Hi everyone, how you doing?. By the view of the communities, everything seems rocking good on platform. Without much ado, would like to make post on Mandibular Fractures a very interesting topic in surgical dentistry.
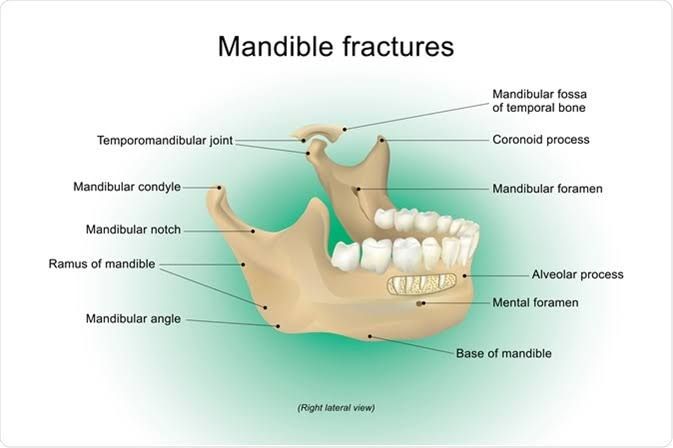
First of, mandibular fracture simply means a break or discontinuity in the mandibular bone giving rise to bony fragments and is sometimes called fracture of the jaw. In like 60% of cases the break occurs in two different places. Mandibular fractures may result in a decreased ability to fully open the mouth thereby restricting the jaw opening.
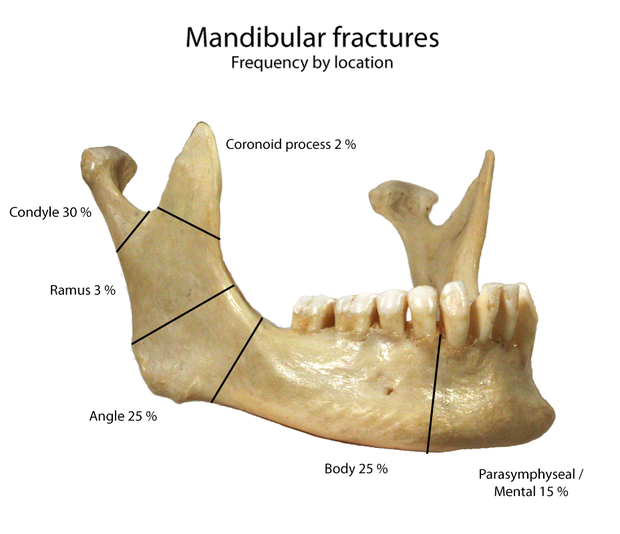
"Mandibular fractures are typically the result of trauma. This can include a fall onto the chin or a hit from the side. Rarely they may be due to osteonecrosis or tumors in the bone. The most common area of fracture is at the condyle (36%), body (21%), angle (20%) and symphysis (14%). Rarely the fracture may occur at the ramus (3%) or coronoid process (2%). While a diagnosis can occasionally be made with plain X-ray, modern CT scans are more accurate."Source
In most cases the teeth will not feel properly aligned and arranged or there may be excessive bleeding of the gums. Mandibular fractures occur usually and mostly among males in their 30s.
Immediate surgery is not a conventional thing in most facial fractures cases sometimes to avoid details for diagnosis and also for the swellings and edemas to subside following fracture.
Occasionally some patients may choose to go home and follow up for surgery in the next few days or a week. A number of surgical procedures may be employed during the treatment including intermaxillary fixation otherwise known as maxillomandibular fixation and open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF). People are often put on antibiotics to avoid bacterial actions with the fractures such as penicillin, ampicillin among for a brief time though this practice lacks solid and reliable evidence based on physician opinions.
