
It has been a while since I last provided an update on the open-source libraries I have developed for the Blurt blockchain. Given that I have recently created a new library and updated some existing ones, I believe it is the opportune time to write a dedicated post addressing these developments.
Let's save the best for last, i.e. the Blurt Voting Trail Bot that I've just created, and focus first on updates to existing libraries.
Blurt RPC nodes checker version 1.1.2
Your library for ensuring fault tolerance of RPC nodes on the Blurt blockchain in your dApp. Moreover, it offers the ability to connect your users to the RPC node with the lowest latency and fastest call response time.
- Gitlab: https://gitlab.com/beblurt/blurt-nodes-checker
- Npm: https://www.npmjs.com/package/@beblurt/blurt-nodes-checker
- License: GPL-3.0-or-later

Updates:
- The nexus option is now set as true by default
- Add Nexus tests get_account_posts, get_discussion, get_ranked_posts
- Add Condenser tests get_account_history, lookup_accounts
Usage example on BeBlurt:
On BeBlurt, the Blurt RPC Nodes Checker library is employed not only to display the status of RPC nodes on the Blurt blockchain but also in conjunction with the dBlurt library. This combination ensures blockchain calls are made with minimal latency from your device while excluding RPC nodes encountering errors. Availability tests and response time tests of RPC nodes are conducted at five-minute intervals.
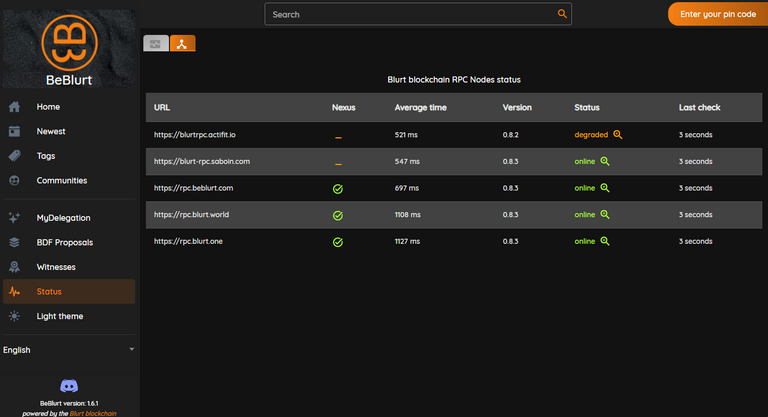
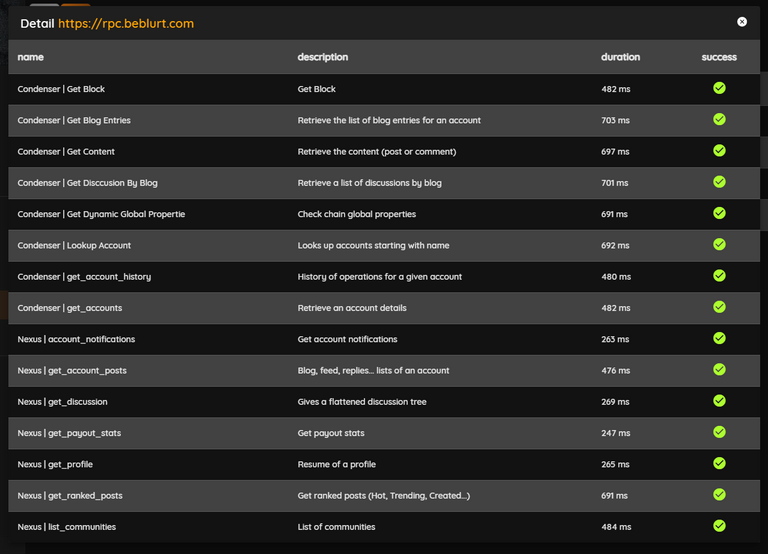
dBlurt version 0.9.29
I've just realized that it has been three months since my last post about dBlurt updates, but since then I've updated dBlurt seventeen times (updating repositories at the same time) and forgot to make a post about it hahaha.
