An eating disorder is a psychological issues that has to do certain abnormal patterns which can adversely influence a person's physical or mental health.The observed behaviours can be eating either too much or even too little.
Types of eating disorders:
1- Anorexia Nervosa
2- Bulimia Nervosa
3- Binge Eating Disorder (BED)
4- Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID)
Anorexia Nervosa:
This is a serious eating disorder characterized by a distorted body image and an intense fear of gaining weight, leading to restrictive eating habits and significant weight loss.
Characteristics:
- Restrictive eating patterns
- Significant weight loss
- Fear of gaining weight
- Distorted body image
- Denial of the seriousness of their condition
- Over fasting owing to fears
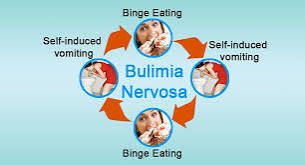
Bulimia Nervosa
: is a serious eating disorder characterized by recurring episodes of binge eating followed by purging or compensatory behaviors to rid the body of consumed calories.
Characteristics:
- Recurring episodes of binge eating
- Purging behaviors (vomiting, laxatives, diuretics)
- Compensatory behaviors (excessive exercise, fasting)
- Fear of gaining weight
- Self-criticism and guilt after bingeing
- Secretive behavior related to eating and purging.
Binge Eating Disorder (BED):
It is a type of eating disorder characterized by recurring episodes of binge eating, which can lead to feelings of guilt, shame, and weight-related problems.
Characteristics:
- Recurring episodes of binge eating
- Eating large amounts of food in a short time
- Feeling a lack of control
- Eating rapidly or secretly
- Being self critical
- No compensatory behaviors (as compared to Bulimia Nervosa)
Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder (ARFID)
- Lack of interest in eating
- Avoiding foods due to sensory concerns
- Being underfed due to nutritional content concerns or fears
- Significant weight loss or nutritional deficiencies
Causes of Eating Disorders
- Genetic predisposition: Family history and genetic factors can contribute.
- Sociocultural pressures: Unrealistic beauty standards and societal expectations.
- Emotional and psychological factors: Low self-esteem, anxiety, depression, and trauma.
- Environmental factors: Family dynamics, peer influence, and media exposure.
- Biological factors: Hormonal imbalances, nutritional deficiencies, and medical conditions.
Treatment Options for Eating Disorders
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive- behavioral therapy (CBT), family-based therapy (FBT), and individual therapy.
- Nutrition counseling: Working with a registered dietitian to develop a healthy meal plan.
- Use of relevant medications such as antidepressants, anti-anxiety, tranquilizers, mood stabilizers and so on.
- Hospitalization: In patient treatment for severe cases, providing 24/7 care and support.
- Support groups: Group therapy and online forums for individuals and families.
Awareness and Advocacy
- Educate others about eating disorders
- Reduce stigma and promote understanding
- Support individuals and families affected
Be an Advocate
Healthy Eating Habits
- Take complete classes of food in the appropriate proportions daily such as fruits, vegetables, milk, fat and oil, water among others
- Drink clean and plenty of water throughout the day.
- Watch portion sizes: Eat until satisfied, not stuffed.
- Limit processed foods: Choose whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
- Eat regularly: Three main meals and one or two snacks per day.
- Avoid excessive sugar and salt: Limit added sugars and sodium.
- Use fresh ingredients for cooking
- Mindful eating: Pay attention to hunger and fullness cues, savor food.
That's all as regards brief notes on common eating disorders and happy reading
Happy Blogging and Reading 💥💥💥💥
Video from Asapscience YouTuber