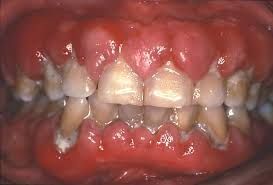
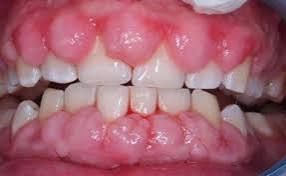
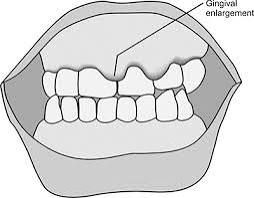
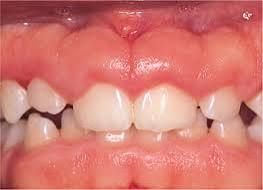
Gum disease generally comes from poor oral environment maintenance and hygiene. However, other factors can be of etiological reasons:
1- Plaque Accumulation and Buildup
Irregular or lack of tooth brushing and flossing properly allows plaque to pile up amounting to gum inflammation.
2- Smoking
Tobacco consumption whether smoking or even smokeless ones (chewing) use is a major risk factor for gum disease and most especially oral cancer, as it reduces blood flow which prevents inflammatory response and impedes healing.
3- Hormonal Changes
Due to changes in the normal hormonal balance during some certain natural conditions most especially in females such as pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can bring about sensitivity of gums and make them more open and susceptible to disease.
4- Medications
Soome antidepressants and some heart medications, can have impact on gum health due to their inhibition or reduction of salivary production. Some anticonvulsants too such as Phenytoin can also cause gingival enlargements.
5- Poor Nutrition
Lack of some essential vitamins and minerals, most especially vitamin C, can compromise the immune system and body protection against foreign microbes and increase the gum susceptibility to infections. Deficient or lack of enough of enough vitamin C is also associated with scurvy.
How To Maintain Healthy Gums
Getting and having a healthy gums is very easy if a consistent routine is sustained and adopted. Here are some oral maintenance practices that can be incorporate into daily oral care routine and practice:
1- Regular Brushing of Teeth for atleast twice on daily basis
Using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to brush and scrub teeth for about two minutes, twice a day. The angle of contact of the brush should be at a 45-degree angle to the gums to effectively and professionally remove the plaque from the gumline.
Tip: A well packaged Electric toothbrushes can be more useful at plaque removal and reducing the occurrence of gingivitis than manually used brushes especially in people that do not know how to incline the brush for effective contact during tooth brushing.
2- Floss Daily
Flossing is as useful as tooth brushing for removing food debris and plaque buildup between teeth and also along the gumline, especially in those areas where a toothbrush can’t reach. Regular flossing can reduce high risk of gum disease or infections as a result of plaque building which are prevented by dental floss application.
3- Use An Antibacterial Mouthwash
Mouth rinsing and washing with an antimicrobial mouthwash generally assists a lot in reducing the bacteria that brings about plaque and inflammatory response of gums. A mouthwash that’s specifically made for gum health can be gotten from any approved pharmaceutical company.
4- Balanced Diet Consumption
A diet which is highly composed of vitamins and minerals, majorly vitamin C, can strengthen the immune system and stimulates tissue regeneration. A diet can Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, foods containing proteins, fat and oil, grains that can support gum health.
5- Stay Hydrated
Consumption of plenty of water throughout the day assist a lot in washing away food particles and also stimulates saliva production and maintains it, which in turn serves as a natural defense and firewall against bacteria or plaque buildup.
6- Regular Dental Checkups and Cleanings
Visiting a dentist or periodontist at every six months for normal routine checkups and professional cleanings (scaling and root planning) can assist a lot and detect any gum disease that may be present in your mouth as early as possible especially when the tartar are removed off with scalers.
Although regular home care is the major key to gum wellness, there are some additional managements and strategies for those that are suffering from gum disease.
1- Scaling And Root Planing
A gingivitis or periodontitis patients, can easily undergo scaling and root planing. This deep-cleaning clinical work can effectively removes plaque and calculus from supragingival and subgingival region of the teeth followed by smoothing the tooth roots to avoid further bacterial accumulation.
2- Antibiotic Therapy
A dentist may prescribe antibiotics to aid in reducing infection and inflammation of gums in some clinical cases. Antibiotic gels, mouth rinses, or oral medications can be employed in some debilitating cases.
3- Surgical Options
"In advanced stages of gum disease, surgery may be necessary. Procedures such as flap surgery (to remove deep pockets of bacteria) or bone grafts (to restore lost bone) can help save teeth and restore gum health."Source
That's all as regards this post atleast for now. More would be discussed further in the subsequent posts as it is and happy blogging.
Happy Blogging and Reading 💥💥💥💥
Video from 5 mins dentistry YouTuber