Source
In general notion, people are known to have some prior understanding that smoking is disastrous to both the lungs and heart, while a very small fraction of the society actually know that it can also deliver mind blowing disaster to the oral health. The first entrance for smoking into the body system is the oral cavity and as such it is not spared to have its own quota from the effect that can be gotten from the negative impact of smoking.
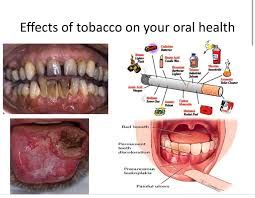
Most especially, fom stained teeth and halitosis breath to more worsening conditions like gum disease and oral cancer. Smoking can wreak havoc on oral cavity and its entire tissues.
In this post, we’ll dive into negative effects smoking on oral health, beginning from aesthetic issues to life-threatening diseases.
Having solid understanding these risks and it's devastating outcomes can deter a potential smoker or a smoking person to make informed decisions on quitting and taking good care of the oral health.
Smoking produces deleterious reactions on almost every structures of the mouth, which includes; teeth, gums, and the soft tissues that line the oral cavity. Here is brief analysis of how smoking impacts negatively different components of the oral health:
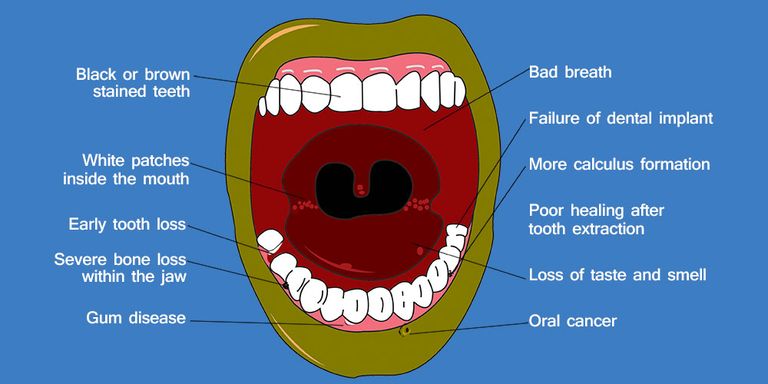
1- Stained Teeth And Discolored Tongue
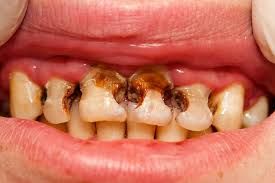
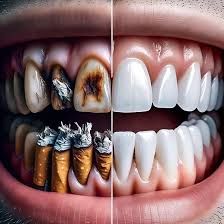
Stained teeth is an easily observed feature of a smoker. For instance, among the Tobacco constituent is tar and nicotine, which get absorbed to the enamel of your teeth and give them a yellow or brown colour. This discoloration with time can be extended to the tongue, making it to have brownish or blackish appearance.
2- Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Smokers in most cases were known to struggle with chronic bad breath or halitosis, especially for long term smokers. Smoking dehydrates the mouth, reduces saliva production, and as such gives an enabling environment for bacteria to thrive. This bacterial buildup and accumulation can bring unpleasant odors that are not easy to eliminate or even mask out with mouthwash or any form of mints.
3- Increase Susceptibility to Gum Disease (Gingivitis or Periodontitis)
"Smoking is one of the leading risk factors for gum disease, also known as periodontitis. It impairs blood flow to the gums, making it harder for your body to fight infections. As a result, smokers are more prone to developing infections in the gums, leading to inflammation, receding gums, and even tooth loss if left untreated."Source
Signs of gum disease include:
Bleeding gums on brushing or flossing, swollen or tender gums, persistent bad breath, loose teeth or gaps forming between teeth.
4- Slow Healing After Dental Procedures
Smoking impacts negatively the body’s ability to heal itself, especially in the mouth. After dental procedures that has to do with incisions such as tooth extractions or gum disease, smoking usually experience delayed healing and are prone to high risk of infection. This can also bring about an increase or possibly shoot up the chances of complications such as dry socket, which is a painful condition that occur as a result of blood failing to clot in the tooth socket after dental extraction.
5- Black Hairy Tongue
Smoking is a common cause of black hairy tongue which is a benign but an awkward condition. The chemical component of tobacco can cause an overgrowth of the papillae on the tongue, providing a dark, hairy structure. Though it’s usually not life-threatening condition, a black hairy tongue is a clinical sign of poor oral care and can be aesthetically disappointing.
6- Weakened Immune System
Smoking disorganises immune system . This makes smokers more prone to oral infections such as thrush (a fungal infection) and even cold sores. This makes opportunistic infections occur on regularly especially the ones caused by candida albicans . The body’s reduced capacity to go against these infections means they may occur more frequently and expend longer moment to heal.
7- Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is possibly the most disastrous effect of smoking on oral health. Based on some researches, smokers are like up to six times more likely to develop oral cancers than non-smokers, which can affect some parts of the oral cavity, including the gums. Symptoms of oral cancers:
i- Persistent sores or ulcers in the mouth that don’t disappear or heal over long periods
ii- Lumps or thickening in the cheek
iii- White or red patches on some structures of the oral cavity which includes the gums, tongue, or lining of the mouth( Leukoplakia or Erythroplakia) though not limited to them
iv- Difficulty in mastication, swallowing, or moving the jaw due to strained muscles
In a nutshell, early diagnosis is the key to curb oral cancer successfully, and such periodic regular dental check-ups and self-examinations are very essential and important for smokers.
Gum disease together with bone loss and tooth decay can eventually result tooth loss for smokers over longer periods. Smoking is known generally to weakens the supporting structures of the teeth especially the gums and jawbone.
Chronic or long term smokers are more prone losing teeth prematurely. In fact, they are twice likely to experience tooth loss when compared to non-smokers.
That's all as regards the write-up on smoking effects on the oral cavity, more would be discussed in the concluding subsequent post. Thanks and happy reading.
Happy Blogging and Reading 💥💥💥💥
Video from ehowhealth YouTuber