cuniform bones (The ankle bones)
iv. Scaphoid bone ( The wrist bone)

Short Bones
Flat bones: These kinds of bones are thin and they are generally curved and they have two parallel layers of compact bone fit into a layer of spongy bone. In some cases they provide mechanical protection to soft tissue that is covered by the flat bones, for example, the cranial bone covers the brain so it protect the brain. Examples are;
i. Sternum
ii. Cranial bone
iii. Rib
iv. Scapula

The scapula
Irregular bone: This type of bone has complicated shapes which mean they cannot be classified to long, short or flat and this is due to the center of ossification. They consist of thin layer of compact bones surrounding a spongy interior also provide mechanical support for the body and protect the spinal cord. The examples are ;
i. Atlas bone
ii. Axis bone
iii. Hyoid bone
iv. Zygomatic bone
v. Facial bones
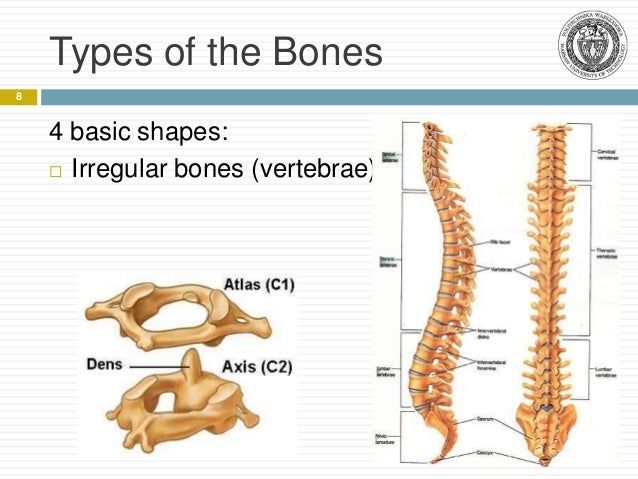 Irregular bones
Irregular bones Sesamoid bones: These are bones which are embedded in tendons i.e. they develop in tendons in locations where there is friction, tension, and physical stress. Examples are
i. Patella
ii. Pisiform
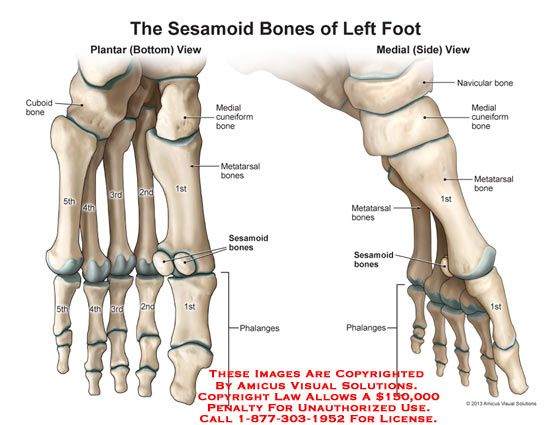 Sesamoid Bones
Sesamoid Bones Sutural bones: these types of bone are very small bones which are located specifically within the sutural joints between cranial bones
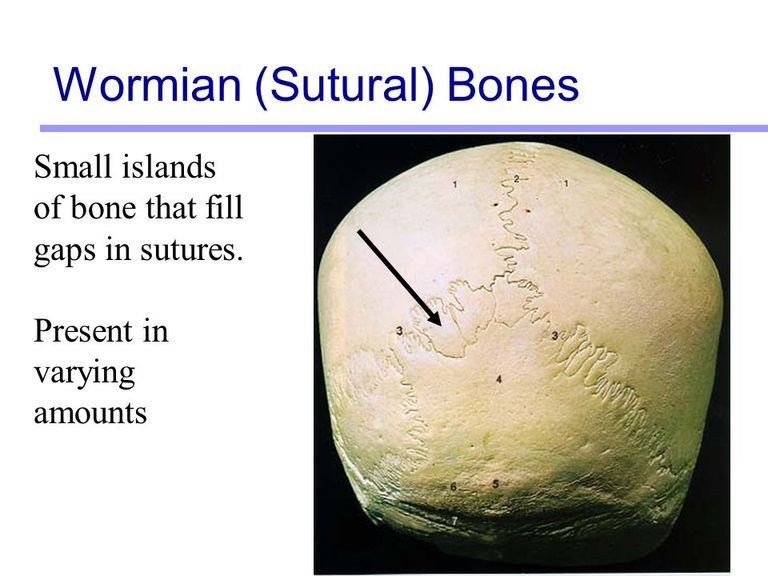
Sutural bones
Layers of bone
The bone is made up of four layers which are moving from outside of the bone to inside, The layers are;
- Periosteum layer
- Cortical/Hard bone layer
- Spongy/Cancellous
- Bone marrow
- Bone tissue
Bone cells
The following cells are present in the bone;
- Osteoblasts
- Osteocytes
- Osteoclast
Functions of bone
Despite the fact that bones have so many functions in the body, I will like to list some functions viz;
- Bones enable movement of the body
- Bone serves as reservoir for calcium, phosphorus, and essential minerals in the body
- Bone is a good site for hematopoiesis (production of blood)
- Bones protect internal organs
- Ones provide framework for the attachment of muscles and tissues
Bone Formation
The process whereby new bones are formed is called ossification. This start in the early third month of fetal life in human and the formation completes at late adolescence.
The following are the list of the period in which bones are formed;
a. Third month of fetal development: Ossification in long bones start developing
b. Fourth month: Most primary ossification centers will appear in the diaphyses of bone
c. Birth to 5years after birth: Secondary ossification centers appear in the epiphyses
d. 5years to 12years (female): Ossification starts spreading rapidly from the centers of ossification. This takes place in 5years to 14 years in male
e. 17years to 20years: Bones of the upper limb and scapulae is ossified
f. 19years to 23years: Bones of the lower limb become completely ossified
g. 23years to 25yers: The sternum bone, clavicle, and vertebrate is ossified
h. 25years: Nearly all bones are completely ossified
Bone disorders
- Osteomalacia: This is a condition caused by deficiency in vitamin D in adult. It can be treated by consuming vitamin D and Calcium.
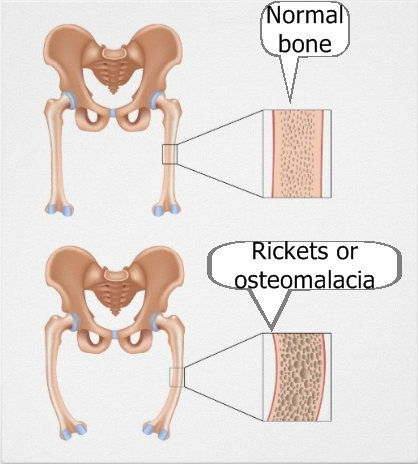
Osteomalacia
- Fracture: This refers to the break in the continuity of bones. The sign and symptoms are generally suggestive of a severe injury and discomfort, limited range of motion etc. The treatment for this can be open surgery.

Fracture
Conclusion:Bones play important role n the general activities performed by the body, I am sure you can now agree with me. Without bone there is no movement etc.
I believe you gain somethings from this, Kindly Upvote, Reblog, and follow me for more interesting post.......Comments are allowed please.
Thanks!!!
