Diabetes mellitus
Most common endocrine/metabolic disorder of childhood. It is due to a deficiency of insulin and abnormal metabolism of carbohydrate, protein, and fat
Its divided into two parts namely;
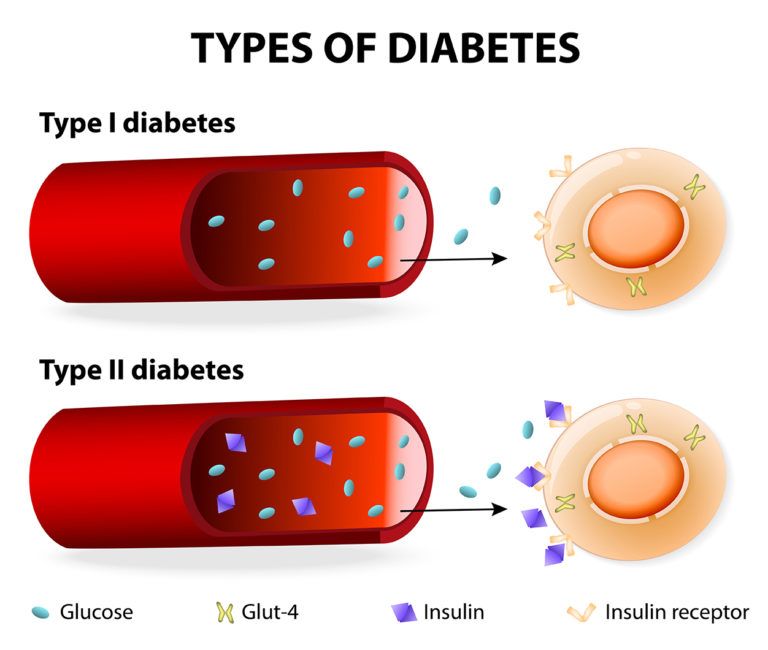
1- Type 1 diabetes can occur due to abnormally directed destruction of the insulin-producing β cells of the pancreas by the body immune system when it appears as a foreign body or harmful segment of the body. It can be of “viral origin or toxic insults” as regards its etiology. It is usually noted in paediatric patients.
Sometimes medication toxicity can also be the cause of beta cells destruction.
The issue in this case is absence of endogenous insulin that would store the glucose constituent in the blood into the body tissues which includes liver organ among other cells in the body.
2- Type 2 diabetes is a tissue impaired disease of tissues that stored insulin in the body cells.
Its main clinical manifestations include; polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia and weight loss due to hormonal imbalance.
Diabetes mellitus
Diagnosis depends on the demonstration of hyperglycaemia in association with glucosuria.
The aims of treatment are to control the symptoms, prevent acute metabolic crises of hypo-and hyperglycaemia
Administration of a insulin medication for longer duration either once two times daily and augmented with short working duration insulin at meals
One of the major hazards of insulin treatment is the development of hypoglycaemia due to chronic use of insulin medication.
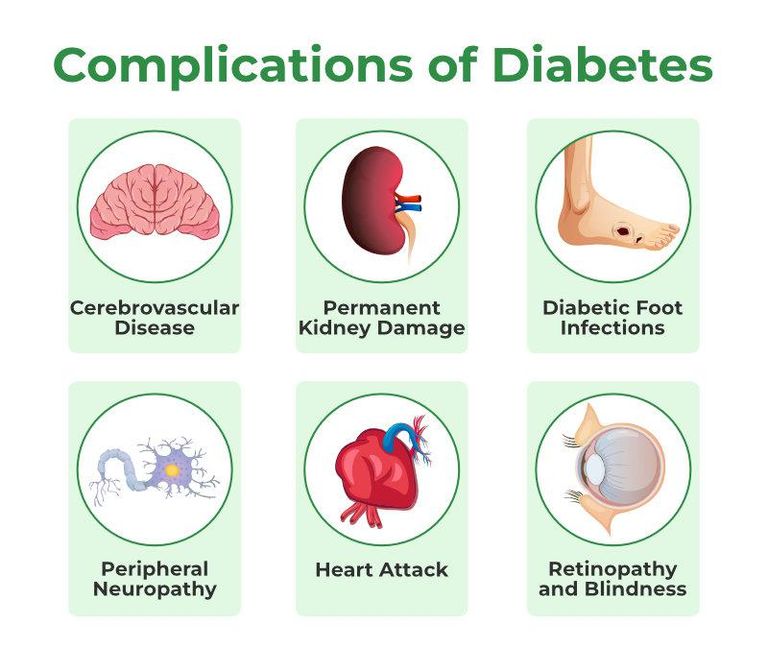
Patients with uncontrolled DM are at increased risk of developing ;
1- Periodontal diseases
2- Dry mouth
3- Tooth decay
4- Oral candidiasis
5- Burning mouth syndrome (BMS)
6- Taste disorders
7- Delayed wound healing
8- Increased susceptibility to infection
9- Impaired tooth eruption among others.
Dental Management of Children with Diabetes Mellitus
First of all, before any treatment should be done, blood sugar level should be checked using the finger- stick glucometer
i- For a short (less than 1 hour) procedure, and the glucose level is about 100 mg/dl, treatment can proceed without intervention having the patient already taken his/her medication with a normal meal
ii- If the procedure is expected to last several hours and/or the pretreatment test result is less in quantity of 100 mg/dl, the patient should be administered some amount of oral carbohydrates or glucose additives to help increase the blood glucose constituent
iii- Last but not least,Prophylactic antibiotic therapy is recommended prior to surgical procedures
Diabetic mellitus is one of the most encountered medical conditions in dental practice and as such a dentist is required to have good knowledge and management of this condition especially among the old age patients, though sometimes paediatric patients can also be suffering from it in case of type 1 diabetes mellitus.
That's all as regards diabetes mellitus in brevity with reference to paediatric patients, more would be revealed on it in the subsequent posts and write-ups.
Thanks for the usual support and follow-up up to the concluding part of the paragraphs.
Happy Blogging and Reading 💥💥💥
Video from Mental Dental YouTuber

Telegram and Whatsapp