Signs and Symptoms of Mandibular Fractures
There are lots of signs and symptoms associated with mandibular fractures which include the following; both intraorally and extraorally which includes;
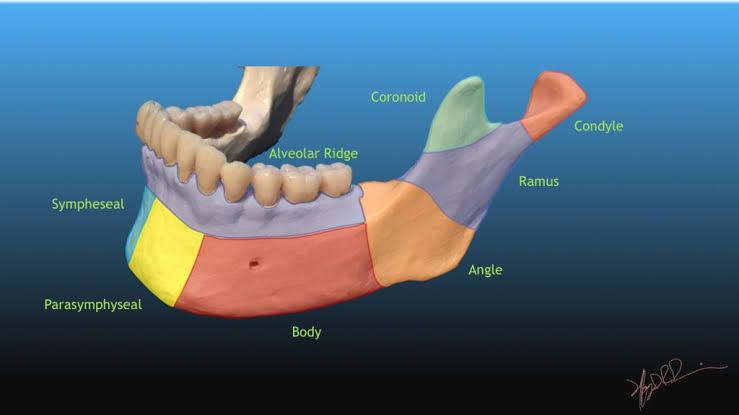
Tenderness, misaligned teeth and disocclusion, loosened teeth, partial numbness, sublingual haemorrhage and ecchymosis, fractured condyles, fractured ramus and angle or any other fractured parts of the Mandible,open bite, swellings among others.
Now let's explain some of these signs and symptoms one after the other;
The two most common symptoms described are (tenderness)pain and the feeling that teeth no longer correctly alignment and function (traumatic malocclusion, or disocclusion).
The teeth become sensitive to pressure (proprioception). People will also be very sensitive to touching the area of the jaw that is fractured, or even in condylar fracture the area becomes very tender and sensitive just by side of the ear's tragus.
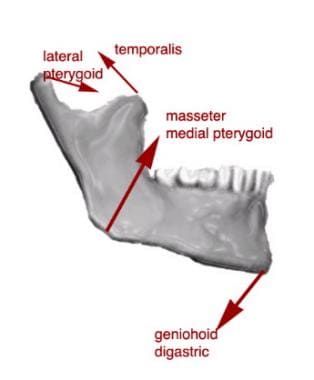
Teeth may become loosened (teeth on either side of the fracture will feel loose due to mobility caused by fracture), numbness also (because the inferior alveolar nerve branch of the trigeminal nerve runs along the jaw and can be compressed by a fracture) and trismus (difficulty opening the mouth) due to muscular pull and swellings.
Extraorally, there are signs of swelling, bruising and deformity are all obvious. Due to proximity of the condyles to the ear, the trauma can cause fracture of the bone on the anterior aspect of the external auditory meatus which can lead to bruise, bleeding or pain that can sometimes be felt in the ear canal. Mouth opening can be drastically reduced (less than 3 cm). There can be numbness or altered sensation (anesthesia/paraesthesia in the chin and lower lip due to impingement on the the mental nerve or its distribution.
Inside the mouth, if the fracture occurs in the alveolus of the mandible that holds the teeth , some missing or toothless areas may be noticed (often mistaken for a lost tooth) and excessive haemorrhage from the gingiva tissues is another common Symptom. There can be an open bite where the lower teeth and the the upper teeth no longer meet. In the case of a unilateral condylar trauma the posterior teeth on the affected side will occlude prematurely and the open bite will get increasingly apparent and more pronounced at the unaffected side
Sometimes bruising will develop in the floor of the mouth (sublingual haemorrhage or ecchymosis) and the fracture can be moved by moving either side of the fracture segment up and down. For fractures that occur in the non-alveolar parts of the mandible which holds the teeth such as the condyle, ramus, and sometimes the angle an accompanying open bite is a significant clinical feature and sign since little as other than pain and swelling, may be obvious and observable.
To avoid lengthy and much voluminous paragraphs, this post would be concluded at the this juncture. Thanks for the usual support and attention given the blogs and write-ups all of it are highly appreciated and welcomed.
Happy blogging and reading
Video from Dr Teeth YouTuber
Telegram and Whatsapp