The determination of asset pair prices varies significantly between Centralized Order Books (CLOBs) and Automated Market Makers (AMMs). In a CLOB, market makers set prices through buy and sell orders, with other participants deciding whether to transact at these prices.
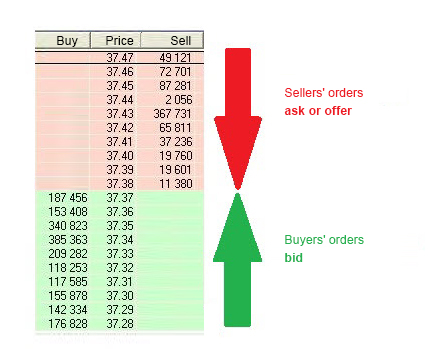
Conversely, in AMMs, a mathematical formula considers the balance of assets within the liquidity pool to determine prices.
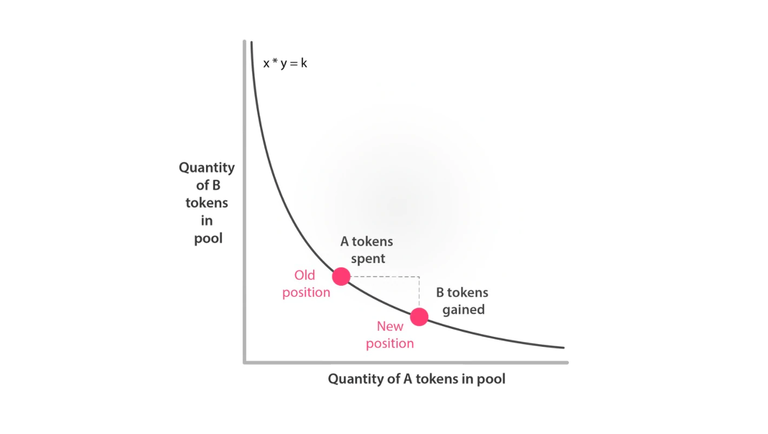
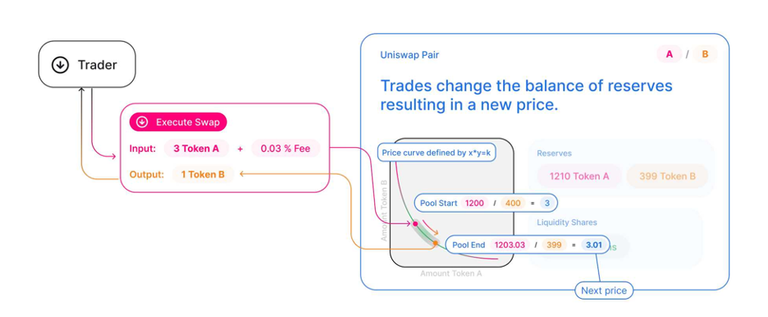
For instance, Uniswap's trading pools exclusively support two assets, with the price determined by the x*y=k formula.
In essence, the price of the pair hinges on the equilibrium reached by the assets in the pool, exemplifying the unique AMM pricing mechanism.
These disparate price discovery methods in CLOBs and AMMs pave the way for arbitrage cases.
Such cases may manifest between a CLOB and an AMM or even between two distinct AMMs.
It's essential to recognize that within AMMs, the price of an asset pair can only change when a swap is executed, underscoring the indispensable role of arbitrageurs in aligning prices with other marketplaces.
Notably, certain AMM protocols permit users to provide liquidity solely on one side of the pool, which can influence the asset pair's price. Consequently, a thorough understanding of the specific AMM protocol and its governing rules is paramount when gauging the price of an asset pair.
Comprehending the intricacies of price discovery mechanisms in both CLOBs and AMMs is imperative for traders and investors seeking to make well-informed trading decisions.
Harry Potter Library (HPL) Community
Please join the HPL community. You will get upvotes for your posts. Simply join and post there using the tags "hpl" or "harrypotterlibrary" in your post.
- Community Address: https://steemit.com/trending/hive-140602
- About HPL Community:
EN: Harry Potter Library - HPL
KR: 해리포터의 도서관 (Harry Potter Library, HPL)