
In the Argentine economic context, with a constant and accelerated devaluation of the national currency, the US dollar is the preferred safe haven asset.
Given the obstacles and limitations to acquiring dollars (or any other foreign currency) legally, 'crypto dollars' are an increasingly chosen alternative.
Technically called stablecoins, these are cryptocurrencies that replicate another asset in their price, in this case, the US dollar.

En el contexto económico argentino, con una constante y acelerada devaluación de la moneda nacional, el dólar estadounidense es el activo de refugio de valor preferido.
Ante las trabas y limitaciones para adquirir dólares (o cualquier otra moneda extranjera) por vía legal, los 'dólares cripto' son una alternativa cada vez más elegida.
Técnicamente llamadas stablecoins, estas son criptomonedas que replican en su cotización a otro activo, en este caso, el dólar estadounidense.
What are the different types of 'crypto dollar' that exist? / ¿Cuáles son los diferentes tipos de 'dólar cripto' que existen?
However, there are also stablecoins for the euro, gold and even the Argentine peso.
Basically, there are three types of stablecoins, which are as follows:
Backed by fiat money and traditional financial instruments (USDT, USDC and BUSD, among others).
Backed by cryptocurrencies (DAI, GHO and DoC, among others).
Algorithmic (UST and USDD, among others).

Sin embargo, también existen stablecoins del euro, del oro y hasta del peso argentino.
Básicamente, existen tres tipos de stablecoins, que son los siguientes:
- Respaldadas por dinero fíat e instrumentos financieros tradicionales (USDT, USDC y BUSD, entre otras).
- Respaldadas por criptomonedas (DAI, GHO y DoC, entre otras).
- Algorítmicas (UST y USDD, entre otras).
A continuación, veremos cómo funciona cada una de ellas, sus ventajas, desventajas y potenciales riesgos.
Stablecoins backed by fiat money and traditional financial instruments. / Stablecoins respaldadas por dinero fíat e instrumentos financieros tradicionales.
Fiat money is that which is issued by an entity authorized by law, usually the Central Bank of a country. Among bitcoiners, the term is often used—occasionally in a derogatory way—to refer to national currencies and differentiate them from bitcoin.
There are stablecoins that are backed 1:1 by traditional currencies (such as fiat, Treasury bonds, corporate bonds, etc.) in bank accounts. That is, for every token in circulation, there is one US dollar (or other corresponding currency) deposited in a financial institution.
Among the stablecoins that meet this characteristic are Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), Binance USD (BUSD) and True USD (TUSD), among many others.
One of the main advantages, which makes them the most used, is price stability. Since they are directly backed by their underlying asset (dollars or dollar financial instruments), their price tends to be very stable.
As for trust, its value is guaranteed by real money reserves, which are often audited by third parties.
But, despite being the most used stablecoins, they have their disadvantages. The main one is the centralization that implies the need to maintain reserves in bank accounts. These accounts are subject to regulations and potential intervention by financial authorities. Additionally, if the bank or entity holding the fiat backing fails or there are problems, the 1:1 peg of the stablecoin could be called into question.
The latter was what happened with USDC in March 2023. The bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank, where the Circle company, issuer of that currency, had part of its reserves, caused its price to fall by about 10 cents. For a couple of days, each USDC was trading at $0.90. As Circle had reserves in other entities to back the circulating USDC, it eventually regained peg to the dollar.

El dinero fíat es el que es emitido por una entidad autorizada por mandato de Ley, usualmente el Banco Central de un país. Entre bitcoiners, el término suele usarse —ocasionalmente de manera despectiva— para referirse las monedas nacionales y diferenciarlas de bitcoin.
Hay stablecoins que están respaldadas 1:1 por divisas tradicionales (como dinero fíat, bonos del Tesoro, bonos empresariales, etcétera) en cuentas bancarias. Es decir, por cada token en circulación, hay un dólar estadounidense (u otra moneda correspondiente) depositado en una entidad financiera.
Entre las stablecoins que cumplen con esta característica se encuentran Tether (USDT), USD Coin (USDC), Binance USD (BUSD) y True USD (TUSD), entre muchas otras.
Una de las principales ventajas, que las convierte en las más utilizadas, es la estabilidad del precio. Dado que están respaldadas directamente por su activo subyacente (dólares o instrumentos financieros en dólares), su precio tiende a ser muy estable.
En cuanto a la confianza, su valor está garantizado por reservas de dinero real, que a menudo son auditadas por terceros.
Pero, a pesar de ser las stablecoins más utilizadas, tienen sus desventajas. La principal de ellas es la centralización que implica la necesidad de mantener reservas en cuentas bancarias. Estas cuentas están sujetas a regulaciones y a la potencial intervención de autoridades financieras. Además, si el banco o la entidad que custodia el respaldo fíat falla o hay problemas, podría cuestionarse la paridad 1:1 de la stablecoin.
Eso último fue lo que ocurrió con USDC en marzo de 2023. La quiebra del Sillicon Valley Bank, donde la empresa Circle, emisora de esa moneda, tenía parte de sus reservas, hizo que su cotización cayera cerca de 10 centavos. Durante un par de días, cada USDC cotizaba a 0,90 dólares. Como Circle tenía reservas en otras entidades para respaldar los USDC circulantes, finalmente recuperó la paridad con el dólar.
Cryptocurrency-backed stablecoins. / Stablecoins respaldadas por criptomonedas.

