In the rapidly evolving world of decentralized finance (DeFi), bonding curves have emerged as a powerful mechanism, offering innovative solutions for token distribution, pricing, and liquidity.
This article delves into the concept of bonding curves, exploring their applications and potential impact on the future of decentralized economies.
The Essence of Bonding Curves
At its core, a bonding curve is a mathematical function that defines the relationship between a token's price and its supply. It acts as an automated market maker, allowing tokens to be minted or burned as they are bought and sold, with the price adjusting dynamically based on the total supply.
The most common implementation is the continuous token model, where the price increases as more tokens are minted and decreases as tokens are burned. This self-regulating economic system incentivizes early adoption while maintaining liquidity, creating a unique dynamic in the token ecosystem.
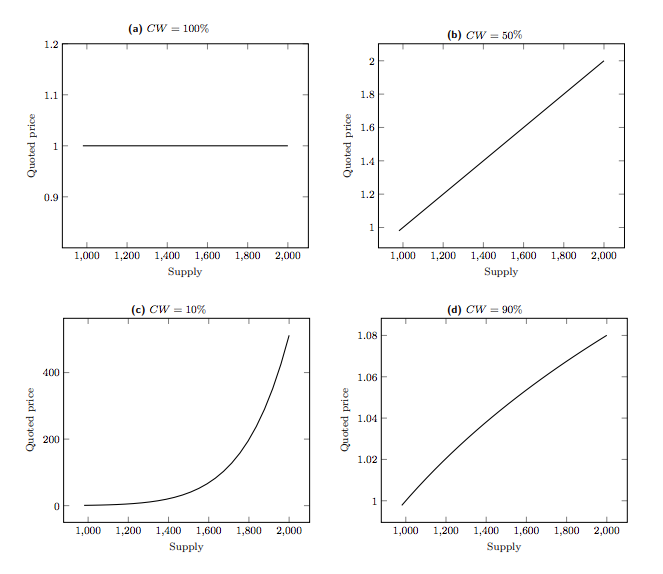
DeFI Bonding Curves, Source: Yos Riady
Mechanics and Functionality
The mechanics of a bonding curve revolve around three key components: token minting, price calculation, and token burning. When a user buys tokens, new ones are minted and added to the total supply. The price of each token is determined by its position on the curve, typically increasing as the supply grows. Conversely, when a user sells tokens, they are burned, reducing the total supply and decreasing the price.
This mechanism ensures constant liquidity in the system, as tokens can be bought or sold at any time. The continuous nature of the curve means that there's always a price at which tokens can be traded, eliminating the need for traditional market makers or order books.
Real-World Applications in DeFi
Bonding curves have found practical applications across various sectors of the DeFi ecosystem. In token launch platforms, they offer a fair and transparent method of distribution, allowing projects to avoid the pitfalls of traditional initial coin offerings (ICOs). The gradual price increase incentivizes early participation while preventing large investors from dominating the token supply.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) have also embraced bonding curves for managing the issuance and pricing of governance tokens. This approach allows for a more dynamic and responsive governance model, where the value of voting power can adjust based on the organization's needs and growth.
In the realm of prediction markets, bonding curves facilitate the trading of outcome tokens. As more participants bet on a particular outcome, the price of that outcome's token increases, creating a self-reinforcing mechanism that can lead to more accurate predictions.
Perhaps one of the most intriguing applications is in continuous funding models. Unlike traditional one-time token sales, organizations can use bonding curves to raise funds on an ongoing basis. This model allows projects to align their funding with their growth and development, potentially creating more sustainable and resilient organizations.
Advantages and Challenges
The use of bonding curves brings several significant advantages to the DeFi ecosystem. The continuous liquidity they provide eliminates many of the issues associated with low-liquidity tokens, such as high slippage and difficulty in exiting positions. The transparent and algorithmic nature of the pricing mechanism can lead to fairer token distribution, reducing the impact of market manipulation.
Moreover, the incentivized early adoption model encourages community building from the outset. Early participants can benefit from lower prices, creating a natural growth mechanism for the project. This programmable economics allows for the creation of customized models tailored to specific project needs, opening up new possibilities for token design and distribution.
However, these benefits come with their own set of challenges. The complexity of the mathematical models underpinning bonding curves can be a significant barrier to understanding for average users. This complexity not only makes it difficult for potential participants to assess the risks and benefits accurately but also creates challenges in explaining the model to regulators and traditional finance stakeholders.
The potential for price volatility is another concern. Depending on the specific curve design, prices can change rapidly, leading to potential instability in the token's value. This volatility can be particularly problematic for projects aiming to use their tokens as a stable medium of exchange or store of value.
The Road Ahead
As the DeFi space continues to evolve, we can expect to see further innovations in bonding curve design. Research is already underway on dynamic curves that can adjust algorithmically to market conditions, potentially creating more stable and resilient token economies. There's also growing interest in multi-asset curves, which could allow for more complex interactions between different tokens within a single ecosystem.
The integration of bonding curves with traditional finance is another exciting frontier. As DeFi grows and matures, these models may be adapted for use in traditional financial instruments, potentially revolutionizing how we think about asset issuance and trading.
Bonding curves represent a significant innovation in the DeFi space, offering a novel approach to token economics and liquidity provision. While they present certain challenges, their potential to create more efficient and fair token ecosystems is undeniable. As the technology matures and new use cases emerge, bonding curves are likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of decentralized finance.
For investors and project creators alike, understanding bonding curves is crucial to navigating the evolving landscape of DeFi. As with any emerging technology, it's essential to approach bonding curves with both enthusiasm and caution, recognizing their potential while being mindful of the risks involved. The future of bonding curves in DeFi is bright, but it will require continued innovation, education, and careful implementation to fully realize their transformative potential.