Dnamic fees are a mechanism used by some DeFi protocols to adjust transaction fees based on current market conditions. This approach helps maintain the protocol's efficiency and fairness for its users. Here's a general overview of how dynamic fees might work and their purpose:
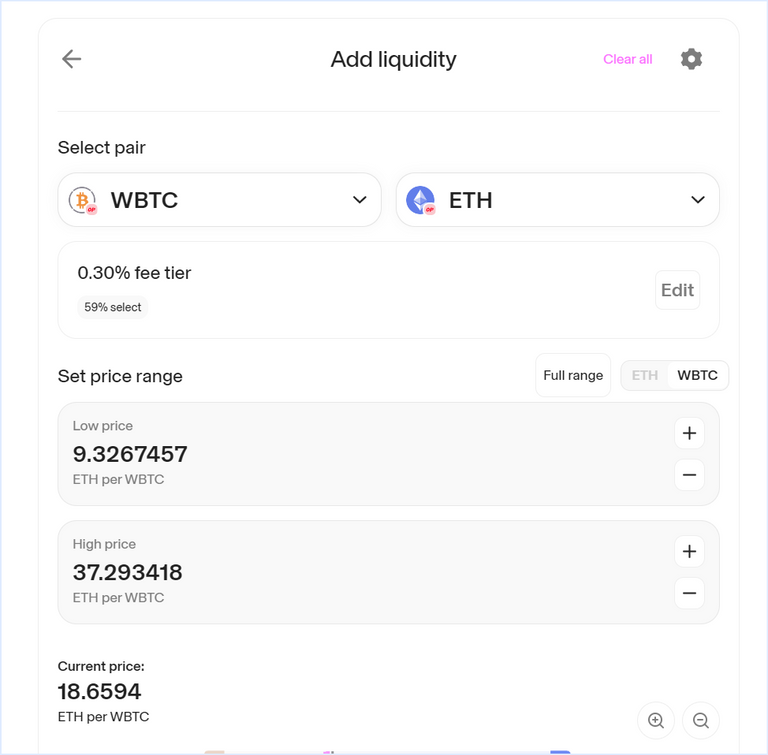 Uniswap
Uniswap
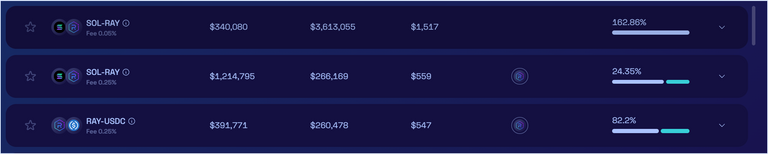 Raydium
Raydium
Base Fee
Many DeFi protocols implement a base fee, which is the minimum fee charged for transactions. This fee can fluctuate based on network congestion, demand for transaction processing, or other factors defined by the protocol.
Dynamic Fee Adjustment
On top of the base fee, protocols can dynamically adjust fees to respond to changes in liquidity or trading volumes. During times of high demand or volatility, fees might increase to manage congestion and incentivize liquidity providers. Conversely, in quieter periods, fees might decrease to encourage more trading activity.
Purpose of Dynamic Fees
- Liquidity Optimization: Adjusting fees dynamically helps manage liquidity by incentivizing users to add to pools or trade at optimal times.
- Fair Pricing: Dynamic fees ensure that users pay a fair price for the services they consume, reflecting the current state of the market.
- Network Efficiency: By modulating demand through fee adjustments, the network can operate more efficiently, balancing the load and ensuring faster transaction processing.
Example of Dynamic Fee Implementation
A DeFi protocol might start with a base fee of 0.3% for swaps between tokens.
If the market becomes highly volatile, the protocol could increase the fee to 0.5% to manage the surge in demand and to better reward liquidity providers.
Conversely, during stable periods, the fee might drop to 0.2% to attract more trades.
Protocols like Uniswap (on Ethereum) and others on Solana or different blockchains might implement their versions of dynamic fees, tailored to their specific ecosystem's needs and challenges.