These stablecoins are backed by other cryptocurrencies such as ether (ETH), bitcoin (BTC) or even other stablecoins such as USDT or USDC. Parity is maintained through collateralization and automatic settlement mechanisms.
DAI, issued by the decentralized organization MakerDAO, is the leading cryptocurrency collateralized by other digital assets. As seen in the following graph, among the currencies that guarantee the value of DAI are USDC and ETH. Additionally, they have recently incorporated real-world assets (RWA), which can be real estate or bonds.
The main advantage of this type of stablecoins is their decentralization. They do not depend on traditional financial institutions to maintain their value.
Its transparency is also notable. The 'smart contracts' that govern them are public and verifiable by anyone, unlike what happens with stablecoin reserves backed by fiat money in bank accounts.
But they also have disadvantages, including the volatility of the collateral. If the price of the supporting cryptocurrency falls drastically, it can lead to massive liquidations. In addition, depending on smart contracts makes them more vulnerable to hacking.

Estas stablecoins están respaldadas por otras criptomonedas como ether (ETH), bitcoin (BTC) o inclusos otras stablecoins como USDT o USDC. La paridad se mantiene mediante mecanismos de colateralización y liquidación automática.
DAI, emitida por la organización descentralizada MakerDAO, es la principal criptomoneda colateralizada por otros activos digitales. Como se observa en el siguiente gráfico, entre las monedas que garantizan el valor de DAI se encuentran USDC y ETH. Además, recientemente han incorporado activos del mundo real (RWA), que pueden ser bienes raíces o bonos.
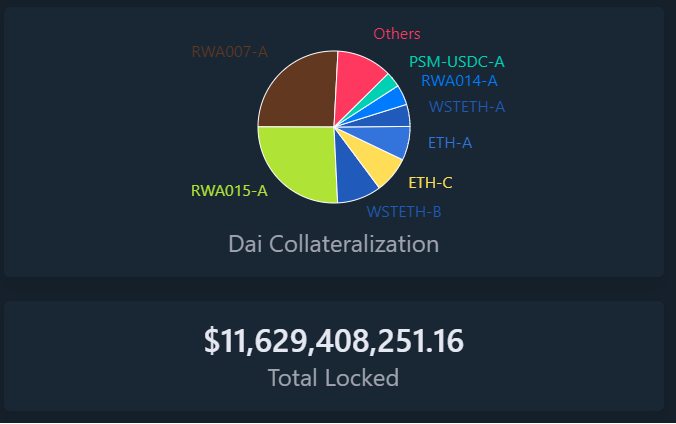
La principal ventaja de este tipo de stablecoins es su descentralización. No dependen de instituciones financieras tradicionales para mantener su valor.
También es destacable su transparencia. Los 'smart contracts' (contratos inteligentes) que las rigen son públicos y verificables por cualquiera, a diferencia de lo que ocurre con las reservas de las stablecoins respaldadas por dinero fíat en cuentas bancarias.
Pero también tienen desventajas, entre ellas, la volatilidad del colateral. Si la cotización de la criptomoneda de respaldo cae drásticamente, puede llevar a liquidaciones masivas. Además, el hecho de depender de contratos inteligentes las hace más vulnerables a hackeos.
Algorithmic stablecoins. / Stablecoins algorítmicas.
Algorithmic stablecoins maintain their pegs through algorithms that automatically adjust circulating supply based on demand. They can do so without the need for collateral, or using a token issued by the same organization as collateral (the supply of which is regulated by algorithmic mechanisms).
The advantages of such an instrument are that they do not require physical or cryptocurrency backups, which means they are exempt from the risk of closing bank accounts, for example. Plus, in theory, they can quickly adjust their supply to meet changes in demand.
The main disadvantage is that, so far, there has not been any algorithmic stablecoin that has managed to be successful and scalable for mass use. Therefore, we can consider this type of cryptocurrencies within an experimental category. They should be used with extreme caution.
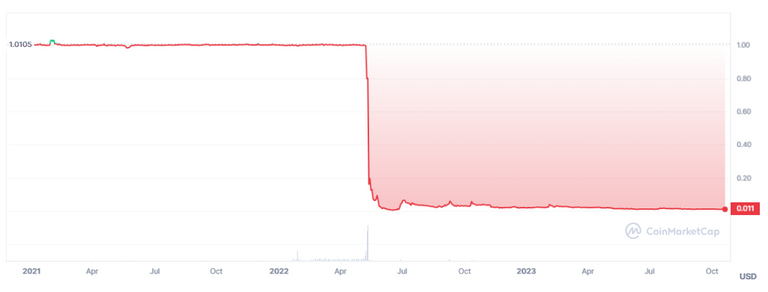
If the market loses confidence in the algorithm or there is a failure in its operation, it could trigger a rapid destabilization of the currency's value. That is what happened in 2022 with UST (stable cryptocurrency of the Terra-Luna ecosystem). Liquidations in its collateral (the TERRA cryptocurrency, issued by the same organization) caused a 'death spiral', which ended up collapsing the price of UST as seen in the graph below:

