Hi everyone, how is everything an used day to day transactions?. It seems like everything is going fine and smooth.
Today would like share information with you as regards the different irrigants used in root canal treatment which sub-branch of Endodontic in dentistry. On this post we are going to discuss the basics aspect of the Endodontic Irrigants. So stay tuned.
Irrigants are the are concentrated solutions used the cleaning of prepared root canals in order to kill the pathogenic bacteria and to flush out the debris from the root canal system of the tooth.
Now let's discuss about the ideal requirements of root canal Irrigants:
1- Antimicrobial action
2- Mechanical flushing
3- Non-toxic to tissues and biocompatibility
4- Dissolve Necrotic and Vital pulp tissues
5- Lubrication action on the canal walls
6 - Ability to remove the smear layer from the root canal walls
7- Low surface tension
Some of the Irrigants used in root canal treatment include the following:
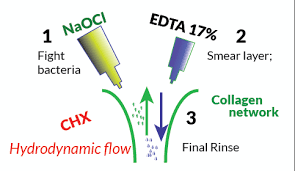
1- Sodium Hypochlorite (NaClO)
2- Ethylene Diamine Tetra-acetic acid (EDTA)
3- Chlorhexidine Diglucoronide
4- MTAD ( A mixture of Tetracycline isomer, citric acid and a detergent)
5- Hydrogen peroxide
6 - Saline solution
7- Potassium iodide or iodine
8- Citric acid
9- Phosphoric acid and so on.
Now, let's start with the sodium hypochlorite which is the most common and widely used root canal Irrigant.
Sodium Hypochlorite (Dakin Solution)
Sodium peroxide is the most common bacteria killing irrigants which has been in use for long time in dentistry but not effective in dissolving inorganic debris and the smear layer.
It contains 5% of chlorine. NaOClO contains Hypochlorous acid and Hypochlorite ions which they both provide antimicrobial activity. Its concentration usually ranges from 0.5-5.2% solution. However, in Endodontics 2.5 or 2.6% is usually employed for irrigation due to its potential toxicity for organic tissues.
The funny part of it is that, its effectiveness increases with increasing concentrations so in order to compensate for the reduced concentration there some procedures that needs to be done in order to achieve standard efficacy. These include the following;
1- Increase the volume of NaClO
2- Increase duration
3 - Warming it
4- Passive ultrasonic activation during the irrigation.
Mechanism of Destruction of Bacteria 🦠 by NaClO
This mechanism occurs in two phases:
1- Penetration into the bacteria 🦠🦠 cell wall
2- Chemical Combination with protoplasm followed by disruption of DNA synthesis in the cell.
However as it is well known that there is no single irrigant in endodontics with ideal properties so does NaOClO is not an Ideal irrigant
Its Drawbacks include the following:
1- Potential Cytotoxicity
2- It doesn't remove the inorganic components of the smear layer
3- It has unpleasant taste
4- It requires cool place for storage to maintain its effectiveness in treatment.
Another important irrigants we would cover in this post is the EDTA.
Ethylene Diamine Tetra-acetic Acid (EDTA)
EDTA is a chelating substance used by a scientist Nygard. It is a non-toxic and can irritate in weak solution on ionization. It has the ability to chelate with heavy metals including Calcium. When EDTA is used as irrigants the dentin becomes more friable and easier to instrument and make it more exposed to demineralisation.
Another important aspect of EDTA is that, it has the ability to remove the smear layer.
Method of Using EDTA
A 17% concentrated EDTA is usually used for irrigation. A clinician could wait for a minute for proper penetration of the issue or could employ an activator. It could also be applied on instruments to assist in lubrication and avoid friction with the walls.
Saline solution is used for rinse and lastly NaClO is used for the final rinsing
Chlorhexidine Digluconate - (2% CHX Required)
It is a broad spectrum antimicrobial agent. Also used as mouth wash in periodontology. It is usually used in failed cases or retreatment. Enterococcus Faecalis bacteria is usually found in retreatment cases and Chlorhexidine is used with it.
It has a prominent distinction among other irrigants due to its substantivity
It is less toxic.
Substantivity means sustained availability that it gets absorbed, it will still be released in between durations.
Its drawback is that, it can't be used to remove smear layer and also it can't be used alone as an irrigants, it needs to be combined with other irrigants for effective action.
Its mechanism of action inside the cell is Coagulation of cytoplasmic contents inside the bacteria cell thereby rendering the bacteria cell inactive and harmless.
Last but not least as regards this post, we have the MTAD irrigants.
MTAD
MTAD is a mixture of Tetracycline isomer which could be Doxycycline, Citric acid and Detergent ( sometimes Tween 80).
It has the ability to remove the smear layer due to citric acid presence in the mixture and bacteriostatic ability due to Tetracycline isomer presence but not as effective as hypochlorite Irrigant and as such sometimes 1.3 % of NaOClO could be used first and then complemented with MTAD irrigant.
That's all for this post at least for now.
Thanks for the following up and usual support.
In the subsequent posts we will discuss on factors affecting irrigation techniques and Irrigation guidelines.
References
You can Watch the Below Video for more Understanding
Source


Upvoted. Thank You for sending some of your rewards to @null. Read my last posts to make sure that BLURT burning is profitable for you. Before using this bot please make sure your account has at least 100 BP. Get more BLURT:
@ mariuszkarowski/how-to-get-automatic-upvote-from-my-accounts@ blurtbooster/blurt-booster-introduction-rules-and-guidelines-1699999662965@ nalexadre/blurt-nexus-creating-an-affiliate-account-1700008765859@ kryptodenno - win BLURT POWER delegation@ ctime/burn-bot-liquid-blurt