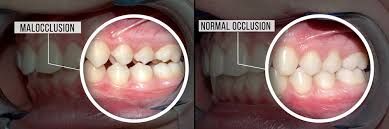
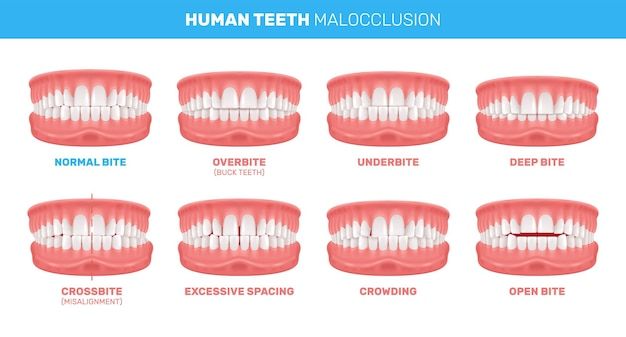
Consequences Of Uncorrected Class II Malocclusion
Allowing Class II malocclusion to progress without taking action can have a devastating and significant impact on oral health, function, and overall well-being of the patient. The possible and likely potential outcomes of untreated malocclusion include:
Dental Health Issues:
Tooth Wear and Damage:
The abnormal contact or bite of the teeth can cause uneven wear and tear on the enamel, which can undoubtedly increase the risk of tooth decay and fracture.
Periodontal Problems:
Malocclusion can lead to gum recession or even aggravate the existing ones, periodontal disease, together with some other oral health issues due to lack of proper maintenance of oral hygiene.
Functional Impairments:
Chewing and Digestion:
An unnatural alignment can cause abnormal bite which can potentially affect the efficiency of chewing, resulting in digestive problems and nutritional deficiencies or indigestion.
Speech Difficulties:
Malocclusion can affect speech articulation and even pronunciation of letters and sounds, or at worse affects overall speech clarity and audibility.
Aesthetic Concerns:
Facial Appearance:
Class II malocclusion when progressed severely can alter the facial profile, eventually leading to a compromised aesthetics which appears as an unbalanced or asymmetrical appearance. This can undoubtedly lead to phobia and social trauma, affecting self-esteem and posing a lack of confidence.
Social and Psychological Impact:
The aesthetic and functional consequences of malocclusion can have a significant psychological impact, most especially in children and adolescents. Social interactions, confidence, and overall social life may be affected negatively and badly.
Genetic factors being among the contributory factors to Class II malocclusion cannot eliminated and as such certain measures can help lower the risk and manage the condition effectively and professionally.
Early Dental Visits:
Regular dental visits early from childhood age can assist in earlier identification and managing the dental issues promptly and without hindsight. Early detection of malocclusion gives chances for timely intervention and better prognosis outcomes.
Habit Control:
"Discouraging harmful oral habits, such as thumb sucking and prolonged pacifier use, can reduce the risk of developing malocclusion. Parents should encourage proper oral hygiene practices and monitor their child’s dental development."Source
Orthodontic Evaluation:
By the age of seven, it better that children undergoes orthodontic evaluation as they are getting closer to mix dentition stage. This assists orthodontists to check jaw bone growth and tooth contact, and to employ appropriate interventions if required.
Retention and Maintenance:
After orthodontic appliance, the use of retainers is important to achieve desired results and avoid relapse. Regular interaction and consultation with orthodontist in order to ascertain that the teeth are aligned together in the right order.
Lifelong Oral Care:
Consistent good oral hygiene, a balanced diet, and regular dental visits are very important factors for long-term oral health. Patients who have took orthodontic treatment should be very consistent in their oral care routines to avoid dental problems in order to achieve the desired results of their treatment
Happy Blogging and Reading 💥💥💥💥
Video from boundless dentistry YouTuber