Las stablecoins algorítmicas mantienen su paridad mediante algoritmos que ajustan automáticamente la oferta circulante en función de la demanda. Pueden hacerlo sin necesidad de colateral, o usando un token emitido por la misma organización como colateral (cuya oferta es regulada por mecanismos algorítmicos).
Las ventajas de un instrumento así es que no requieren respaldos físicos ni de criptomonedas, con lo cual están exentas del riesgo de cierre de cuentas bancarias, por ejemplo. Además, en teoría, pueden ajustar rápidamente su oferta para satisfacer cambios en la demanda.
La principal desventaja, es que, hasta el momento, no ha habido ninguna stablecoin algorímica que haya logrado ser exitosa y escalable para un uso masivo. Por lo tanto, a este tipo de criptomonedas podemos considerarlas dentro de una categoría experimental. Deberían utilizarse con suma precaución.
Si el mercado pierde confianza en el algoritmo o hay un fallo en su funcionamiento, podría desencadenar una rápida desestabilización del valor de la moneda. Eso fue lo que ocurrió en 2022 con UST (criptomoneda estable del ecosistema Terra-Luna). Las liquidaciones en su colateral (la criptomoneda TERRA, emitida por la misma organización) provocaron un 'espiral de la muerte', lo que terminó derrumbando la cotización de UST tal como se observa en el gráfico a continuación:
Final suggestion. / Sugerencia final.
Para aquella persona que decida poner parte de sus ahorros en alguno de estos 'dólares cripto', podría resultar de utilidad la diversificación entre distintas stablecoins. De ese modo, se mitigarán los riesgos y se equilibrarán las ventajas y desventajas de todas ellas.
Además, puede resultar conveniente enfocarse solo en las que tienen mayor capitalización de mercados, como USDT, USDC y DAI, y no en las más pequeñas que, por lo tanto, son menos utilizadas o más nuevas y que podrían tener riesgos aún no descubiertos.

Para aquella persona que decida poner parte de sus ahorros en alguno de estos 'dólares cripto', podría resultar de utilidad la diversificación entre distintas stablecoins. De ese modo, se mitigarán los riesgos y se equilibrarán las ventajas y desventajas de todas ellas.
Además, puede resultar conveniente enfocarse solo en las que tienen mayor capitalización de mercados, como USDT, USDC y DAI, y no en las más pequeñas que, por lo tanto, son menos utilizadas o más nuevas y que podrían tener riesgos aún no descubiertos.
Source images / Fuente imágenes: Errepar.
Sources consulted (my property) for the preparation of this article. Some paragraphs may be reproduced textually.
Fuentes consultadas (de mi propiedad) para la elaboración del presente artículo. Algunos párrafos pueden estar reproducidos textualmente.
| Argentina Discovery. |  |
|---|---|
| Galería Fotográfica de Argentina. |  |
| Viaggio in Argentina. |  |
Upvoted. Thank You for sending some of your rewards to @null. Read my last posts to make sure that BLURT burning is profitable for you. Before using this bot please make sure your account has at least 100 BP. Get more BLURT:
@ mariuszkarowski/how-to-get-automatic-upvote-from-my-accounts@ blurtbooster/blurt-booster-introduction-rules-and-guidelines-1699999662965@ nalexadre/blurt-nexus-creating-an-affiliate-account-1700008765859@ kryptodenno - win BLURT POWER delegationNote: This bot will not vote on AI-generated content
Thanks!!