The life-sustaining liquid that circulates through the body's capillaries, veins, and arteries is called blood. To the bodily tissues, blood transports the following:nourishment, mineral salts, supplements, hormonal agents, heat, and oxygenation. The following are transported by blood out of the body tissues: The carbon dioxide and waste.
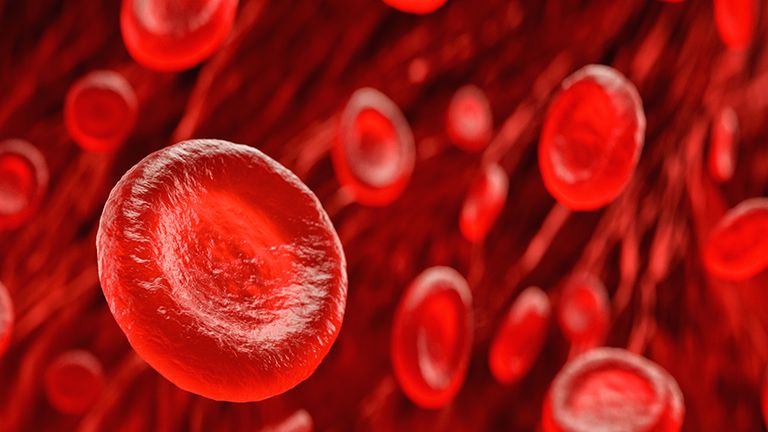
Among the several components of human blood are plasma. The liquid portion of blood is this. The plasma has the subsequent blood cells suspended in it: Chrythrocytes are the red blood cells. They transport oxygen through the lungs throughout the body. neutrophils, or white blood cells. These support immunity and the body's defense against illnesses. platelets, or thrombocytes. They aid in reducing bleeding.
In the tissues of the bone marrow, blood cells are produced. What's soft and spongy in the middle of the bones is called bone marrow. The body uses it to create around 95% of its blood cells. Spinal bones, pelvic bones, and breastbones contain the majority of the bone marrow in a mature individual body.
Our bodies also have various organs and systems that aid in blood cell regulation. The liver, spleen, and lymph nodes all play a role in controlling the synthesis, breakdown, and differentiation (the development of a particular function) of cells. Stem cells are the precursors of blood cells that develop in the bone marrow. The precursor to all blood cells is a stem cell. A number of unique cells develop as the roots cell becomes older. These consist of platelets, white blood cells, as well as red blood cells. Blasts are another term for immature blood cells. Certain blasts remain in the marrow to develop. Others go to different areas of the human body to mature into fully functional red blood cells.
Oxygen is transported through the lungs into the body's tissues by red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes. Furthermore, to transport carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs as a waste product. As oxygen is carried across the lungs to every area of the body by red blood cells, hemoglobin is a crucial protein. Fighting infection is the primary role of leukocytes, or white blood cells. White blood cells come in many kinds. When combating bacteria, viruses, fungal and parasitic infections, each has a specific function to perform. Particularly crucial for aiding in the body's defense against infection and alien cells .
White blood cells promote wound healing. They accomplish this by both consuming materials and battling illness. This comprises aged red blood cells, tissue fragments, and dead cells. are what shield us from substances that shouldn't be in our blood, such allergies. aid in preventing diseases like cancer caused by altered (mutated) cells. Blood clotting is platelets' primary purpose. Compared to other blood cells, platelets are substantially smaller. To halt bleeding, they cluster together to form a plug in the vessel's hole.
The size, quantity, and maturity of the various blood cells within a given amount of blood are measured by a blood test called an extensive blood cell count, or CBC. A tiny sample of your blood is drawn from the vein in your arm or hand and examined in a laboratory. Several anomalies involving the synthesis or breakdown of blood cells can be detected by a complete blood count (CBC). Deviations from the typical blood cell count, size, or maturity might be utilized to indicate the presence of an infection or illness. White blood cells are frequently more prevalent during an infection. The formation of blood cells in the bone marrow can be impacted by a variety of cancers.
Upvoted. Thank You for sending some of your rewards to @null. Get more BLURT:
@ mariuszkarowski/how-to-get-automatic-upvote-from-my-accounts@ blurtbooster/blurt-booster-introduction-rules-and-guidelines-1699999662965@ nalexadre/blurt-nexus-creating-an-affiliate-account-1700008765859@ kryptodenno - win BLURT POWER delegationNote: This bot will not vote on AI-generated content