Written in Typescript, dBlurt allows frontend/backend developers to connect to the Blurt blockchain to perform queries or broadcast operations through the JSON remote procedure call protocol JSON-RPC. dBlurt is an adaption for the Blurt blockchain of the dSteem library from Johan Nordberg created in 2017.
- Gitlab: https://gitlab.com/beblurt/dblurt
- Npm: https://www.npmjs.com/package/@beblurt/dblurt
- Documentation: https://dblurt.beblurt.com
- License: BSD-3-Clause-No-Military-License
Updates (non-exhaustive list):
- Addition of Proposals interfaces and serializers for broadcast operations
- Fixing some missing serializers and properties
- Creation of Nexus interfaces
- Add pagination to
list_subscribers - refactor the NexusPost type definition
- TransferToVestingOperation
- Account History API with bitmask
- Condenser lookup_accounts & lookup_witness_accounts
Usage example:
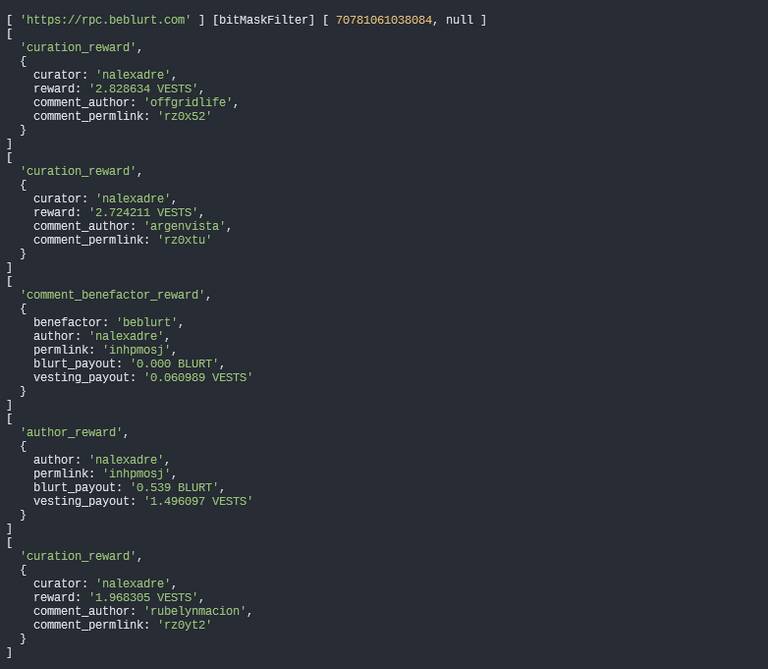
Thanks to @saboin's implementation of filters on the condenser_api.get_account_history and account_history_api.enum_virtual_ops methods. This significant update allows for filtering based on operations and virtual operations. His effort in carrying out this complex update is highly appreciated. To provide you with a better understanding, I believe offering a brief example of these two cases would be beneficial.
