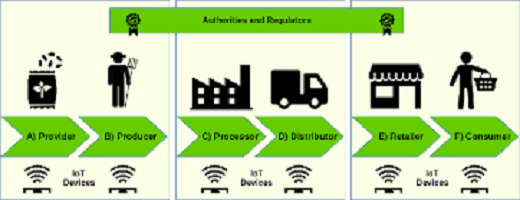
Understanding agricultural supply chains is essential for ensuring the efficient movement of goods from farm to consumer and addressing challenges in the agricultural sector. These supply chains encompass a complex network of interconnected components, each playing a crucial role in the production, distribution, and delivery of agricultural products.
Key components of agricultural supply chains include:
- Production: The first stage of the supply chain involves the cultivation and harvesting of crops or the raising of livestock. This stage is influenced by factors such as weather conditions, soil health, and agricultural practices.
- Processing: After harvest, agricultural products undergo processing to transform them into value-added goods such as food products, animal feed, or biofuels. Processing facilities may include mills, refineries, and packing plants.
- Distribution: Once processed, agricultural products are distributed to wholesalers, retailers, or directly to consumers. Distribution channels vary depending on the type of product and market demand.
- Transportation: Transport plays a critical role in moving agricultural products efficiently and cost-effectively from production facilities to end consumers. This may involve road, rail, air, or sea transportation, depending on the distance and perishability of the products.
Challenges in agricultural supply chains include:
- Seasonality: Agricultural production is often subject to seasonal fluctuations, leading to challenges in matching supply with demand throughout the year.
- Infrastructure: Inadequate infrastructure, such as roads, ports, and storage facilities, can hinder the efficient movement of agricultural products, leading to delays and inefficiencies.
- Market Access: Limited access to markets, particularly for small-scale farmers in remote areas, can restrict opportunities for selling agricultural products and accessing inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, and equipment.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Natural disasters, political instability, and other unforeseen events can disrupt agricultural supply chains, leading to shortages, price volatility, and food insecurity.
By understanding the key components and challenges of agricultural supply chains, stakeholders can work together to develop strategies for improving efficiency, resilience, and sustainability in the agricultural sector. This may involve investing in infrastructure, improving market access for small-scale farmers, and implementing technologies to enhance supply chain visibility and coordination.
Upvoted. Thank You for sending some of your rewards to @null. Get more BLURT:
@ mariuszkarowski/how-to-get-automatic-upvote-from-my-accounts@ blurtbooster/blurt-booster-introduction-rules-and-guidelines-1699999662965@ nalexadre/blurt-nexus-creating-an-affiliate-account-1700008765859@ kryptodenno - win BLURT POWER delegationNote: This bot will not vote on AI-generated content