There are numerous terms that must be understood in the world of audio, especially Sound / Music engineering. The importance of understanding these terms in detail aims to find out a sound result given by a plugin.
Likewise in software plugins, there are writings or knobs that can provide settings to produce different sounds between input and output.
As sound engineering, the understanding that must be possessed is not only in the form of practice. but must master theoretically.
I have put together various terms that I will explain to beginners. Because of the many terms, I will divide this post into several parts.
The terms I will explain are:
|
Acoustical
Amplifier
Amplitude
Audio Mixer
Bar
Beat
BeatsPerMinute
Clipping
Compressor
DAC
DAW
Decibels / dB
delay
Diffuser
Equalizer
Frequency
Hertz (Hz)
Hi-Z
Infrasonic
Impedance
Latency
Lo-Z
loop
Mastering |
Sample Rate
Sound Card
SPL |
High
Imaging |
Bookshelf Speaker BNC Bitrate Bipolar Speaker Binding Post Bi-Amplify Bass-Reflex Bandwidth Baffles audiophile Aspect Ratio Artifact Anamorphic AES/EBU Fun Harsh D'Appolito Crosstalk crossover Mellow dynamic | Microphonics
Mids/Midrange
Muddy
Natural |
1. Acoustic / Acoustical

Source
Acoustic / Acoustical: Physical symptoms of sound or sound that can be heard by the ear. The sound that is reflected by a room without soundproofing (reflection) and able to be heard by humans is also called acoustical.
As I have explained in a previous post, that in the world of mixing, the room where the mixing works must be carried out "Acoustical treatment" with the aim that the sound heard by the mixing engineering is purely coming out of the monitor speakers, not from the reflection of the room. The sound produced by reflection in the room is not just one sound. For example, if you are in a room where there is no "Acoustical treatment" then the sound you hear comes from: speakers, reflection from the left wall, right wall reflection, floor reflection, attic reflection, then right wall reflection reflected the wall left, left wall to right wall, right wall to floor, floor to the right wall, and so on. You will hear more than ten sound sources if you listen in a room that does not do "Acoustical Treatment".
In a future post, I will cover how to do a great “Acoustical Treatment” for a studio room. With the explanation above and the case examples that I gave, hopefully, you can understand what is meant by Acoustical.
2. Amplifiers
The amplifier is an electronic device that works to produce a larger sound signal (output) than the given sound signal (input). The sound in question is not only a vocal sound, but also the sound of other electric instruments, such as guitar, bass, and others.
In the Amplifier device, there are components that work, including the Transformer as the main power source for the amplifier, Transformer serves to reduce power from electricity (220V) to the amount of power that suits your needs. Furthermore, Elcho (capacitor) functions to change the surging electric current to be flat. The capacitor also affects the bass sound on the amplifier, the larger the capacitor (Elcho) the better the sound produced. Then on the amplifier, there is also a Sanken component (transistor) which functions as a power amplifier.
The sound quality produced by the amplifier is highly dependent on this component. Because this component works more optimally than other components, then the transistor must be given a cooler in the form of a cooling plate and a fan. Most of the amplifiers are also equipped with an equalizer which works to adjust the sound frequency signal that we want to reduce or add. Amplifiers are also divided into two types, mono, and stereo. Mono has one input and one output while stereo has more than one.
Without an amplifier, the sound that has been converted by the DAC from analog to digital will not be heard without being processed by the Amplifier. So the DAC has a close relationship with the amplifier.
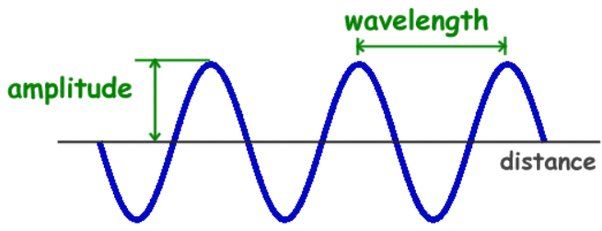
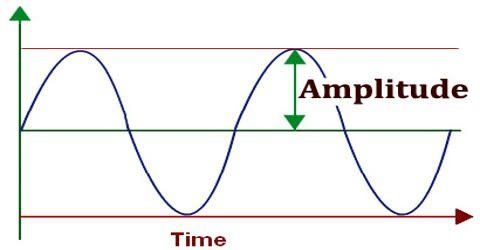
3. Amplitude
Source
Amplitude: Volume of an audio signal. A wave's amplitude is measured from the centerline distance. The size is in dB (decibel).
Amplitude is the maximum deviation of a wave that will affect the strength or weakness of the sound or in other words is the farthest deviation from the equilibrium point. A simple example is when you hear a sound from the source (speakers) at a distance of one meter (strong), it will differ in volume when you are at a distance of 5 meters (weak).
In theory, Amplitude can be drawn like this:
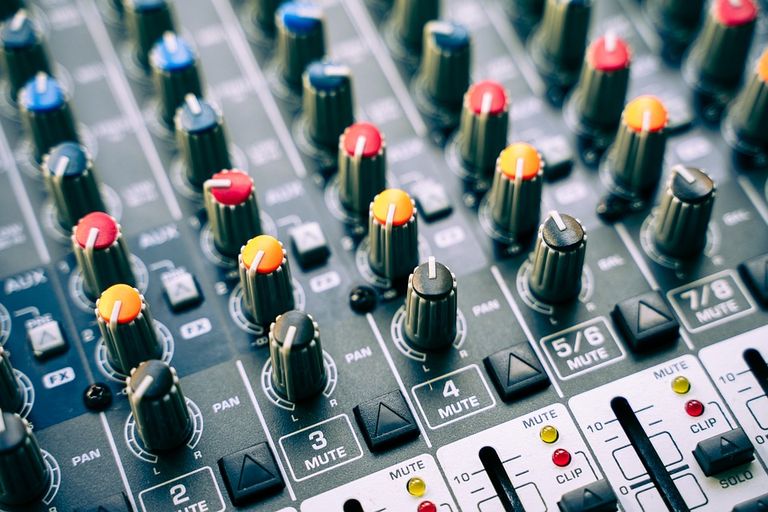
4. Audio Mixer