Get Account History
Let's consider a scenario where we need to retrieve the history of recent rewards (author rewards, curation rewards, beneficiary rewards) as well as transfers for an account. Below is the code that can be utilized for this purpose:
const rpc = ['https://rpc.beblurt.com']
const account = 'nalexadre'
import { Client, utils } from "@beblurt/dblurt"
const client = new Client(rpc, { timeout: 1500 })
const op = utils.operationOrders
const bitMaskFilter = utils.makeBitMaskFilter([
op.author_reward,
op.comment_benefactor_reward,
op.curation_reward,
op.transfer
])
console.log(rpc, '[bitMaskFilter]', bitMaskFilter)
client.condenser.getAccountHistory(account, -1, 400, bitMaskFilter)
.then(async accountHistory => {
for await (const history of accountHistory) {
console.log(history[1]?.op)
}
})
.catch(e => console.log(e))
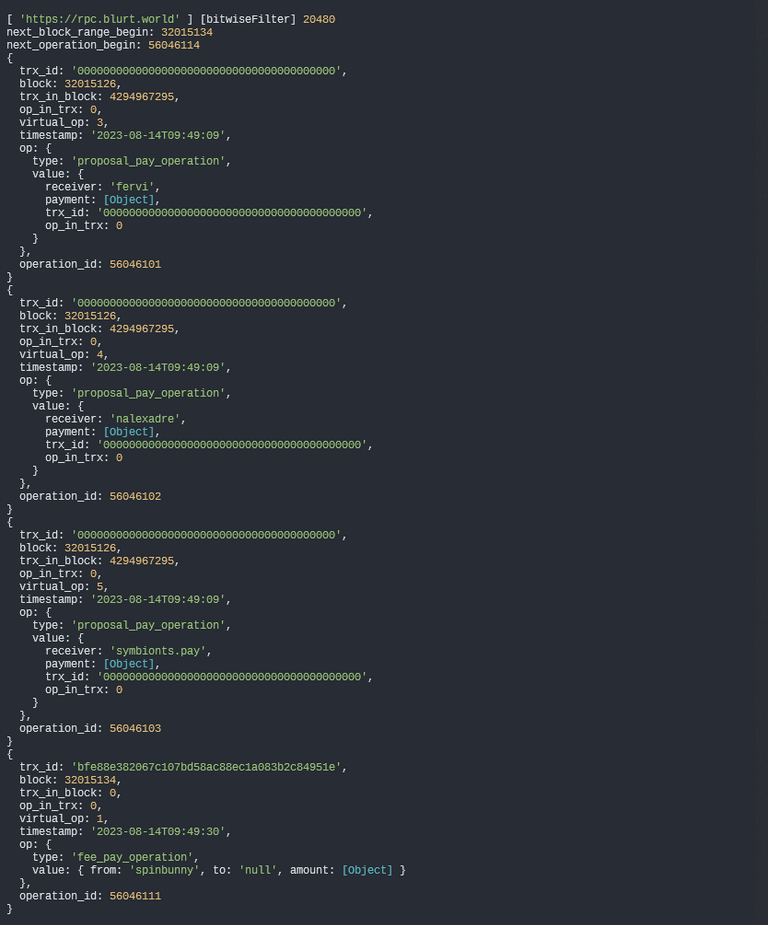
Enum Virtual Operations
Let's assume we want to retrieve payment on proposals as well as operation fees from block 32015120 to 32015200. Below is the code that can be utilized for this purpose:
const rpc = ['https://rpc.blurt.world']
import { Client, utils } from "@beblurt/dblurt"
const client = new Client(rpc, { timeout: 1500 })
const vop = utils.virtualOps
const bitwiseFilter = utils.makeBitwiseFilter([
vop.proposal_pay,
vop.fee_pay
])
console.log()
console.log(rpc, '[bitwiseFilter]', bitwiseFilter)
client.accountHistory.enumVirtualOps({
block_range_begin: 32015120,
block_range_end: 32015200,
include_reversible: false,
limit: 4,
filter: bitwiseFilter
})
.then(async enumVirtualOps => {
console.log('next_block_range_begin:', enumVirtualOps.next_block_range_begin)
console.log('next_operation_begin:', enumVirtualOps.next_operation_begin)
for await (const op of enumVirtualOps.ops) {
console.log(op)
}
})
.catch(e => console.log(e))
Blurt Tools CMD
Blurt Blockchain Operation tools in common interactive command line user interfaces (Inquirer). It allows you to create accounts, make transfers...
- Gitlab: https://gitlab.com/beblurt/blurt-tools-cmd
- License: GPL-3.0-or-later

I haven't made any changes since my post about the TESTNET, but I thought it would be a good idea to provide a brief refresh on its existence here.
Blurt Voting Trail Bot
As an author, I'm not particularly fond of curation trails due to a trauma from my experience with the Curie curation group and its 500 accounts automatically following its upvotes. While receiving significant curation is indeed gratifying, being read and upvoted by real individuals holds considerable value for me, and it's something I truly appreciate here on Blurt. Some time ago a Blurtian user of a trail bot made for Steem 5 years ago encountered problems with it, so I decided to make one for Blurt using my dBlurt and Blurt RPC nodes checker libraries.
