Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) refers to the maximum value that blockchain miners or validators can extract from transaction manipulation within a block. This manipulation can involve including, excluding, or reordering transactions to maximize profit, often at the expense of other network participants. MEV is a significant factor in decentralized finance (DeFi) and can impact the profitability of various strategies, as well as the overall security and decentralization of blockchain networks.
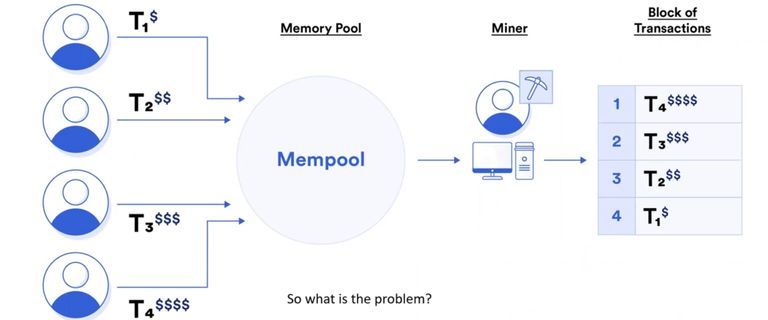
What is MEV and What is the problem?
Differences Between MEV on Ethereum and Solana
Ethereum
- Transaction Ordering: On Ethereum, MEV is often extracted through transaction reordering, where miners prioritize transactions that offer higher fees or potential arbitrage opportunities. This can lead to front-running, where miners or bots insert their transactions ahead of others to capture profits.
- Block Production: Ethereum's block production is periodic, meaning miners have discrete opportunities to reorder transactions within each block.
- MEV Tools: Ethereum has more sophisticated MEV extraction tools and techniques, such as Flashbots, which provide a private transaction pool to mitigate some negative externalities of MEV.
Solana
- Continuous Block Production: Solana uses continuous block production and state updates, which means that reading state updates quickly is crucial for capturing MEV opportunities. This continuous nature makes it harder to conduct out-of-protocol blockspace auctions.
- Optimistic Transactions: Solana allows for "optimistic" MEV transactions, where searchers can send transactions assuming a state update has occurred and revert if it hasn't. This reduces the dependency on read latency but can incentivize spam.
- Latency Sensitivity: Due to frequent state updates, latency is more critical on Solana. Searchers need to be colocated with the current leader and connected with a large amount of stake to optimize MEV extraction.
- Fee Distribution: Unlike Ethereum, Solana burns a portion of priority fees, necessitating out-of-protocol markets for blockspace.
Will MEV Disappear or Survive?
MEV is likely to persist in some form due to its inherent nature in blockchain networks. Several factors contribute to this:
- Inherent to Decentralization: MEV arises from the decentralized and permissionless nature of blockchain networks, where miners and validators have the freedom to order transactions as they see fit.
- Economic Incentives: The financial incentives for miners and validators to extract MEV are significant, making it a persistent feature of blockchain ecosystems.
- Mitigation Efforts: While there are ongoing efforts to mitigate MEV, such as fair sequencing services (FSS) and off-chain transaction batching, completely eliminating MEV is challenging. These strategies can reduce the impact of MEV but are unlikely to eradicate it entirely.
MEV is a fundamental aspect of blockchain networks that impacts their security, decentralization, and user experience. While the methods of MEV extraction and its implications differ between Ethereum and Solana, the concept itself is likely to endure due to the economic incentives and the decentralized nature of these ecosystems.