VITAL PULP THERAPY-PULPOTOMY
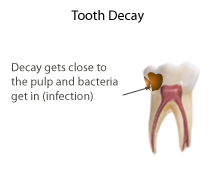
Pulpotomy is dental management of carious or exposed portion vital pulp which requires removal so as to avoid spread to other areas and thereby eventually preserving the radicular vitality and permit completion of apical root development (apexogenesis) with dentinal deposition.
Pulpotomy is a treatment of choice following traumatic occurrence in which the pulp has been exposed to the mouth for more than twenty four hours. It can also be a treatment of choice in superficial carious attack that has not reach the radicular pulp of the tooth.
Pulpotomy procedures is as follows;
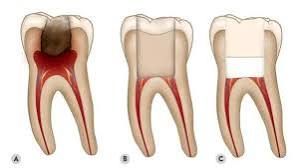
1- Application of local anaesthesia and rubber dam, pulp tissue is excised with a diamond bur running at high speed under constant water sprinkling.
The water cooling is done to maintain least injury to the underlying pulp and is preferred to hand excavation or the use of slow-speed steel burs.
2- Microbial attack of an exposed vital pulp is usually superficial and usually requires only 2-3 mm of pulp tissue should be removed as done in Cvek pulpotomy.
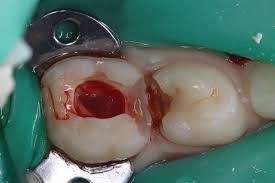
3- Excessive bleeding from the remnants of extirpated pulp which is unstoppable with light wet cotton wool pressure or if no bleeding is observed denotes that further removal of the pulp is expected so as to reach healthy portion of the coronal pulp
4- Removal of tissue may occasionally extend more deeply into the tooth as in full coronal pulpotomy in bid to maintain and preserve the apical portion of the pulp and protect apical closure.
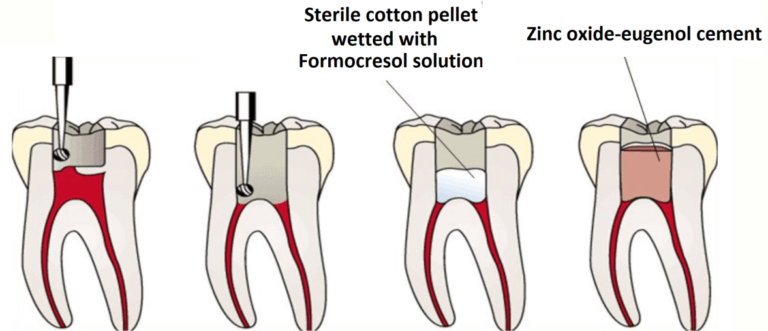
5- Rinsing of the wound with sterile saline or sodium hypochlorite with concentration of (1-2%)and removal of any shredded tissue. Formocresol can also be used to condense the remaining pulpal tissues.
6- Apply a calcium hydroxide dressing to the pulp to destroy any remaining microorganisms and to promote calcific repair.
7- Overlay the calcium hydroxide dressing with a hard cement to prevent its downward penetration into the pulp by masticatory forces and a final coronal seal restoration which will seal off the preparation against re-colonization by harmful microorganisms.
REVIEW of PULPOTOMY PROCEDURES AFTER TREATMENT
PULPOTOMY can be reviewed after the following durations which be as follows depending on the presented cases and clinician expertise.
1- After a month,
2- 3 months,
3- 6 monthly intervals for up to 4 years in order to evaluate pulp vitality and patient compliance with the treatment management.
4- Constant radiographic review on each review visit should be done to check out for bridge formation, continuous root growth and rule out necrosis and radicular pathosis or infection spreading.
However, in the course of review if a vitality is observed to have lost, non-vital pulp therapy should be undertaken right away either with the presence of calcific bridge or not.
Based on reports and researches, success rates for partial (Cvek) pulpotomies are reported to be at 97% and that of coronal pulpotomy to be as 75% as it is.
Elective pulpectomy and root canal treatment of a vital pulp may be considered later on only if the root canal is needed for restorative purposes and treatment.
In a nutshell, the following underlisted points should be noted by every clinician as regards pulpotomy procedures
1- Better prognosis is achieved with pulpotomy than pulp capping for small exposures exposed for more than 24 hours either through tooth decay or fracture.
2- Pulpotomy is not recommended if there are signs and symptoms of radicular infection or pathosis.
That's all as regards the write-up on Pulpotomy procedures in paediatric patients. Thanks for the usual support and follow-up with the brief lectures and descriptions. More on pulp therapy in the subsequent posts to be discussed.
Happy Blogging and Reading
Video from Taughtwell YouTuber
Telegram and Whatsapp