- Gitlab: https://gitlab.com/beblurt/blurt-voting-trail-bot
- License: GPL-3.0-or-later

Overview
Resilient Restart: The bot features a resilient restart capability, allowing you to resume processing from the last block processed. This is made possible by the
START_BLOCKconfiguration parameter, which is continually updated after each block processing. This ensures that the bot seamlessly picks up where it left off, even if there's an interruption.Adaptive Upvote Weights: With the
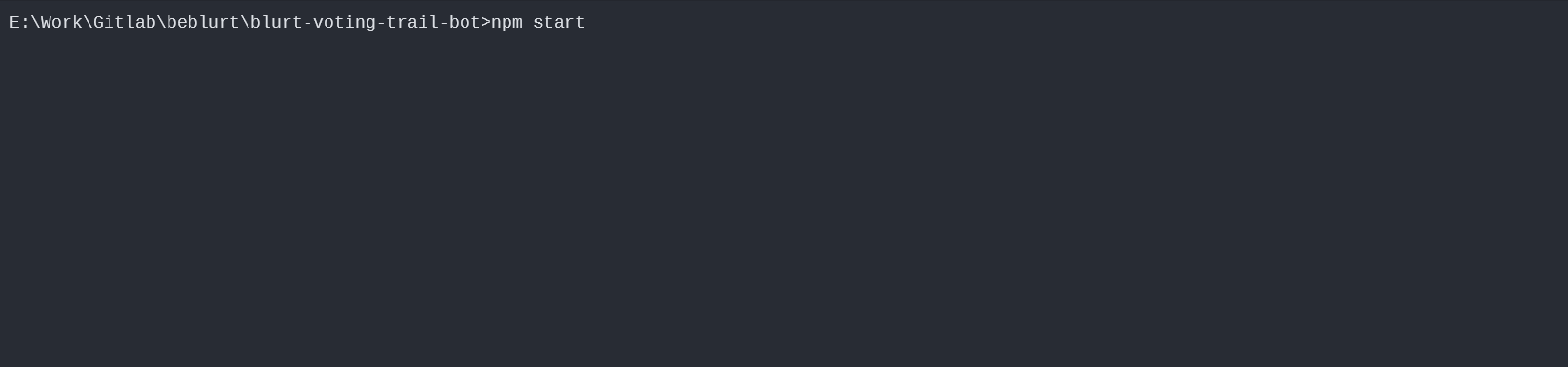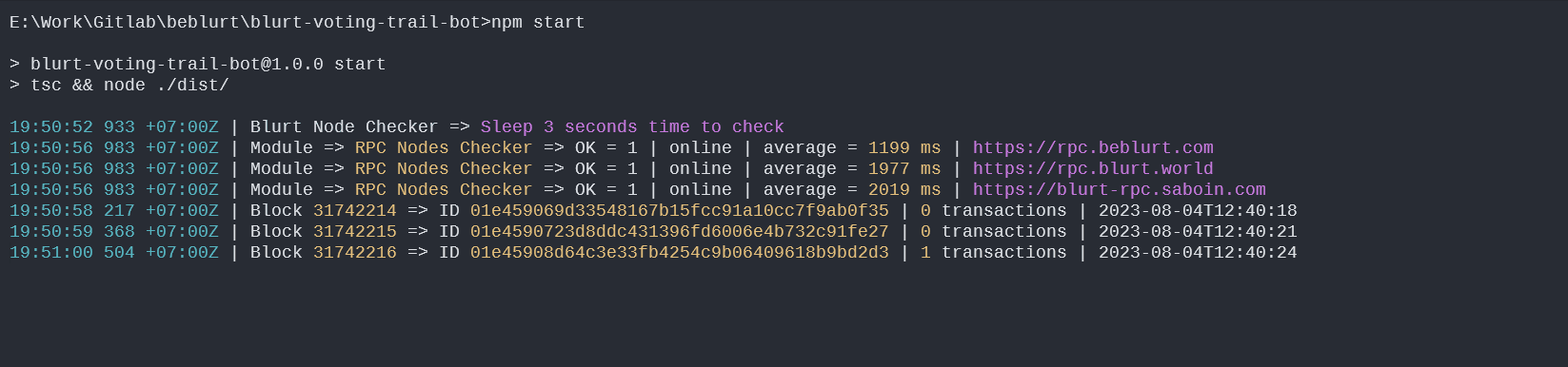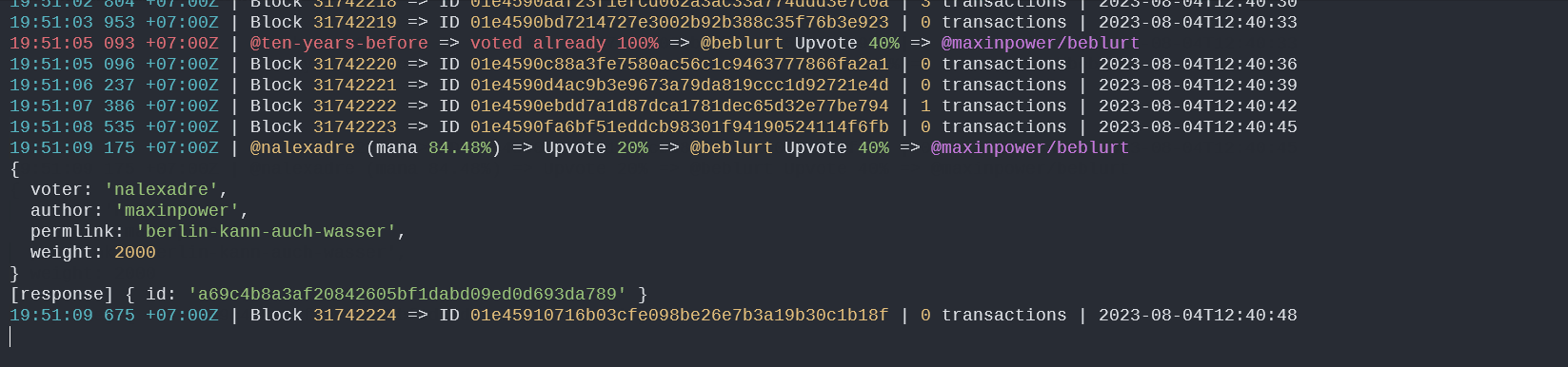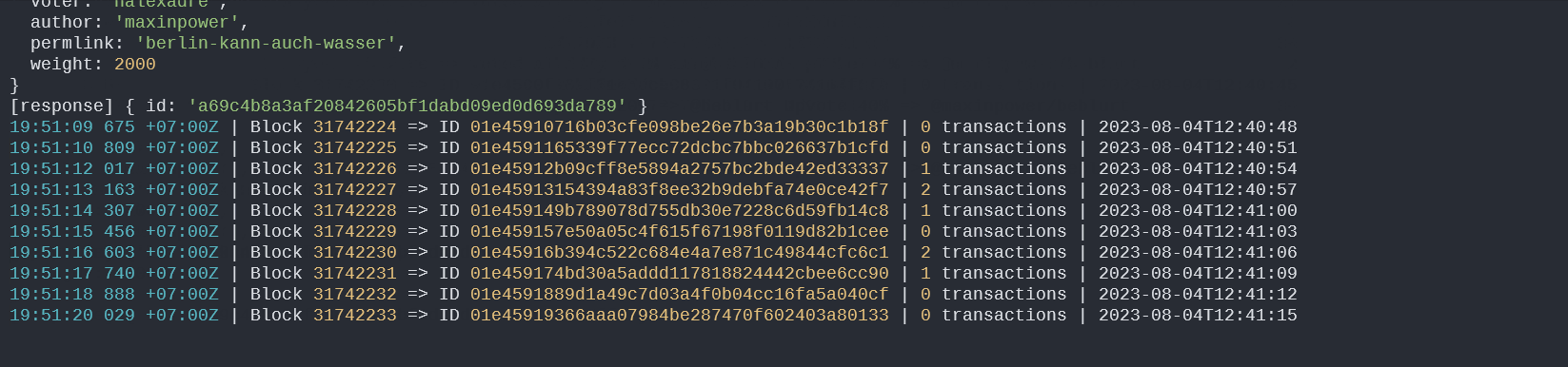
TYPEconfiguration set to 'coeff', the bot provides you with adaptive upvote weights. Unlike fixed-percentage upvotes, the 'coeff' type allows your upvote weight to dynamically adjust based on the upvotes made by the accounts you follow. For instance, if the accounts you follow upvote with a total weight of 50%, your upvote will be 25% (ifVALUEis set to 0.5).Smart Upvote Logic: The bot incorporates intelligent logic to protect against redundant upvotes. If a curator from the 'CURATORS' list has already upvoted a post or comment, any subsequent upvotes from the bot are skipped to avoid duplication.
