Understanding the Internet of Things (IoT) and its Applications
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects or "things" embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity, allowing these objects to collect and exchange data. This technology has been around for several decades, but recent advancements in cloud computing, big data, and the falling cost of connected devices has made it a rapidly growing industry with an estimated 20.4 billion connected devices in use worldwide by 2020 and a projected 75.44 billion by 2025.

What is IoT?
IoT refers to the connection of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and connectivity which enables these objects to connect and exchange data, creating opportunities for more direct integration of the physical world into computer-based systems, resulting in improved efficiency, accuracy and economic benefit.
In simple terms, IoT refers to the ability of everyday objects to communicate and send data over the internet. For example, a smart thermostat that can be controlled from your smartphone, or a smart refrigerator that can order groceries when it runs low on food.
Components of IoT
The Internet of Things is made up of four key components: devices, connectivity, data, and the cloud.
- Devices: These are the physical objects that make up the IoT network. They can range from everyday household items such as refrigerators and washing machines to industrial equipment and vehicles.
- Connectivity: This refers to the communication methods used by the devices to exchange data. Examples include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and cellular networks.
- Data: IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, which is collected, stored, and analyzed to derive insights and take action.
- The Cloud: The cloud is the backbone of IoT, providing storage and processing capabilities for the data generated by IoT devices.



Applications of IoT
The Internet of Things has a wide range of applications across various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and consumer goods, among others. Some of the most notable applications of IoT include:
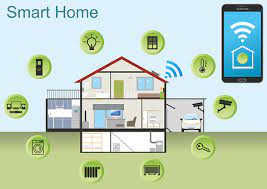
- Smart homes: IoT devices such as smart thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras can be controlled and monitored remotely, providing greater convenience and security for homeowners.
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): IoT is revolutionizing manufacturing and industrial processes, enabling real-time monitoring and control of industrial equipment, predictive maintenance, and improved operational efficiency.
- Connected vehicles: IoT is playing a key role in the development of connected and autonomous vehicles, providing real-time data for improved safety, fuel efficiency, and traffic management.
- Healthcare: IoT is transforming healthcare, from telemedicine and remote patient monitoring to smart hospitals, improving patient outcomes and reducing costs.
- Agriculture: IoT is helping farmers to optimize crop yields, reduce waste, and improve sustainability through real-time monitoring and control of soil and weather conditions.
- Smart cities: IoT is being used to improve urban living by reducing traffic congestion, improving energy efficiency, and enhancing public safety through smart lighting, traffic management, and waste management systems.


Challenges and Risks of IoT
Despite the many benefits of IoT, there are also several challenges and risks associated with the technology. These include:
- Security: As more devices become connected, the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches increases. IoT devices may be vulnerable to hacking and other security threats, putting sensitive information and personal data at risk.
- Privacy: With the increasing amount of data generated by IoT devices, there is a risk that personal information may be collected and used without consent.
- Standardization: With so many different IoT devices and protocols, there is a need for standardization to ensure interoperability and seamless communication between devices.
- Cost: The cost of IoT devices and infrastructure can be prohibitive for some individuals and businesses, especially for those in developing countries.
- Complexity: The sheer number of connected devices and the vast amount of data generated by IoT can be overwhelming, making it difficult for businesses and individuals to effectively manage and make use of the information.


Conclusion
The Internet of Things is a rapidly growing technology that has the potential to transform various industries and improve our daily lives. However, there are also several challenges and risks associated with IoT that must be addressed. As the technology continues to evolve, it is important for individuals and businesses to be aware of the potential benefits and challenges of IoT and to take appropriate measures to secure their connected devices and data.