Today, we're talking about an urgent issue that's silently threatening global health: antimicrobial resistance, or AMR. Imagine a world where minor infections or routine surgeries become life-threatening because the medications we rely on no longer work. This is the reality we could face if AMR continues to spread.
WHAT ARE ANTIMICROBIALS?
Antimicrobials are agents that eliminate or ward off the effects of harmful microorganisms that can disrupt the health of the body system. These include bacteria, fungi, viruses among others. Unlike antibiotics, which specifically target bacteria, antimicrobials encompass a broader range of drugs designed to fight different types of pathogens.
Here’s a breakdown of common types of antimicrobials:
- Antibiotics:Target and eliminate bacteria (e.g., penicillin, and amoxicillin for bacterial infections).
- Antivirals :Target viruses by inhibiting their replication (e.g., acyclovir for herpes viruses).
- Antifungals: Treat fungal infections by destroying or stopping the growth of fungi (e.g., fluconazole for yeast infections).
- Antiparasitics : Combat parasitic infections caused by organisms like protozoa and helminths (e.g., ivermectin for certain parasitic infections).
Antimicrobials are critical for treating infectious diseases and are widely used in healthcare, agriculture, and even household products. However, just like with antibiotics, the misuse of any antimicrobial can lead to antimicrobial resistance (AMR), making infections increasingly difficult to treat across all types of microorganisms.
WHAT IS RESISTANCE?
Resistance is the act of opposing flow, influence, movement, or change. For example, psychological resistance refers to a reluctance to accept change or embrace new ideas.
CONCEPTS OF ANTIMICROBIAL RESISTANCE (AMR)
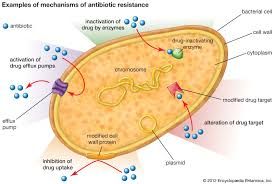
AMR is a phenomenon by microbes that causes disease and illnesses outdo the effect of therapeutic agents which are put in place to eliminate or deactivate them.
This means that drugs, like antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals, lose their effectiveness. It's a natural evolutionary process, but human activity overuse, misuse, and lack of new drug development accelerates it drastically.
Let’s break this down. Think about antibiotics, which transformed medicine in the 20th century. They allowed for safer surgeries, cancer treatments, and saved countless lives. But now, with every unnecessary prescription or incomplete treatment, we give bacteria a chance to adapt. Resistant bacteria spread rapidly, reducing our ability to treat common infections. In fact, AMR is estimated to contribute to over a million deaths annually.
When treatments fail, hospital stays become longer, more complex therapies are required, and costs skyrocket.
Happy Blogging and Reading 💥💥💥💥
Video from Osmosis YouTuber