Voting Power Safety: The Blurt Voting Trail Bot includes a safety feature to prevent the depletion of all your voting mana. The
MIN_POWERparameter ensures that the bot only performs upvotes when your voting power is above the specified threshold. This helps you maintain a balanced voting strategy and avoid overcommitting your voting resources.Customization for Posts and Comments: The Blurt Voting Trail Bot offers granular control over upvote behavior for posts and comments. You can specify different
POST_TYPE,POST_VALUE,COMMENT_TYPE, andCOMMENT_VALUEparameters for posts and comments individually. For instance, you can set a higher upvote value for posts using coefficient-based curation while assigning a fixed percentage-based upvote for comments.Fault Tolerance Management: The bot utilizes the
@beblurt/blurt-nodes-checkerlibrary for fault tolerance management. By providing multiple RPC nodes in theRPC_NODE_LIST, the bot ensures uninterrupted communication with the Blurt blockchain. This robust approach helps prevent disruptions and ensures continuous operation.
Configuration
Customize the configuration parameters to match your preferences. The available options include:
RPC_NODE_LIST: List of RPC nodes for the Blurt blockchain.RPC_NODE_TIMEOUT: Timeout for JSON RPC calls in milliseconds.TRAIL: List of accounts to trail and track their votes.EXCLUDED_AUTHORS: List of authors to exclude from upvotes.EXCLUDED_VOTERS: List of voters of the post preventing from upvoting.CURATORS: List of curators with their account details and preferences.ACCOUNT: The Blurt account of the curator.POSTING_KEY: The posting key of the curator's account.POST_TYPE: The type of curation for posts: '%' for percentage-based or 'coeff' for coefficient-based.POST_VALUE: The curation value for posts, either a percentage or coefficient, based on the TYPE.COMMENT_TYPE: The type of curation for comments: '%' for percentage-based or 'coeff' for coefficient-based.COMMENT_VALUE: The curation value for comments, either a percentage or coefficient, based on the TYPE.MIN_POWER: The minimum voting power required for the curator to upvote.
DEBUG_NODE_CHECKER: Enable/disable debug mode for node checker.DEBUG_BLOCK: Enable/disable debug mode for block processing.DEBUG_VOTE: Enable/disable debug mode for voting operations.START_BLOCK: Start processing from a specific block number (optional, can be null).
Difference between TYPE "%" & "coeff"
When choosing "%" for TYPE, the weight of your upvote will remain the same for all your upvotes. On the other hand, if you choose "coeff" and set the VALUE to, for example, 0.5, it means that for each upvote made by the account you follow, your upvote will be half of their upvote. If the account you follow upvotes by 50%, your upvote will be 25%.
Markus Spiske on Unsplash
Thank you for your continued support through a vote on my witness or a Delegation to the BeBlurt Delegation program. Together, let's continue to thrive within the Blurt blockchain ecosystem.