Source
Audio Mixer: A device that functions as an amplifier and a balancer of several sound sources, becoming an output that meets the criteria to be input on a recording device.
Before the Audio mixer was made in digital form (Plugin), at first this mixer was made in analog form. The difference is that analog mixers have a limited number of preset buttons, while digital mixers have many features that can be used. But in principle, a digital mixer still follows the workings of an analog mixer.
An analog audio mixer at least has knobs that function as follows:
Input/Output that functions as a door for audio signal entry/audio signal exit
Gain serves to increase the incoming audio signal
High functions to increase and decrease the high frequency
The middle function is to increase and decrease the middle frequency
Low function to increase and decrease the frequency of Low
Aux serves as a voice signal transmission from the channel to other devices
Effect functions to increase and decrease the effect that is set, for example, reverb, delay, echo, and others.
Pan serves to shift the sound left or right on the line output
Phantom 48V serves to add power to input devices, such as microphones, and others.
Fader/Volume functions to increase or decrease the overall volume on one channel.
and some other additional features
5. Decibel

Source
Decibel / dB: Unit for measuring sound intensity. One decibel is equivalent to one-tenth of a bel.
The decibel, commonly abbreviated as dB, is a unit of sound intensity. Measurements that produce decibels are not as easy as measurements in general. Measurement of distance (meters) will be easy to understand how far or how close, as well as weight (kilograms), will quickly understand the weight of an object. In contrast to the decibel, the measurement requires something as a comparison. The decibel calculation is almost the same as finding a percentage.
For example, there is a sound (A) has 10dB greater than another sound (B), meaning that A's voice is 10 times bigger than B's voice. Likewise, for example, A's voice has 20dB greater than B's voice, then A's voice is 100 times more powerful. greater than the sound of B.
What if there are no other voices for comparison?
So the ear makes the only one as a comparison. Where we know that the human hearing limit is at 0dB. Humans cannot hear sound signals below 0dB and will experience damage to the ears if they hear sounds greater than 85dB. And keep in mind, humans can only distinguish the ratio of sound with a level of 1dB. Therefore, as I explained earlier, to do the balancing a sound engineer is required to use a meter.
6. Frequency
Frequency is the number of vibrations in the sound, the more vibrations in a sound, the greater the frequency, the higher the sound produced. To prove simply, you can practice by touching your neck when you make a sound, the louder you sound, the stronger the vibration will be.
Frequency is divided into three:
Infrasonic.
Infrasound is sound that has a frequency below 20 vibrations/second (20 Hz). Infrasonic sound is usually able to be heard by small animals, while humans cannot hear infrasonic frequency sounds.
Then the Audiosonic frequency is sound that has a frequency range of 20Hz – 20kHz. Audiosonic frequency is a frequency range that can be heard by humans.
While the third is Ultrasonic Frequency, which is sound that has a frequency above 20kHZ, because the sound at the Ultrasonic frequency is very high, humans also cannot (able) hear sound at that frequency. The size of a sound wave / The number of vibrations that occur in a certain period of time measured in hertz (Hz).
Thus an explanation of some terms in the field of sound/music.
DISCORD FACEBOOK INSTAGRAM TWITTER TELEGRAM
I have previously posted this Article on my blog