"Brush your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste. Clean between teeth regularly, aiming for once a day. Use dental floss or a special brush or wooden or plastic pick recommended by a dental professional. Or try a floss holder, floss threader, or water flosser."Source
Dental Health
Dental health refers to the overall well-being of the teeth, gums, and entire oral cavity. It encompasses not only the absence of disease or infirmity but also the presence of a healthy, functional, and aesthetically pleasing smile.
Components of Dental Health
- Healthy Teeth: Free from decay, cracks, or other damage.
- Healthy Gums: Pink, firm, and free from inflammation or infection.
- Adequate Saliva: Sufficient saliva production to facilitate digestion, remineralization, and oral cleansing.
- Proper Bite: A harmonious relationship between the upper and lower teeth.
- Healthy Oral Tissues: Includes the lips, cheeks.
Mouth and body:
The mouth is a gateway to the body, and bacteria and inflammation in the oral cavity can have far-reaching conseconsequences Diseases Linked to Dental Health
- Diabetes: Research suggests that people with diabetes are more prone to gum disease, and conversely, gum disease can exacerbate diabetes.
- Heart Disease: Studies have shown that bacteria in the mouth can enter the bloodstream and contribute to the development of heart disease.
- Respiratory Infections: Bacteria in the mouth can be aspirated into the lungs, leading to respiratory infections such as pneumonia.
- Osteoporosis: Research has found a link between gum disease and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
- Cancer: Some studies suggest a link between gum disease and an increased risk of certain types of cancer, such as pancreatic cancer.
Some Common Dental issues;
Tooth Decay and Cavities - Causes: Poor oral hygiene, sugary diet, inadequate saliva flow.
- Symptoms: Tooth sensitivity, pain, visible holes or discoloration.
- Treatment: Fillings, inlays, onlays, crowns, or extractions.
Gum Disease (Gingivitis and Periodontitis)
- Causes: Poor oral hygiene, smoking, genetics, hormonal changes.
- Symptoms: Bleeding gums, swelling, redness, bad breath, loose teeth.
- Treatment: Professional cleaning, antibiotics, surgery, or extraction.
Tooth Loss
- Causes: Gum disease, tooth decay, injury, or genetic conditions.
- Symptoms: Missing teeth, changes in bite or facial structure.
- Treatment: Dental implants, bridges, dentures, or crowns.
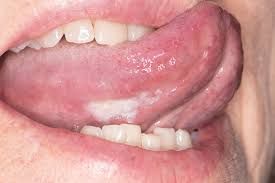
Oral Cancer
- Causes: Tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, HPV infection.
- Symptoms: Unusual bleeding, swelling, or sores in the mouth.
- Treatment: Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or combination.
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
- Causes: Medications, radiation therapy, hormonal changes, or breathing through the mouth.
- Symptoms: Dryness, stickiness, or burning sensation in the mouth.
- Treatment: Saliva substitutes, oral rinses, or medication adjustments.
Tooth Sensitivity
- Causes: Tooth decay, gum recession, cracked teeth, or aggressive brushing.
- Symptoms: Pain or discomfort when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods.
- Treatment: Desensitizing toothpaste, fluoride varnish, or dental restorations.
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
- Causes: Poor oral hygiene, gum disease, dry mouth, or systemic diseases.
- Symptoms: Unpleasant odor or taste in the mouth.
- Treatment: Good oral hygiene, tongue scraping, mouthwash, or professional cleaning.
Preventive measures and treatment options for maintaining good dental health:
Preventive Measures
- Regular Brushing and Flossing: Brush teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss once a day to remove plaque and food particles.
- Dental Check-Ups: Visit the dentist every 6 months for a routine cleaning and examination.
- Fluoride Therapy: Use fluoride toothpaste, mouthwash, or varnish to strengthen tooth enamel and prevent decay.
- Sealants: Apply dental sealants to molars and premolars to prevent decay.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet that is low in sugary and acidic foods and drinks.
- Avoid Tobacco and Smoking: Quit smoking and using tobacco products to reduce the risk of oral cancer and gum disease.
- Mouthguards: Wear a mouthguard during sports and activities to prevent tooth injury.
Treatment Options
- Fillings: Restore teeth with fillings to repair decay or damage.
- Crowns: Cover teeth with crowns to restore shape, size, and function.
- Root Canals: Perform root canals to remove infected pulp and save the tooth.
- Extractions: Remove teeth that are severely damaged or decayed.
- Dental Implants: Replace missing teeth with dental implants to restore function and aesthetics.
- Gum Disease Treatment: Treat gum disease with deep cleaning, antibiotics, or surgery.
- Oral Cancer Treatment: Treat oral cancer with surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
Additional Treatment Options
- Teeth Whitening: Whiten teeth to improve aesthetics.
- Veneers: Apply veneers to improve tooth shape, size, and color.
- Orthodontic Treatment: Straighten teeth with orthodontic treatment to improve function and aesthetics.
- Dental Bridges: Replace missing teeth with dental bridges to restore function and aesthetic
Important Dental Tips
1- Avoid wetting tooth paste even when you use flouride toothpaste, desist from pouring water on it.
I know it's to make it foam ,you can achieve that by rinsing your mouth before washing.
2- Desist from using your mouth as openers.😏 it's quite bad.
This habit can disrupt the anterior occlusion of your incisors in long term.
3- Some people will pick their teeth even when they drink water, sis and bro use Dental floss for interdental cleaning of your mouth.
4- Using toothpicks will damage your gums and possibly lacerate.( it's gradually)
5- Soft brushes for children and medium for adults. Though, at times hard brush could be recommended for smokers in order to removed discolorations from the enamel surface.
That's all as regards the post and happy Blogging
Happy Blogging and Reading 💥💥💥💥
Video from teeth talk girl YouTuber